Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The use of dermatoscopes in rheumatology has been established for several years. However, the application of artificial intelligence for the detection of abnormalities in this field has not yet been reported. The aim of this project was to develop a model for detecting dermatoscope abnormalities obtained with inexpensive equipment for the purpose of understanding the role of dermatoscopy in nailfold assessment.
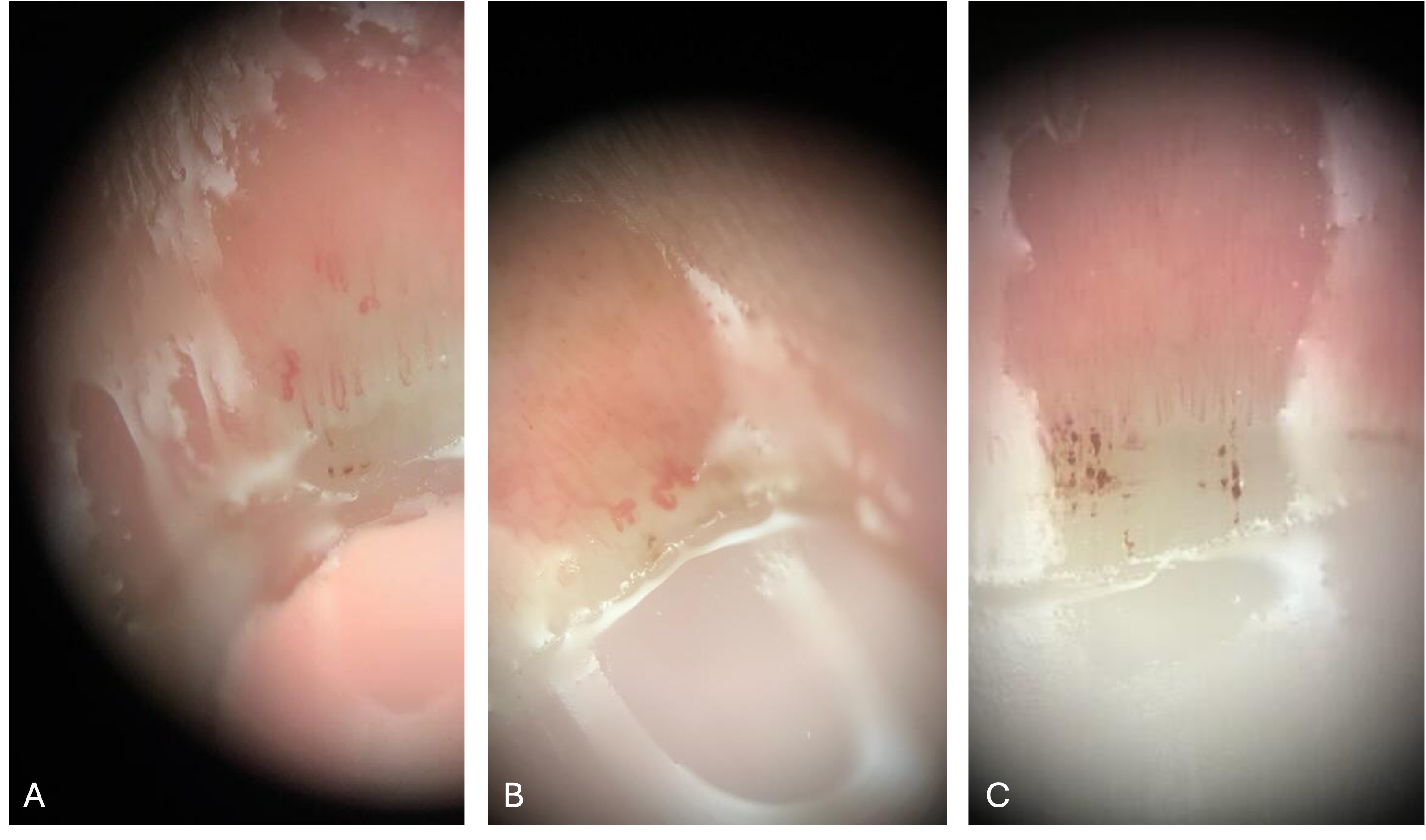
Methods: Images were retrieved from patients referred to the rheumatology clinic for evaluation of positive ANA (IRB # 230636) and a rheumatology clinic at the Hospital Clinico Universitario Lozano Blesa (Act No. 20/2018). After acclimatization, dermatoscopy (value $30) was conducted in 5 minutes using a 200x magnification lens adapted for smartphones. Images were interpreted by 2 capillaroscopists. Each image was assessed for blurriness, hemorrhage, abnormal shape, density, and capillary enlargement. 80% of the data was used for training and 20% for testing the model performance, the data was split randomly.
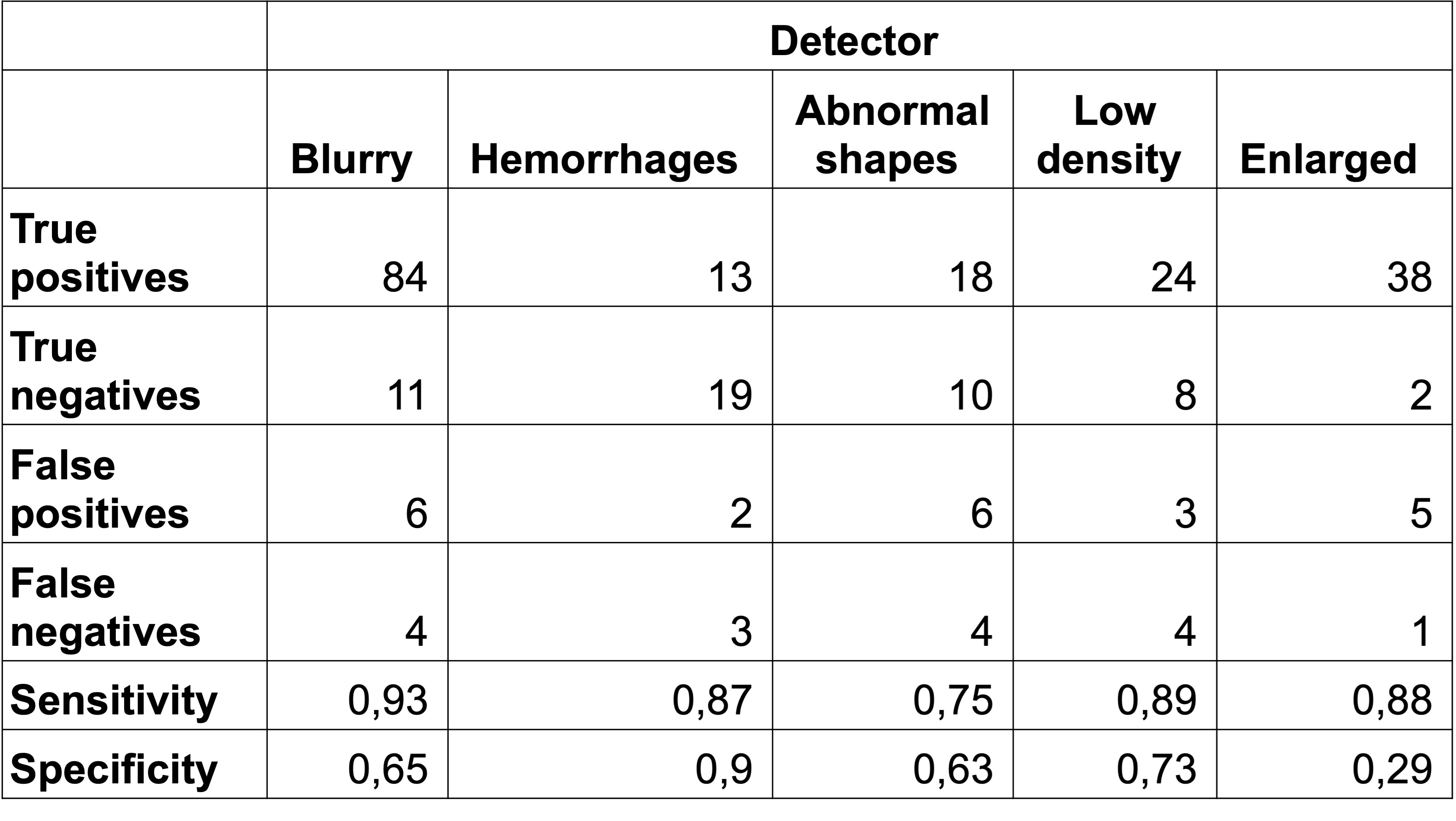
Results: 88 patients were examined with 521 images retrieved (Figure 1). The variables included blurriness, hemorrhages, abnormal shapes, low density and enlarged capillaries. We trained 5 different models on each variable (Table 1). The specificity of the model to detect blurriness was 93%, low density 89%, enlarged capillaries 88%, hemorrhages 87% and abnormal shapes 87%. The sensitivity for blurriness was 65%, low density 89%, enlarged capillaries 29%, hemorrhages 90%, and abnormal shapes 63%.
Conclusion: The model’s results were significantly limited by high class imbalance and small sample size; however, the potential remains promising as a nailfold capillaroscopy screening tool. The model performed well in detecting hemorrhages and low-density areas and showed decent accuracy for identifying abnormal shapes and blurriness. While enlarged capillaries may not be detected precisely, giant capillaries can be interpreted instead. Based on these results, the presence of blurriness, low density, and hemorrhages suggests that further evaluation with inexpensive dermatoscopy a screening tool is warranted. This tool holds great promise due to its low cost and potential availability in primary care centers, aiding in the stratification of referrals to rheumatology.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maldonado G, Ramos-ibañez E, Gracia-Tello B, Mislav R, Frech T. Artificial Intelligence Enhanced Analysis of Nailfold Capillaries by Dermatoscopy in Rheumatology Centers [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/artificial-intelligence-enhanced-analysis-of-nailfold-capillaries-by-dermatoscopy-in-rheumatology-centers/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/artificial-intelligence-enhanced-analysis-of-nailfold-capillaries-by-dermatoscopy-in-rheumatology-centers/