Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Juvenile Dermatomyositis (JDM) is an autoimmune disease characterized by vasculopathy in skin and muscle, where endothelial cell (EC) dysfunction is thought to contribute to JDM pathogenesis. The primary objective of this study is to measure endothelial-derived mediators in plasma to determine circulating factors potentially involved in EC dysregulation and their association with JDM clinical phenotypes.
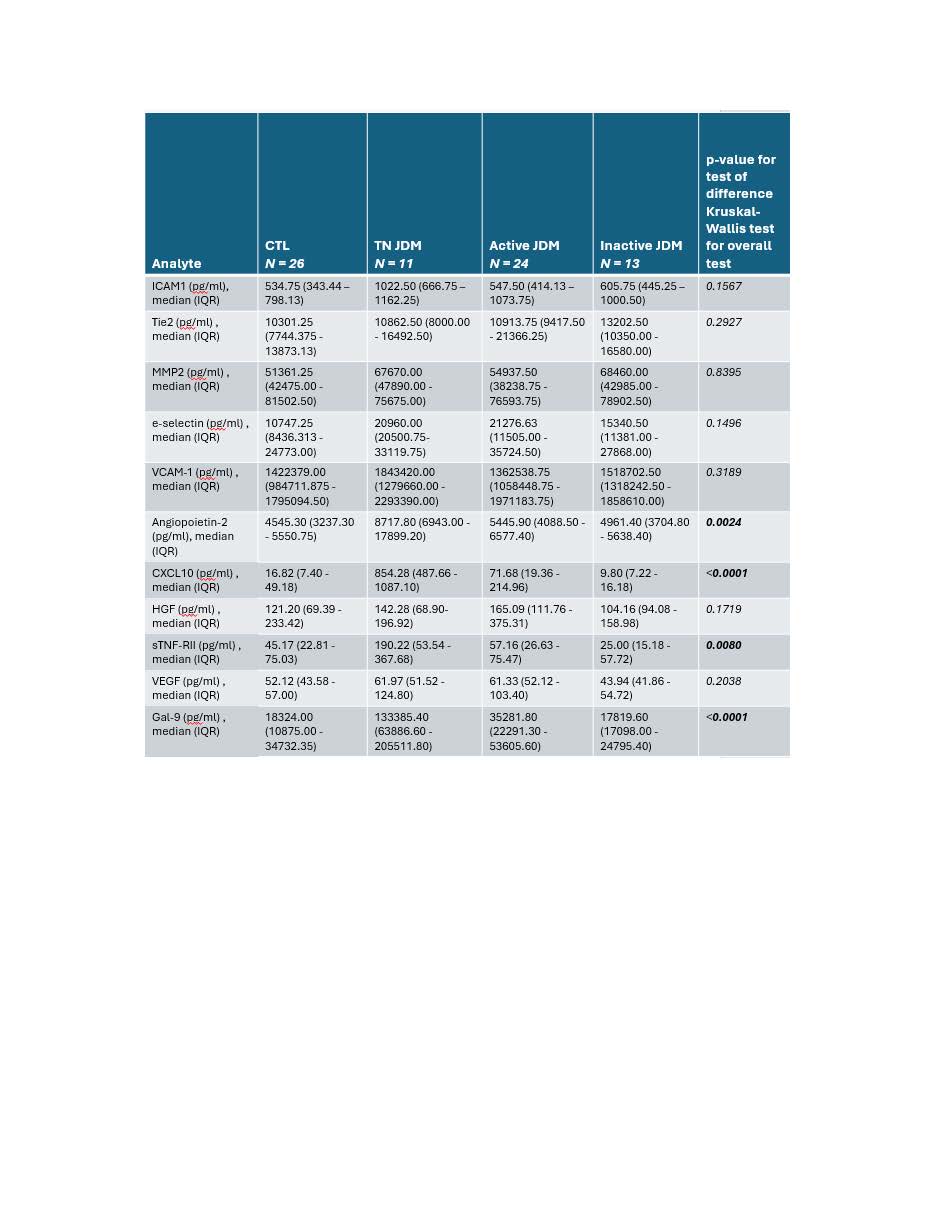
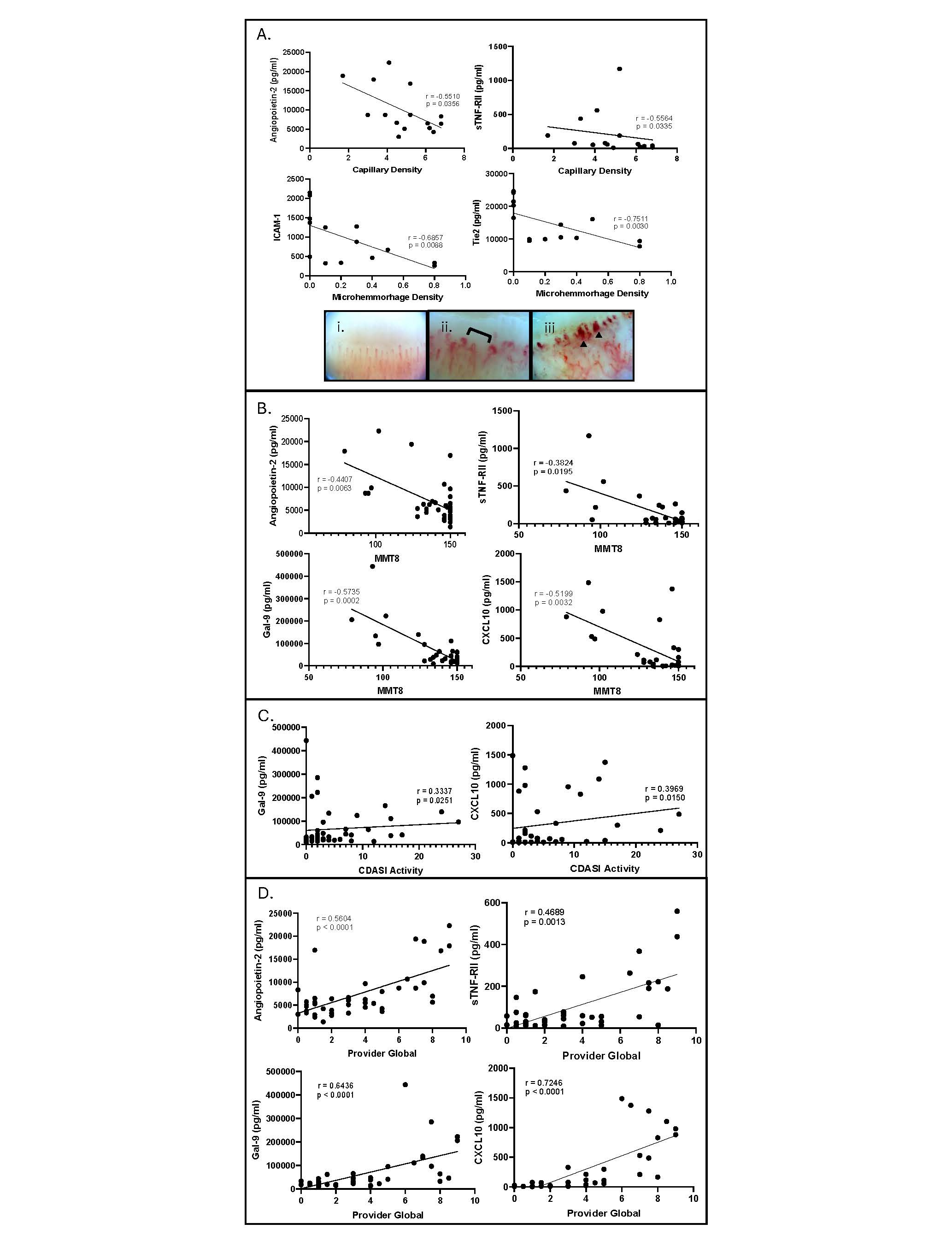
Methods: Eleven plasma angiogenic-related proteins in a cross-sectional cohort of JDM patients (n=11 treatment naïve (TN), n=24 active, n=13 inactive) and healthy controls (CTL) were measured using LEGENDplexTM. All JDM had standardized clinical disease activity scoring for skin (Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index (CDASI) activity), muscle (Manual Muscle Testing (MMT-8)), and global disease (Provider Global Assessment (PGA)). A subset of JDM had paired nailfold videocapillaroscopy (NFC) images collected (n=15), and total capillary density (capillaries/mm) and microhemorrhage density (microhemorrhages/mm) were assessed (Fig 2A). Analyte levels between JDM groups and CTL were compared using the Kruskal-Wallis test and Spearman’s correlation coefficient was used to test for associations between analyte levels, disease activity scores and NFC parameters (p< 0.05 considered significant). In vitro Matrigel tube formation assays after pre-treating human microvascular ECs with JDM or CTL plasma were performed to assess how angiogenic-related proteins in plasma affect angiogenesis in vitro. Angiogenesis was quantified with ImageJ and the Mann-Whitney test was used for statistical analysis.
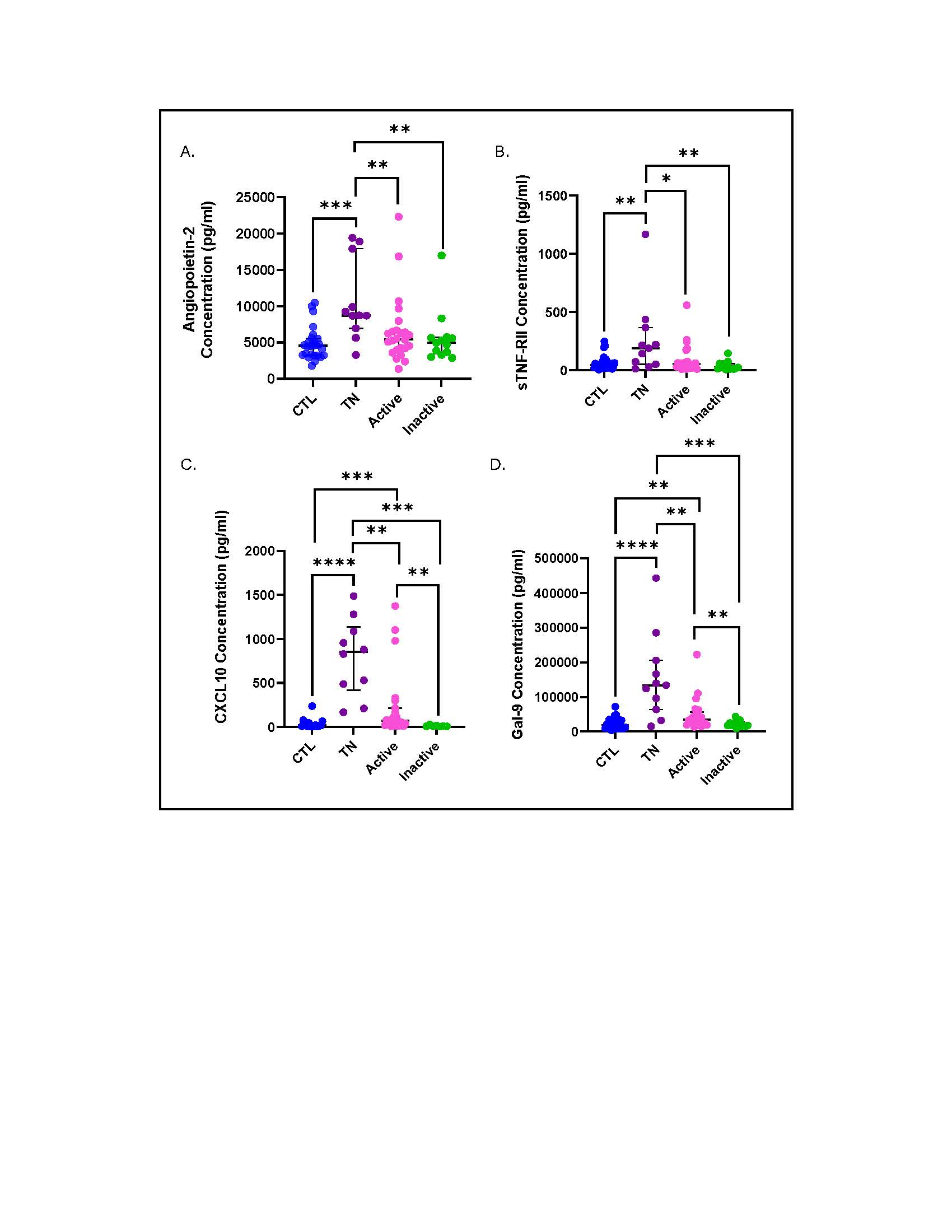
Results: JDM (combining TN, active, inactive) demonstrated an increase in 7/11 plasma analytes compared to CTL. TN as compared to active JDM specifically exhibited increased Ang2, CXCL10, sTNF-RII, and Gal-9 (Table 1; Fig 1). EC protein levels demonstrated a stronger association with muscle and global as compared to skin disease activity. While higher ICAM-1, Ang2, CXCL10, HGF, sTNF-RII, and Gal-9 levels were associated with lower MMT8 scores, only CXCL10 and Gal-9, more traditional interferon-stimulated proteins, associated with CDASI activity scores (Fig 2B, 2C). All analytes except for MMP2 and HGF were positively associated with PGA scores (Fig 2D). Interestingly, higher Ang2, sTNF-RII, VEGF and Gal-9 levels were associated with lower NFC density (Fig 2A). Lower ICAM-1 and Tie2 were associated with higher density of microhemorrhage (Fig 2A). The angiogenic capabilities mediated by active JDM plasma showed lower numbers of tubes, nodes and master junctions compared to TN JDM and CTL (p< 0.05), suggesting an anti-angiogenic phenotype.
Conclusion: Both TN and active JDM display altered angiogenic markers in plasma compared to CTL. Our results suggest a connection between circulating EC mediators and severity of vasculopathy. Furthermore, we identified that different angiogenic markers associate with specific NFC features, thus linking individual EC proteins with underlying disease pathomechanisms. These results present Ang2 as a target for further investigation due to its influence on the integrity of the vascular barrier.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Matossian S, Sturza J, Mattichak M, Brodie W, Goudsmit C, McClellan N, Kahlenberg J, Tsou P, Turnier J. Angiopoietin-2 and Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Type II Are Elevated in Treatment Naïve JDM Plasma and Associate with Increased Muscle Disease Activity and Decreased Nailfold Capillary Density [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/angiopoietin-2-and-soluble-tumor-necrosis-factor-receptor-type-ii-are-elevated-in-treatment-naive-jdm-plasma-and-associate-with-increased-muscle-disease-activity-and-decreased-nailfold-capillary-densi/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/angiopoietin-2-and-soluble-tumor-necrosis-factor-receptor-type-ii-are-elevated-in-treatment-naive-jdm-plasma-and-associate-with-increased-muscle-disease-activity-and-decreased-nailfold-capillary-densi/