Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Data on cellular and humoral immunogenicity triggered by SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases (ARD) are limited. While current vaccine efforts have focused on the induction of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, T-cell immunity may also provide protection against infection. Experimental data suggest that CD8+ T cell responses may have a protective role in the presence of decreasing or sub protective antibody titers.
The aim of this project is to describe the serological and T cell responses to the third dose of vaccine (either with BNT162b2 mRNA or ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 replication-deficient adenoviral vector vaccines) in a cohort of patients with ARD (rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthropathies) treated with biologic therapies, to describe the impact of these treatments on vaccine response in this patient population. As a second objective, we will describe the characteristics of patients who did not present an adequate immunogenic response.
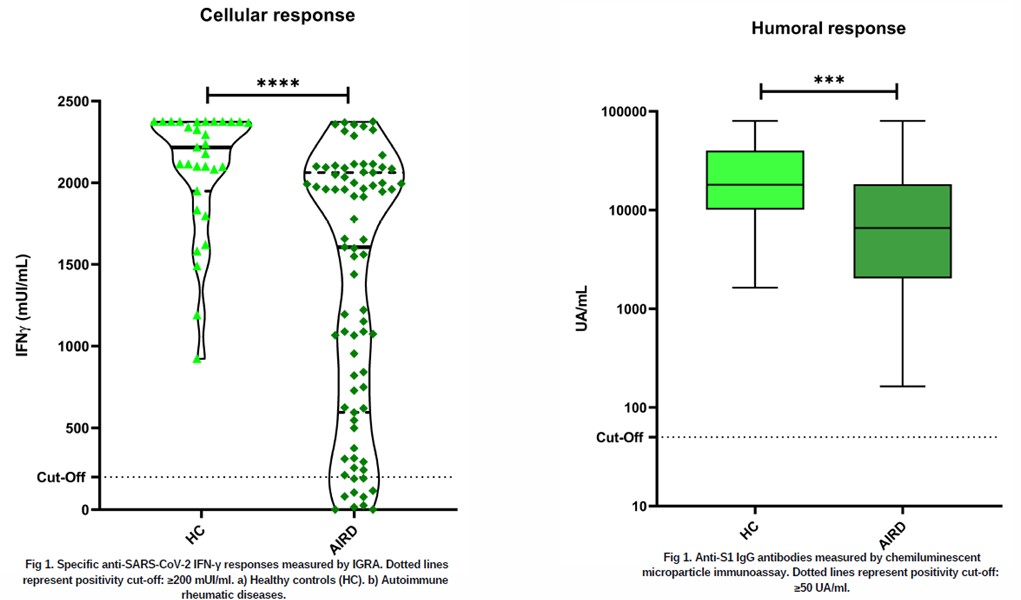
Methods: Case-control study. We studied in 79 patients with ARD and in 31 healthy controls, anti-SARS-CoV-2 specific interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) production measured by IGRA between 8-12 weeks after the third dose of anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. In addition, humoral response was measured by anti-S1 IgG antibody production measured by chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay. Statistical comparison between categorical variables was performed by Fisher’s or χ2 test. For quantitative variables by Kruskal-Wallis test or Mann-Whitney test.
Results: 79 patients with ARD (48 women, 31 men; mean age 58±11.4) 43 (54%), with rheumatoid arthritis and 36 (45.6%) with spondyloarthropathies. 32 (49.5%) of them were on glucocorticoid treatment (mean dose 4.92 mg/day), 25 (31.6%) on methotrexate and 56 (70.9%) on anti-TNF. Post-vaccination results showed positive T-cell immune responses in 68 of 79 (86.1%) ARD patients with mean IFN- γ anti-SARS-CoV-2 titers of 1,606.85 mUI/ml. 7 (8.9%) of ARD patients showed negative IFN-γ SARS-CoV-2 levels, while 4 (5%) had borderline titers. 100% of patients with previous COVID 19 disease had positive cellular responses. Within the group of negative or borderline cellular responses, 7 of 10 were men (70%), with no significant differences in terms of diagnosis, comorbidities or immunosuppressive treatments used. In the control group, 100% presented positive cellular responses. Anti-Spike IgG antibodies were detectable in all patients with ARD as in the control group.
Conclusion: Our preliminary data show that most patients with ARD were able to generate an adequate specific cellular response after vaccination against SARS-CoV-2, emphasizing the relevance of vaccination in this group. Specific antibody responses secondary to anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccination were detected in all patients with ARD. Our data could support the relevance of these immune responses to personalize prevention, vaccination decision-making and treatment in this subgroup of patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pérez Sancristóbal I, Alvarez Hernandez M, Mohamed Mohamed k, Rodriguez Laguna M, Martinez C, Toledano E, Freites D, Fernandez B, Rodero M, Bravo C, Rodrígez de la Peña A, Sanchez - Ramon S, mato Chain G, Candelas G. Assessing Immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Neoantigen S1 in Autoimmune Rheumatic Disease Patients: A Study on Cellular and Humoral Responses [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessing-immunogenicity-of-sars-cov-2-vaccine-neoantigen-s1-in-autoimmune-rheumatic-disease-patients-a-study-on-cellular-and-humoral-responses/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessing-immunogenicity-of-sars-cov-2-vaccine-neoantigen-s1-in-autoimmune-rheumatic-disease-patients-a-study-on-cellular-and-humoral-responses/