Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: Epidemiology & Public Health Poster III: Inflammatory Rheumatic Disease
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Recent research has advanced the understanding of associations between environmental, genetic, and metabolic factors and rheumatoid arthritis (RA), introducing potential to improve risk prediction. A novel weighted genetic risk scored (wGRS) was generated from 90 non-HLA RA-associated risk alleles and five RA-associated amino acid positions of HLA-DRB1 haplotypes. Additionally, several preclinical plasma metabolites were recently associated with seropositive RA. This study investigated whether the addition of variables representing the wGRS and preclinical metabolite levels increased the performance of seropositive RA risk prediction models compared to previously validated models in the Nurses’ Health Studies (NHS).
Methods: This nested case-control study involved individuals with drawn plasma samples from the NHS prior to RA diagnosis or matched date for controls. Incident seropositive RA cases, based on the ACR 1987 criteria and ACR/EULAR 2010 criteria, were matched to two controls on age, blood collection features, and menstrual patterns at time of blood draw. Environmental variables, including age, smoking, alcohol use, socioeconomic status, region, reproductive factors, and BMI, were measured at the questionnaire cycle preceding the blood draw, corresponding to pre-diagnosis exposures. Four models were generated using logistic regression: a) base model with environmental factors (E), b) environmental and genetic and gene-environment interaction factors (E +G+GEI), c) environmental and pre-diagnosis metabolite factors (E+M), and d) all factors (E+G+GEI+M). Matching factors were included in the models to adjust for selection bias due to the matched case-control design. Model fit was assessed using Nagelkerke’s R2 and the Hosmer-Lemeshow test. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) was measured to compare performance of expanded vs. base model. Models were internally validated using a bootstrapped estimate of optimism of the AUC. This measure of overfitting is based on the average difference between the predictive ability of the model built using the original sample, and the predictive ability of the models built using each bootstrap sample.
Results: 150 seropositive RA cases and 456 controls were included in the study. The E model yielded an AUC of 0.665 (95% CI 0.616, 0.714). The E model yielded an AUC of 0.665 (95% CI: 0.616, 0.714). The expanded model including genetic factors presented a strong improvement in discrimination; producing AUCs of 0.727 (95% CI: 0.676-0.770) in E+G+GEI model. The E+M model including preclinical metabolite factors produced a modest improvement in discrimination (AUC 0.694, 95% CI: 0.640, 0.736). The full E+G+GEI+M model yielded the highest AUC of 0.744 (95% CI: 0.697, 0.788). Optimism corrected models yielded an AUC of 0.596 for the E model, 0.666 for E+G+GEI, 0.606 for E+M, and 0.672 for E+G+GEI+M.
Conclusion: The addition of the wGRS and HLA haplotype-smoking interaction improve discrimination of the RA risk prediction model compared to models without genetic factors. However, recently reported preclinical metabolite levels do not appear to significantly contribute to prediction.
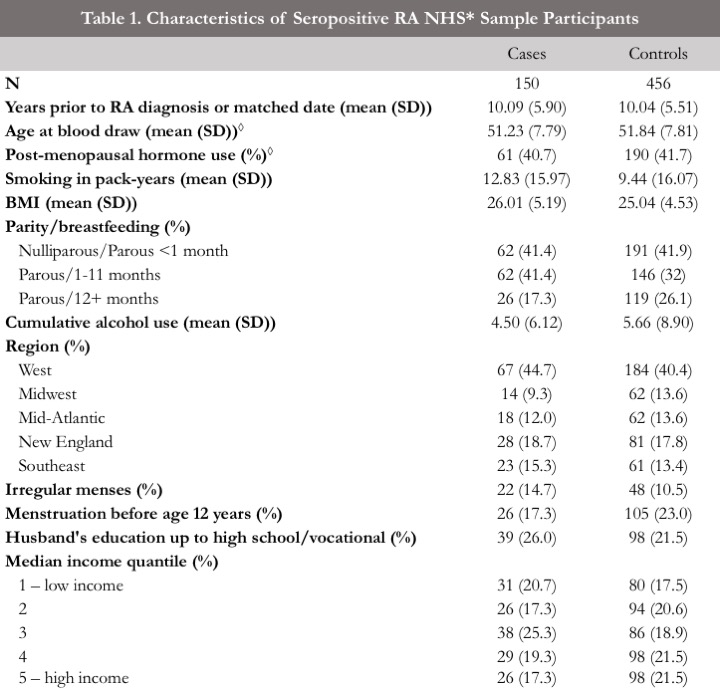 *NHS=Nurses’ Health Studies ◊Matching factors
*NHS=Nurses’ Health Studies ◊Matching factors
 E: environmental- age, smoking pack-years, cumulative alcohol use, husband’s education, income quintile, parity/breastfeeding, early menses, menstrual irregularity, menopausal status, region, BMI. E+G+GEI: environmental and genetic- all environmental variables, 90 SNP wGRS, HLA Haplotype GRS, HLA Haplotype GRS*Smoking. E+M: environmental and metabolite1- all environmental variables, C5 carnitine, 4-acetamidobutanoate, C5:1 carnitine, 3-dehydroxycarnitine, C7 carnitine, N-acetylputrescine, 3-oxooctadecanoate, C3 carnitine, C16:1 CE, C35:0 PE. E+G+GEI+M: environmental, genetic, metabolite- all variables. 1. Chu, S. H. et al. Circulating plasma metabolites and risk of rheumatoid arthritis in the Nurses’ Health Study. Rheumatology (Oxford) (2020) doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keaa125.
E: environmental- age, smoking pack-years, cumulative alcohol use, husband’s education, income quintile, parity/breastfeeding, early menses, menstrual irregularity, menopausal status, region, BMI. E+G+GEI: environmental and genetic- all environmental variables, 90 SNP wGRS, HLA Haplotype GRS, HLA Haplotype GRS*Smoking. E+M: environmental and metabolite1- all environmental variables, C5 carnitine, 4-acetamidobutanoate, C5:1 carnitine, 3-dehydroxycarnitine, C7 carnitine, N-acetylputrescine, 3-oxooctadecanoate, C3 carnitine, C16:1 CE, C35:0 PE. E+G+GEI+M: environmental, genetic, metabolite- all variables. 1. Chu, S. H. et al. Circulating plasma metabolites and risk of rheumatoid arthritis in the Nurses’ Health Study. Rheumatology (Oxford) (2020) doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keaa125.
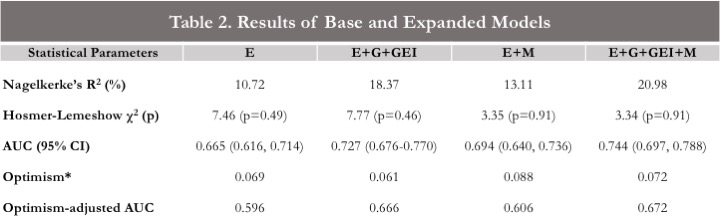 AUC = area under the ROC *Optimism calculated using the Harrell method with 200 bootstrap replications using the 632+ rule.
AUC = area under the ROC *Optimism calculated using the Harrell method with 200 bootstrap replications using the 632+ rule.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Costenbader K, Sparks J, Karlson E, Yoshida K, Cui J, Malspeis S, Bouzit L. Assessing Improved Risk Prediction of Seropositive Rheumatoid Arthritis by Environmental, Genetic, and Preclinical Plasma Metabolite Factors [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessing-improved-risk-prediction-of-seropositive-rheumatoid-arthritis-by-environmental-genetic-and-preclinical-plasma-metabolite-factors/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessing-improved-risk-prediction-of-seropositive-rheumatoid-arthritis-by-environmental-genetic-and-preclinical-plasma-metabolite-factors/
