Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is the leading cause of mortality and morbidity in systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients. Current functional, imaging, and clinical measures of lung involvement could be biased in SSc due to its multiorgan nature, with extra-articular involvement (e.g., cardiac, musculoskeletal, esophageal) potentially affecting pulmonary function tests, high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) findings, and respiratory symptoms. Artificial intelligence (AI) reading of HRCT has emerged as a novel tool for the objective and reliable assessment of pulmonary diseases. The aim of this study is to correlate e-Lung measures, an AI-based software for HRCT image assessment, with current standard measures of pulmonary involvement used in the routine care of SSc-ILD patients.
Methods: e-Lung software (Brainomix Ltd, UK) was applied to baseline HRCT images of consecutive SSc-ILD patients. Measures of total lung volumes (TLV), percentage of ground-glass opacities (GGO%), percentage of abnormal lung (AL%), and (weighted) reticulo-vascular score (RVS-WRVS) reflecting the severity of reticular and vascular changes were derived.
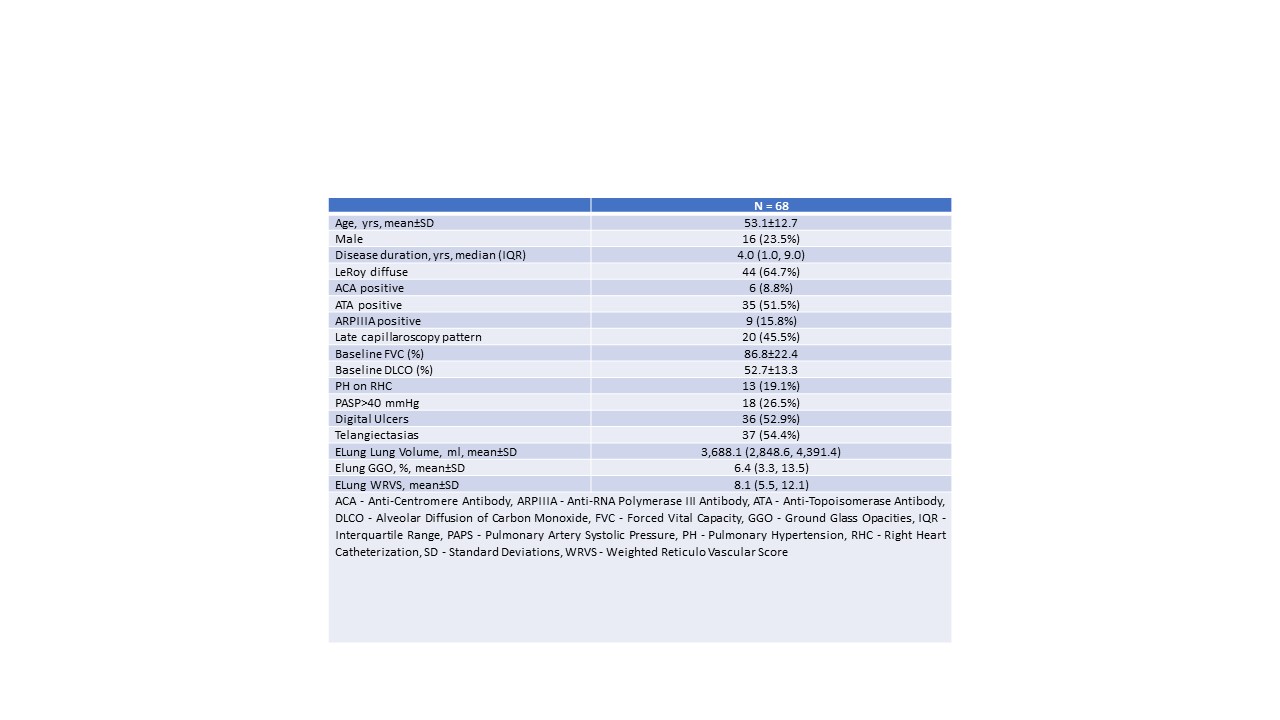
Results: A total of 68 patients’ HRCT scans were assessed by e-Lung. Clinical characteristics of the enrolled patients are reported in Table 1. Forced vital capacity (FVC) showed a moderate positive correlation with TLV (Rs=0.44, p< 0.001) and moderate negative correlations with GGO% (Rs-0.47, p< 0.001), AL% (Rs=-0.63, p< 0.001), and WRVS (Rs=-0.66, p< 0.001). Alveolar diffusion of carbon monoxide (DLCO) showed a moderate positive correlation with TLV (Rs=0.41, p=0.001), AL% (Rs=-0.46, p< 0.001), and WRVS (Rs=-0.55, p< 0.001), and a weak negative correlation with GGO% (Rs=-0.27, p=0.039). Finally, higher median WRVS values were reported in the subgroup patients with pulmonary artery systolic pressure ≥40 mmHg on heart ultrasound [8.73 (IQR 7.21-15.50) vs 7.3 (IQR 5.24-10.61), p=0.032] or with mean pulmonary artery pressure ≥25 mmHg on right heart catheterization [14.01 (IQR 7.21-19.19) vs 7.48 (IQR 5.36-10.22), p=0.012] compared to the rest of the patients.
Conclusion: e-Lung assessment was feasible in SSc-ILD patients and provided AI-derived measures from HRCT images that correlated with FVC and DLCO. WRVS was also higher in patients with pulmonary hypertension. AI could integrate current measures of assessment for pulmonary complications in SSc patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
De Lorenzis E, Thornton L, Di Donato S, Minerba M, Bissell L, Bixio R, Devaraj A, George P, Del Galdo F. Artificial Intelligence Analysis of HRCT Images Reflects Pulmonary Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis Interstitial Lung Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/artificial-intelligence-analysis-of-hrct-images-reflects-pulmonary-involvement-in-systemic-sclerosis-interstitial-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/artificial-intelligence-analysis-of-hrct-images-reflects-pulmonary-involvement-in-systemic-sclerosis-interstitial-lung-disease/