Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1123–1146) Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Gout is s a disease with a high disability rate, resulting in severe social burden and is associated with reduced health-related quality of life (HRQoL). Several studies showed that the violation of adipokine status is factor in the development and progression of crystal-induced inflammation. Therefore, assessing the association between leptin levels, body mass index (BMI) and HRQoL is very relevant. This study aimed to investigate the BMI and HRQoL patients with gout and evaluate its association with leptin levels.
Methods: 151 patients were included; 100% were men. The mean age was (mean±SD) 52.4±9.2 years. The average BMI was 31.9±3.4 kg/m2. The mean disease-specific HRQoL was evaluated using a translated and validated Ukrainian version of the Gout Impact Scale (GIS; scale 0-100); HRQoL was assessed by the SF-36 and calculated summary physical (PCS) and mental component (MCS) scores of the SF-36. Leptin in serum was determined by ELISA using the “Human Leptin ELISA Kit” (DRG, Germany). Statistical analysis was performed using MS Excel and SPSS22 software (©SPSS Inc.).
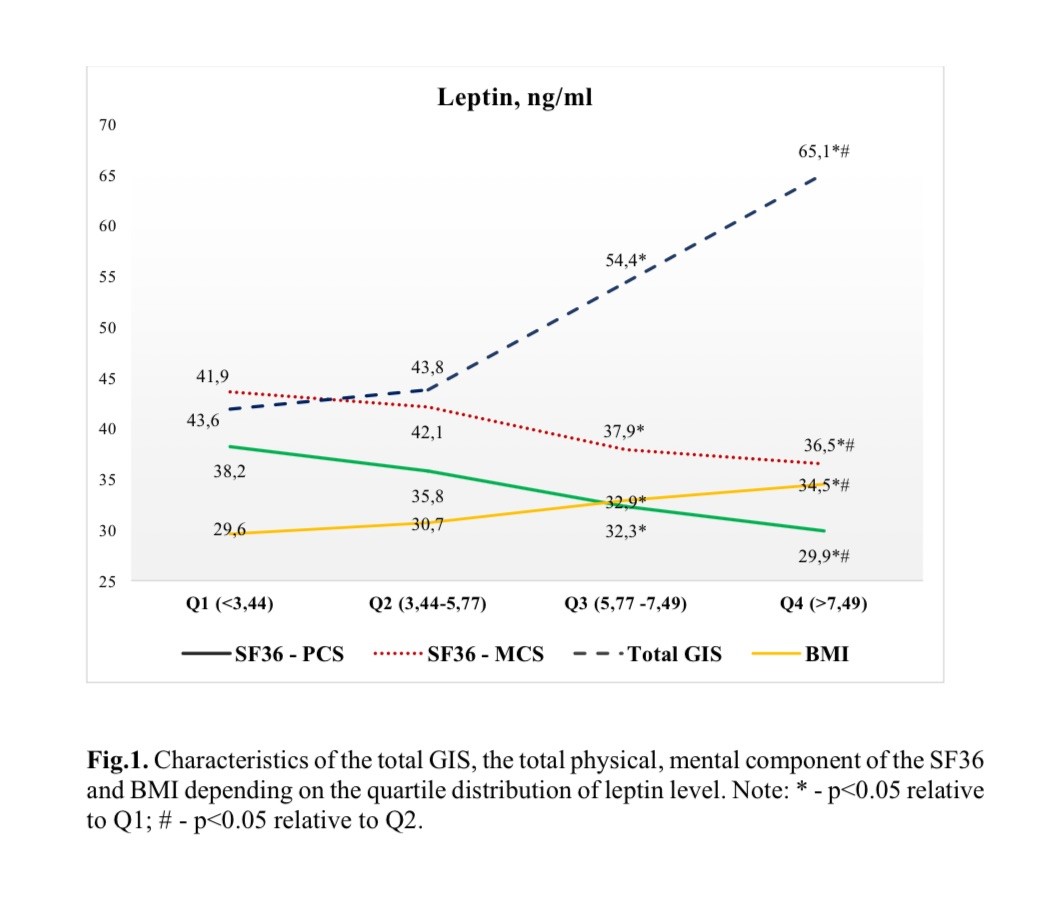
Results: The PCS of the SF-36 was 34.0±7.7, MCS was 40.0±9.2. Total GIS was 51.1±27.5. The leptin level in patients with gout ranged from 2.06 to 18.15 ng/ml (95% CI) and the mean was 6.6±4.3 ng/ml. According to the quartile distribution of serum leptin level, patients with gout were divided into 4 groups: the 1st quartile (Q1) included 36 patients (with indicator level <3.44 ng/ml), the 2nd quartile (Q2) – 37 people (from 3.44 to 5.77 ng/ml), the 3rd quartile (Q3) – 36 people (from 5.77 to 7.49 ng/ml) and the 4th quartile (Q4) – 42 people (>7.49 ng/ml). With increasing leptin levels, there was a decrease in both physical and mental health in gout patients (Fig. 1). The PHS was 22% lower in the 4th quartile than in the 1st, while the MCS was 17% lower in the 4th quartile compared to the 1st quartile. At the same time, the final indicators of the physical and mental sphere in patients in the 4th quartile were significantly different from those in patients in the 1st and 2nd quartiles. The increase in leptin content was accompanied by an increase in the impact of gout on the GIS scale. The total GIS was higher in patients in the 4th quartile and was 35.6% higher than in patients in the 1st quartile. Besides, our analysis showed significant positive association between BMI and leptin level. In patients with leptin levels >7.49 ng/ml (Q4), BMI was significantly higher by 16.5% than in patients with leptin levels < 3.44 ng/ml (Q1).
Conclusion: An increased leptin level was associated with significant reductions in HRQoL in gout patients. A significant relationship is found between leptin and BMI. The results of this study support the role played by body composition and adipocytokines in HRQoL in gout patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Orlova I, Shapoval I, Shkolina N, Kuzminova N, Stanislavchuk M. Association between leptin levels, body mass index and health-related quality of life in patients with gout [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-leptin-levels-body-mass-index-and-health-related-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-gout/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-leptin-levels-body-mass-index-and-health-related-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-gout/