Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 19, 2024
Title: Abstracts: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical III
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Variations in gastrointestinal (GI) microbial communities may influence the development of lung diseases. Patients with SSc-ILD have a unique intestinal microbial signature. To further understand the gut-lung axis in SSc, this study aimed to investigate GI microbial correlates of distinct radiological features of ILD in a multicenter study.
Methods: SSc patients with and without ILD were recruited from 7 international SSc Centers (University of California, Los Angeles [UCLA], USA; Lund University [LU], Sweden; Duke-National University of Singapore, Singapore; Johns Hopkins University, USA; Ghent University, Belgium; University of Adelaide, Australia; Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Chile) and provided a stool sample. Shotgun metagenomics were performed using the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 with a target depth of 10 million 150×2 sequences per sample. Shotgun reads were inputted into MetaPhlAn4 for taxonomic identification of species for compositional analysis and subsequently underwent center log-ratio transformation. High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) scans of the chest underwent quantitative image analysis to determine the radiological extent of fibrosis (QLF) and ground glass opacity (QGG) in patients from UCLA and LU. General linear models were applied to identify differentially abundant species based on ILD presence and determine associations between QLF/QGG scores and species abundance, adjusting for body mass index, current proton pump inhibitor use, current probiotic use, current or prior immunomodulatory therapy, presence of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and site. We considered p< 0.05 at the threshold for reporting and provide 5% false discovery rate corrected p-values (q). We also computed effect size estimates, Cohen’s D for mean differences and standardized Beta for association analyses.
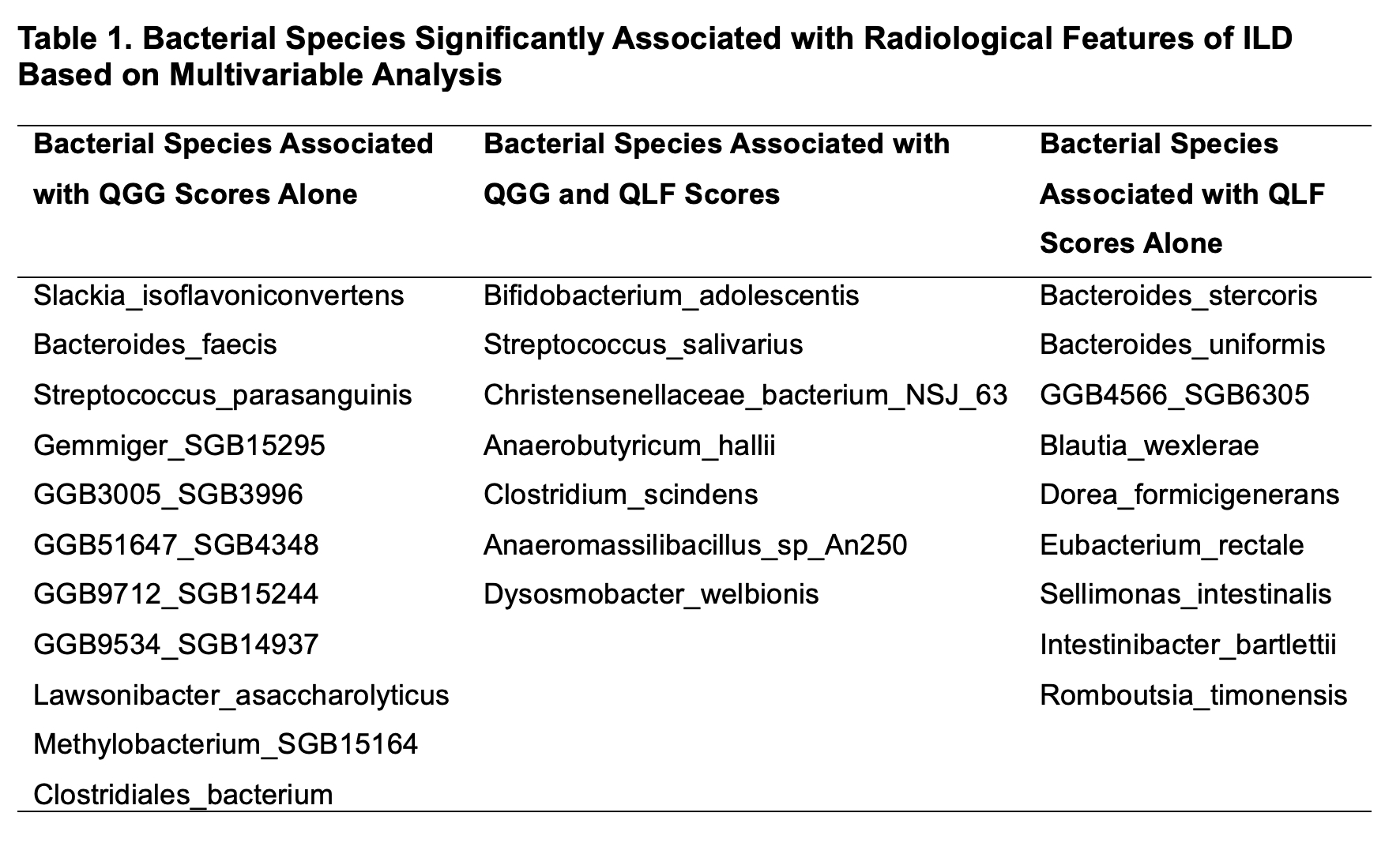
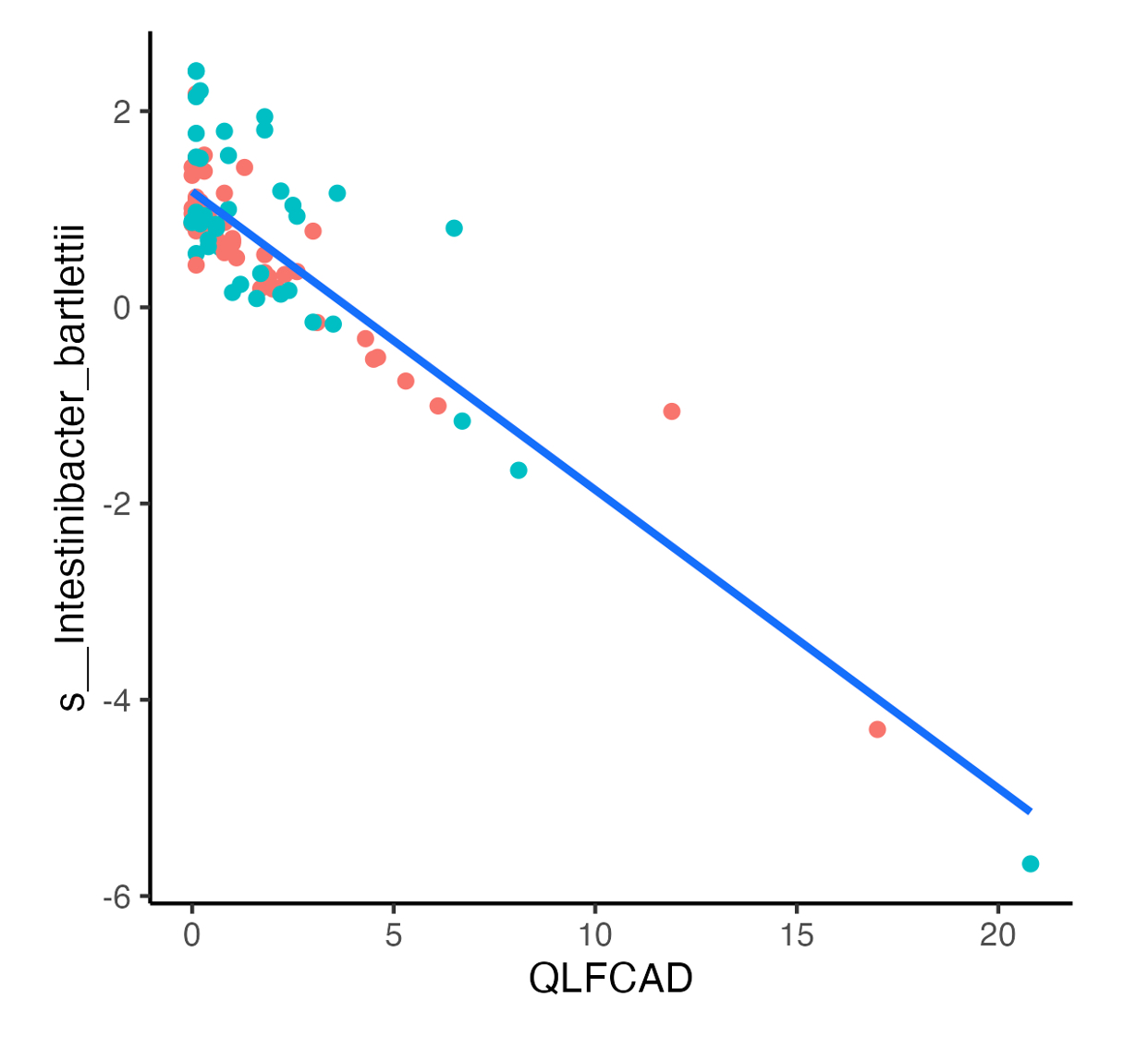
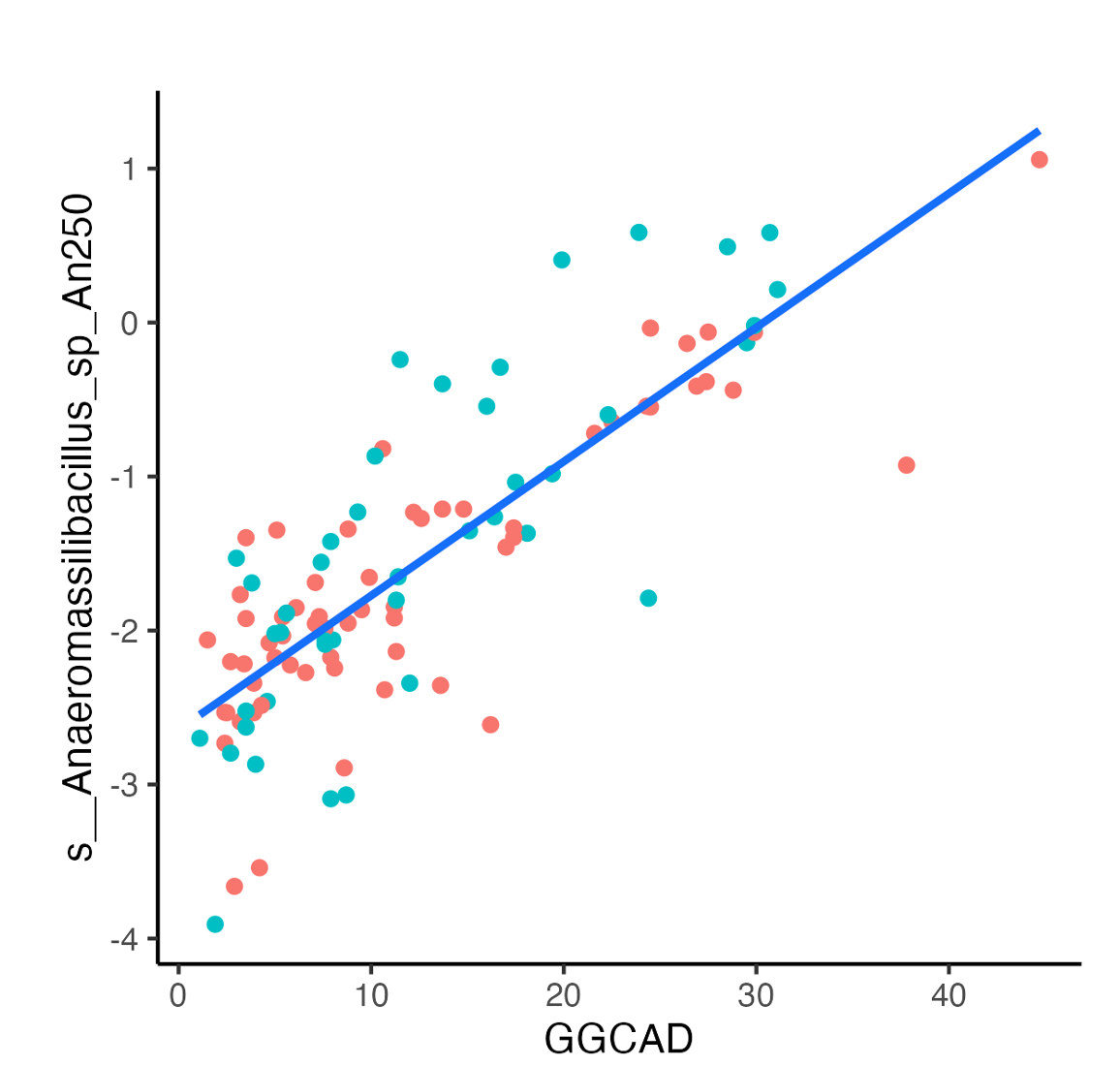
Results: Among 285 participants with SSc, 62.5% had any ILD on HRCT. The mean age was 54.6 (SD 13) years and the median disease duration was 6.8 (IQR 3.5, 12.9) years. Among the 254 species analyzed, the abundance of 11 bacterial species was altered in patients with ILD compared to patients without ILD in all study participants, including Paraprevotella clara, which was increased in patients with ILD (Effect size 0.32 [95% CI 0.06, 0.58; P=0.02; q=0.94) and Sellimonas intestinalis, which was decreased in patients with ILD compared to without (Effect size -0.29 [95% CI -0.55, -0.03; P=0.03; q=0.94). In a multivariable analysis of 113 SSc-ILD patients, the abundance of 16 bacterial species correlated with QLF scores (Figure 1), while abundance of 18 bacterial species correlated with QGG scores (Figure 2). While some species (N=7) were associated with both QGG and QLF scores, 9 and 11 unique species were solely associated QLF and QGG scores, respectively (Table 1).
Conclusion: This multicenter study demonstrates that unique bacterial species are linked to radiological measures of fibrosis and ground glass opacity in SSc. These species and/or their metabolic products may contribute to the pathogenesis of these structural lung changes and may represent novel treatment targets.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Young A, Andreasson K, Joshi S, Labus J, Low Hsiu Ling A, smith v, McMahan Z, Valenzuela Vergara A, Proudman S, Kim G, Bozovic G, Goldin J, Aja E, Jacobs J, Volkmann E. Association Between Gastrointestinal Bacterial Species and Radiological Features of Systemic Sclerosis-Interstitial Lung Disease (SSc-ILD): A Multicenter Study from the SSc Microbiome Consortium Project [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-gastrointestinal-bacterial-species-and-radiological-features-of-systemic-sclerosis-interstitial-lung-disease-ssc-ild-a-multicenter-study-from-the-ssc-microbiome-consortium-proje/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-gastrointestinal-bacterial-species-and-radiological-features-of-systemic-sclerosis-interstitial-lung-disease-ssc-ild-a-multicenter-study-from-the-ssc-microbiome-consortium-proje/