Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: PROs, Biomarkers, Systemic Inflammation & Radiographs
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The efficacy and safety of intravenous (IV) and subcutaneous (SC) tocilizumab (TCZ) in combination with conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) and as monotherapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has been demonstrated in large clinical trials and real-world data studies. The Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI) is commonly used to assess physical function in patients with RA. While HAQ-DI outcomes at Week 24 in TCZ clinical trials have been reported, outcomes at Week 12 and results stratified by treatment response categories at Weeks 12 and 24 have not been previously described. The objective of this study was to report the association between change in HAQ-DI from baseline to Weeks 12 and 24 and Disease Activity Score in 28 joints (DAS28) response categories in patients who received TCZ or comparators in TCZ clinical trials.
Methods: Data from patients with active RA who received TCZ or a comparator from 6 Phase 3 or 4 TCZ-IV studies (OPTION [NCT00106548], RADIATE [NCT00106522], TOWARD [NCT00106574] LITHE [NCT00109408], ACT-RAY [NCT00810199] and ADACTA [NCT01119859]) and 1 Phase 3 TCZ-SC study (BREVACTA [NCT01232569]) were analyzed. Mean change in HAQ-DI score at Weeks 12 and 24 was assessed in patients stratified by DAS28 disease activity level (DAS28 < 2.6 [remission], DAS28 ≥ 2.6 to ≤ 3.2 [low disease activity; LDA], DAS28 > 3.2 to ≤ 5.1 [moderate disease activity; MDA], DAS28 > 5.1 [high disease activity; HDA] at Weeks 12 and 24. The adjusted least squares mean (LSM) change from baseline was estimated using a mixed model with repeated measures, including region (North America vs non-North America), RA duration ( > 2 years vs ≤ 2 years), baseline HAQ-DI and DAS28, treatment, visit, visit by treatment and visit by baseline HAQ-DI.
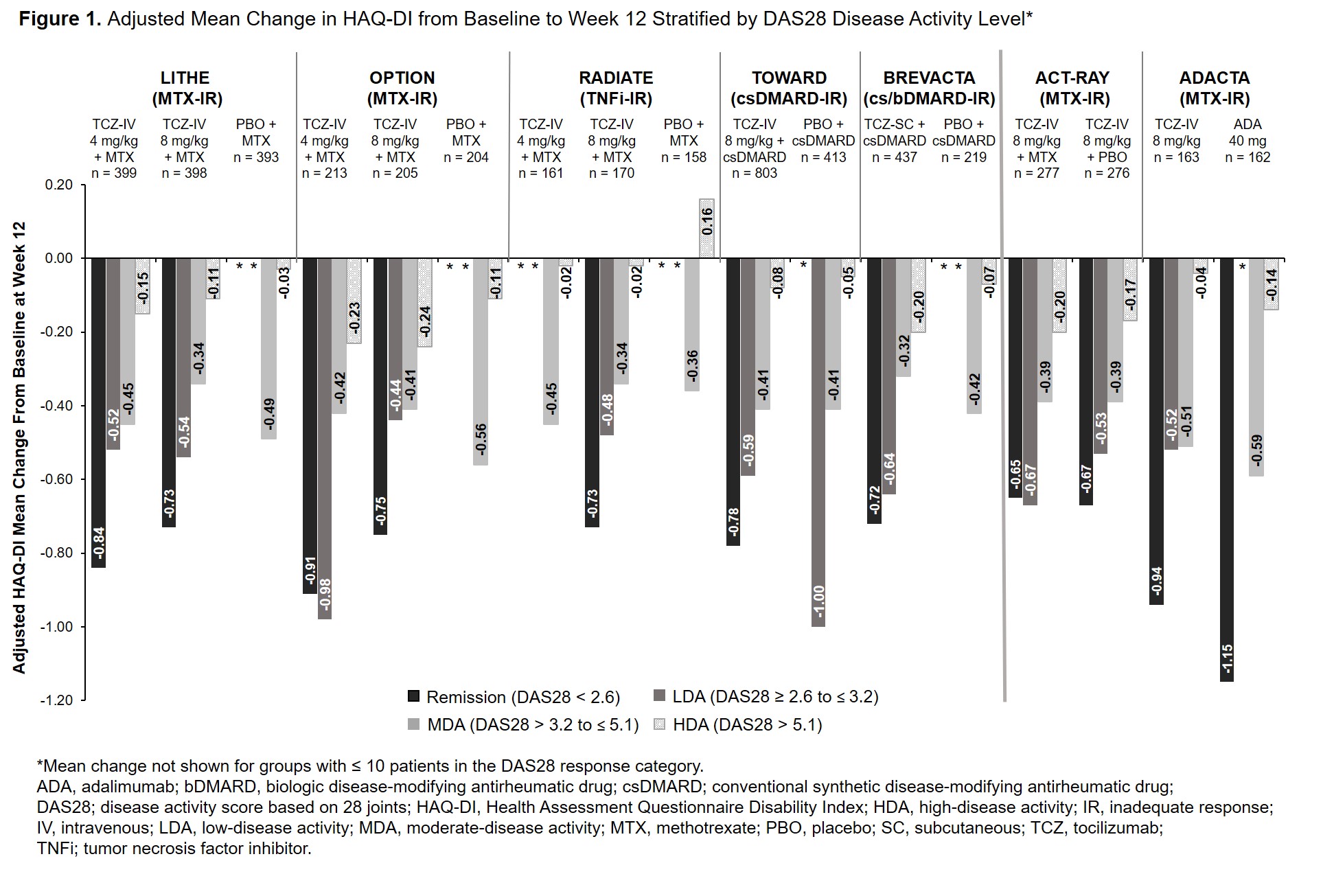
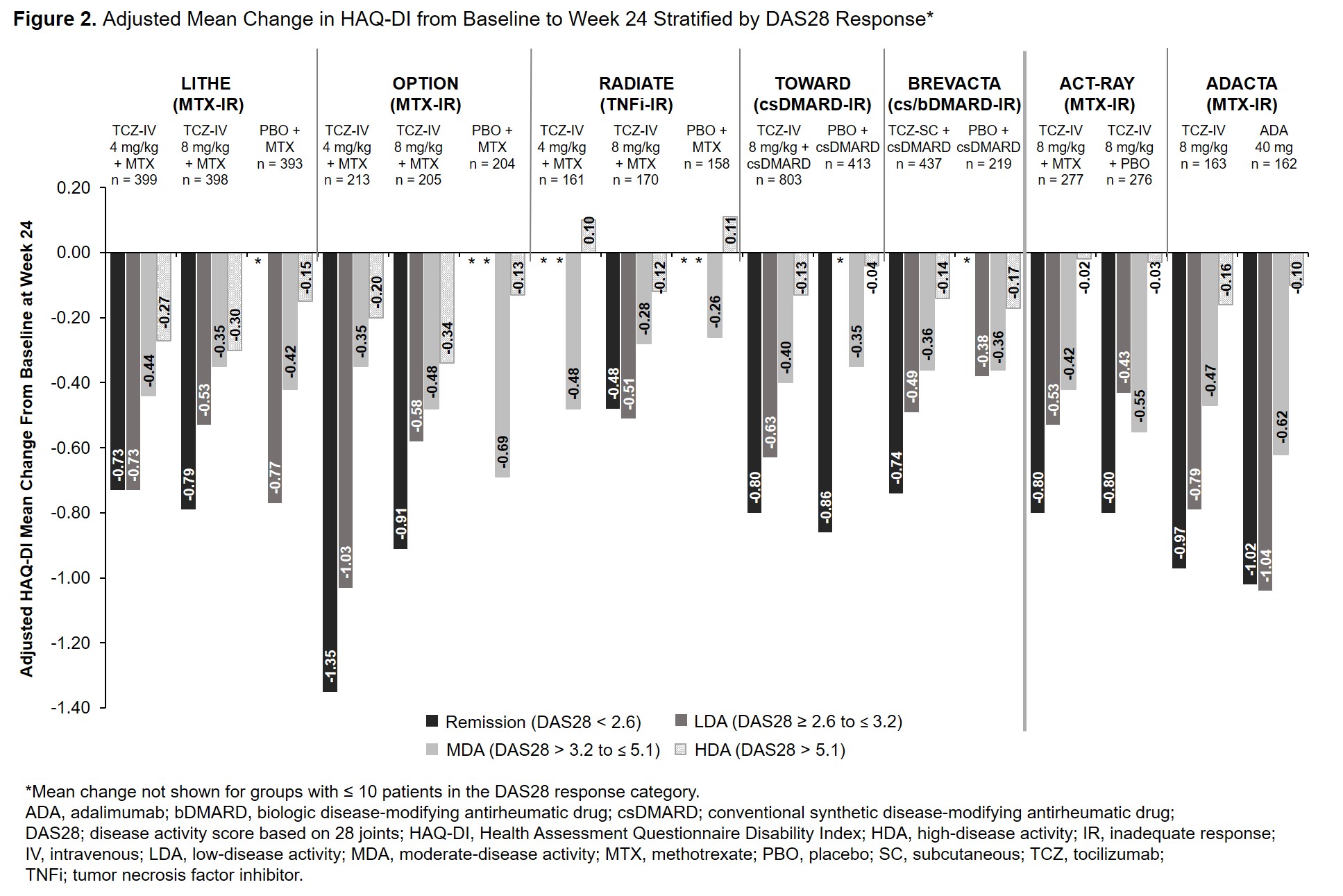
Results: Data from 5051 patients were included. Across all studies, the mean duration of RA ranged from 6.3 to 12.6 years. At baseline, patients had severe RA with a mean DAS28 ≥ 6.3; baseline HAQ-DI was ≥ 1.5. At Week 12, patients who achieved remission or LDA had greater improvements in HAQ-DI than those in MDA or HDA (Figure 1). Results were similar at Week 24 (Figure 2). Among patients who received TCZ and achieved remission or LDA, mean improvement in HAQ-DI was ≥ 0.65 and ≥ 0.44, respectively, at Week 12 (Figure 1) and ≥ 0.48 and ≥ 0.43 at Week 24 (Figure 2). Mean changes in HAQ-DI were similar between patients who received TCZ-IV in combination with MTX or as monotherapy (ACT-RAY) and in those who received TCZ-IV or ADA as monotherapy (ADACTA).
Conclusion: Patients with long-standing, severe RA who received IV or SC TCZ as monotherapy or in combination with csDMARDs had improvement in physical function and disease activity at Week 12 that was maintained at Week 24. Overall, across all the trials, response to treatment was associated with improvement in patient-reported physical function.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Unizony S, Dang J, Han J, Michalska M, Best J. Association Between Change in Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index and Treatment Response in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis in Tocilizumab Clinical Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-change-in-health-assessment-questionnaire-disability-index-and-treatment-response-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-tocilizumab-clinical-trials/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-change-in-health-assessment-questionnaire-disability-index-and-treatment-response-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-tocilizumab-clinical-trials/