Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Membranous nephropathy (MN) is a known manifestation of IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD). Unlike primary MN, most patients with IgG4-related MN do not have anti-phospholipase 2 receptor (PLA2R) antibodies detectable in serum. Anti-THSD7A (thrombospondin type 1 domain containing 7A) antibodies are observed in some patients with anti-PLA2R-negative primary MN and have been reported in one case of IgG4-related MN. We aimed to evaluate the frequency of anti-THSD7A antibody responses patients with IgG4-RD with and without MN.
Methods: Patients who fulfilled ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for IgG4-RD were identified from a single-center cohort. Demographics, disease features, and clinical laboratory values were collected prospectively. Patients were categorized into 3 groups: IgG4-RD with MN (with or without other renal manifestations of IgG4-RD), IgG4-RD with renal involvement but without MN, or IgG4-RD without renal involvement. Anti-THSD7A antibody enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was performed on plasma from patients and age- and sex-matched healthy donors (HD). Optical density (OD) values were compared between IgG4-RD groups and HD. The OD values of the overall IgG4-RD cohort and the HD were compared using a Mann-Whitney U test. Positive antibody responses were defined by OD values either >1 or >2 standard deviations (SD) above the HD mean value. The frequencies of anti-THSD7A responses were compared between patients and HD using Chi-square tests.
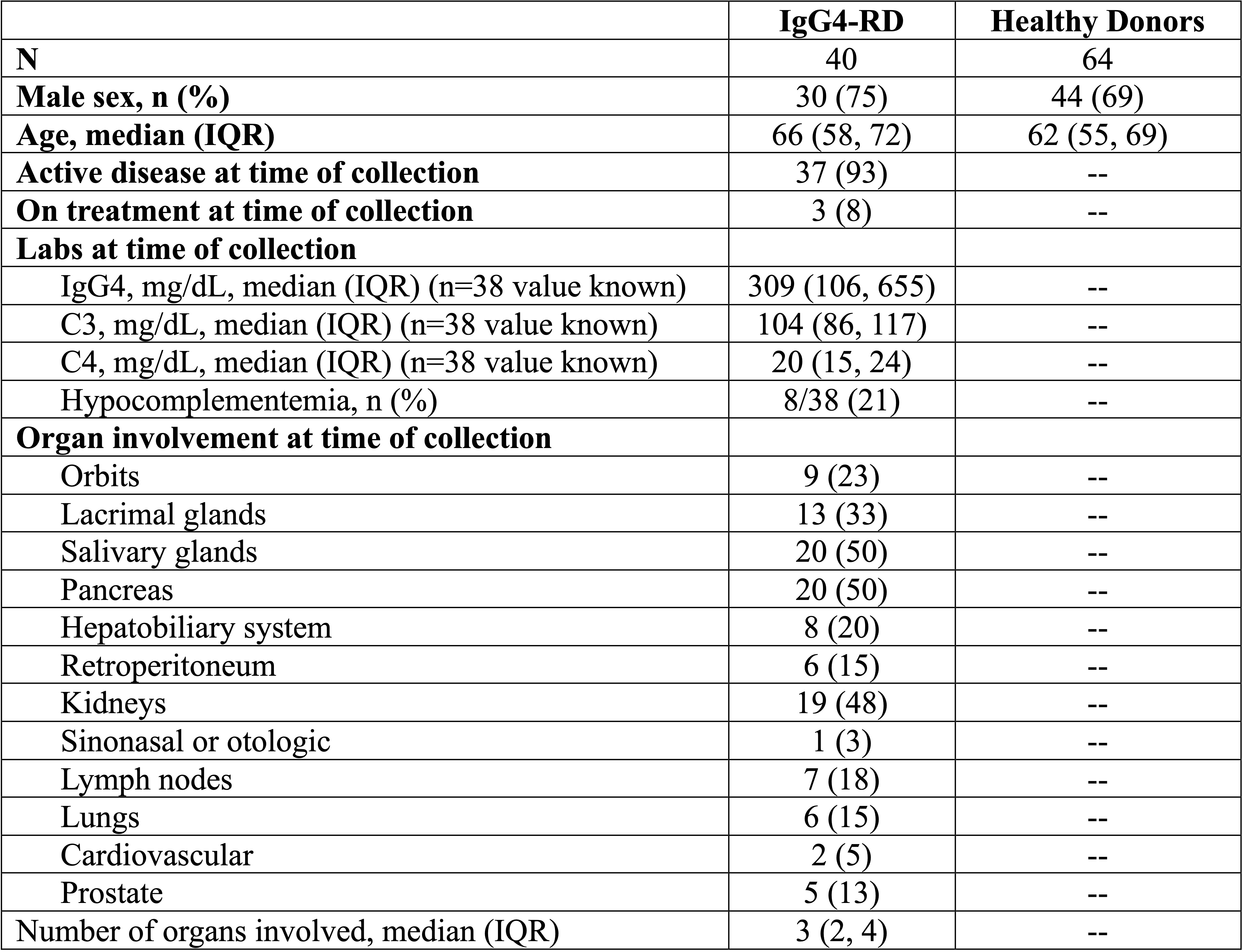
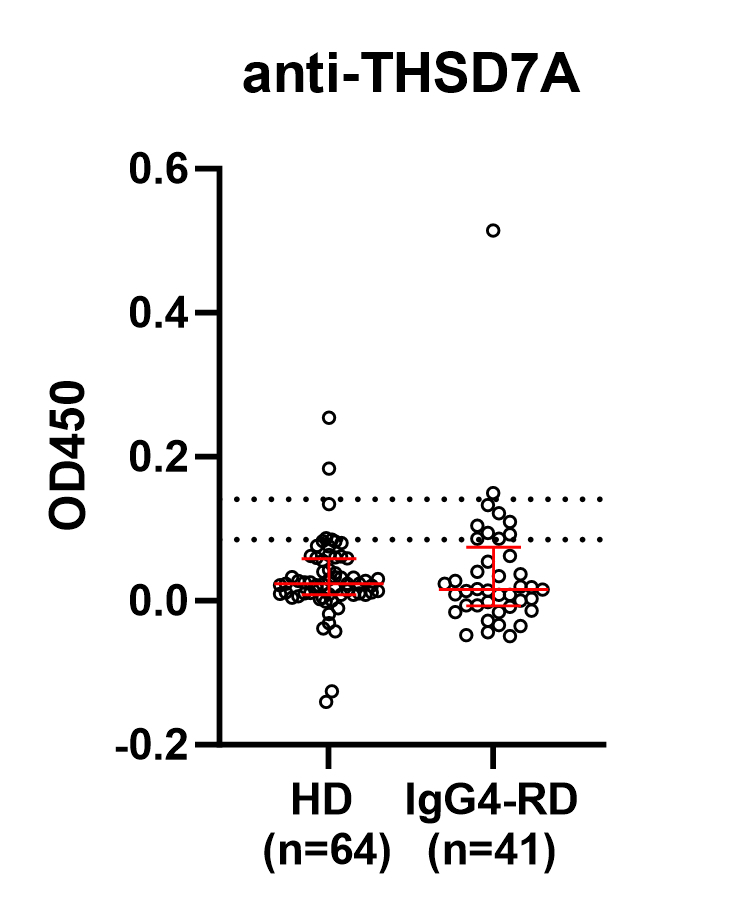
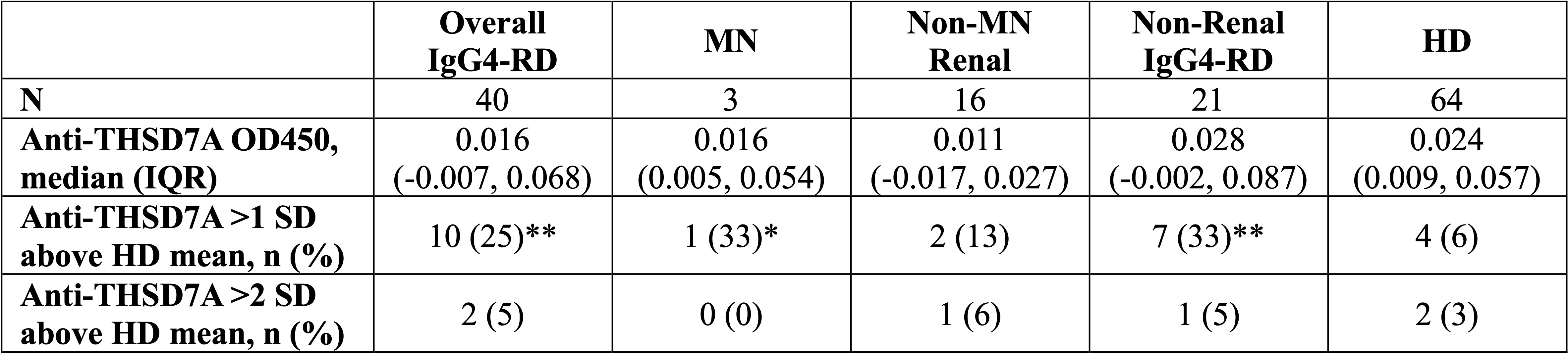
Results: Plasma samples from 40 IgG4-RD patients and 64 matched HD were identified. Demographics and disease features are summarized in Table 1. Among the IgG4-RD patients, 19 (48%) had renal involvement (n=3 with MN). There was no significant difference in anti-THSD7A antibody OD values between the IgG4-RD and HD cohorts (p > 0.05) (Figure 1). Only 5% (2/40) of the IgG4-RD patients had positive anti-THSD7A responses (1 non-MN renal IgG4-RD and 1 non-renal IgG4-RD) defined as >2 SD above HD mean, and this frequency did not differ significantly from that of HD (3.1%, 2 of 64) (all p > 0.05). A portion of patients with IgG4-RD had OD values >1 SD of the HD average and appeared to cleanly separate from the HD cohort. This frequency of low titer responses differed between HD (6%) and the overall IgG4-RD cohort (25%, p < 0.01), MN (33%, p < 0.05), and non-renal IgG4-RD (33%, p < 0.01) (Table 2). We examined the group of patients with low-titer responses compared to all other patients with IgG4-RD but observed no differences in serum IgG4, number of organs involved, or distribution of organ involvement among these patients.
Conclusion: Anti-THSD7A antibody responses do not appear to associate with IgG4-RD. Adding to the one published case report of a patient with IgG4-related MGN and anti-THSD7A antibody responses, we examined an additional 3 patients with this rare IgG4-RD manifestation and did not observe anti-THSD7A antibody responses among them. Anti-THSD7A antibodies do not appear to be common in IgG4-RD, but given the higher percentage of patients with low-titer antibodies of this type, an examination of these antibodies in a larger cohort of IgG4-RD patients, particularly one enriched with patients who have IgG4-related MN, may be worthwhile.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Katz G, Akaa J, McMahon G, Jha I, Doyle I, Fernandes A, Wallace Z, Pillai S, Stone J, Perugino C. Anti-THSD7A Antibodies Are Not Broadly Associated with IgG4-Related Disease or IgG4-Related Membranous Nephropathy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-thsd7a-antibodies-are-not-broadly-associated-with-igg4-related-disease-or-igg4-related-membranous-nephropathy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-thsd7a-antibodies-are-not-broadly-associated-with-igg4-related-disease-or-igg4-related-membranous-nephropathy/