Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) DRB1 alleles with specific common amino acids referred to as the shared epitope (SE) have been linked to endothelial dysfunction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, less is known about the HLA-DRB1 alleles with endothelial dysfunction and subclinical cardiovascular disease (CVD) in people without RA. We aimed to determine associations betweenHLA-DRB1 SE alleles (04:04, 04:05, 04:01, 04:08, 01:01, 14:02, 10:01, 03:01, 03:02) and coronary artery calcium (CAC), abdominal aortic calcium (AAC), and carotid intima-media thickness (cIMT) in a multi-ethnic community-living population.
Methods: Within the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA), a prospective cohort study designed to determine risk factors and progression of subclinical and clinical CVD, a subset of 955 participants who completed the AAC ancillary study and had complete measures of HLA typing and cardiac imaging were evaluated. We defined shared epitope positive, SE(+) for genotypes with the HLA-DRB1 SE alleles listed above; and evaluated associations of SE positivity and each of the individual SE alleles with CAC, AAC, and cIMT. CAC and AAC were evaluated as present vs. absent and as ln(Agatston score) in those with CAC and ACC > 0. cIMT was evaluated in millimeters. We calculated the relative risk (RR) for prevalence of CAC and AAC; and relative difference (RD) for continuous measures of CAC, AAC, and cIMT using linear regression. Our analysis was adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, diabetes mellitus, systolic blood pressure, current smoking, eGFR, current use of anti-hypertensive medications, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, current use of lipid lowering medications, and IL-6.
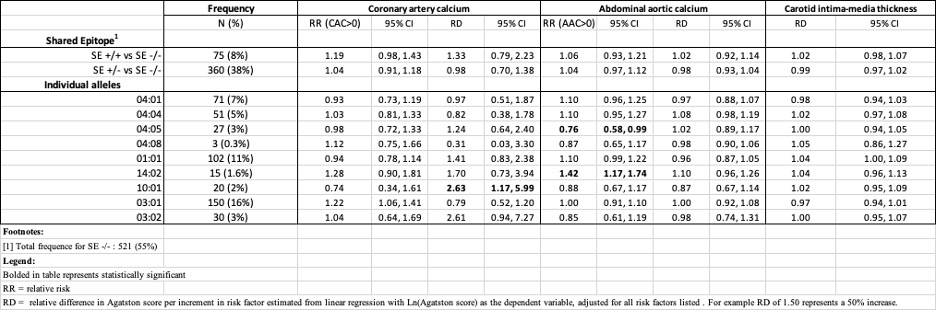
Results: Among the 955 MESA participants, 46% were SE(+)—38% carried a single allele and 8% carried two double alleles. Average age was 60±9, 47% were women, and 51% were White, 9% were Asian, 16% were Black, and 24% were Hispanic/Latino. Age, sex, blood pressure, cholesterol, and inflammatory markers (CRP, TNF-α, IL 6), were similar between SE(+) and SE(-) participants, but racial distributions differed where SE(+) had a higher proportion of White (51% vs 38%) and lower proportion of Asian (9% vs 17%) and Black (16% vs 21%) participants. SE positivity was not significantly associated with a higher risk of CAC, AAC, or cIMT. However, individual allele 10:01 demonstrated 2.63-fold higher risk for CAC (95% CI: 1.17-5.99); 14:02 demonstrated 42% higher risk for AAC, (95% CI: 1.17-1.74); and 04:05 demonstrated 24% lower risk for AAC (95% CI: 0.58-0.99).
Conclusion: SE positivity was not associated with higher risk of CAC, AAC, or cIMT in a multi-ethnic community-living population. Alleles 10:01 and 14:02 were associated with a higher risk for CAC and AAC, respectively, and 04:05 with lower risk for AAC.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kaur M, Katz R, H. Criqui M, Corr M, S. Post W, Budoff M, P. Morris G, M. Hughes-Austin J. Association of HLA-DRB1 Alleles with Coronary Artery Calcium, Abdominal Aortic Calcium, and Carotid Intima-media Thickness in a Multi-ethnic Community-living Population [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-hla-drb1-alleles-with-coronary-artery-calcium-abdominal-aortic-calcium-and-carotid-intima-media-thickness-in-a-multi-ethnic-community-living-population/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-hla-drb1-alleles-with-coronary-artery-calcium-abdominal-aortic-calcium-and-carotid-intima-media-thickness-in-a-multi-ethnic-community-living-population/