Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Advancement in technology has fostered Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM), but it is mainly subjectively measured by patient reported outcomes or non-specifically via wearable data. We recently demonstrated that recognition of finger fold patterns via computer vision and a deep neural network can be used to detect joint swelling in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This study aims to extend the model of quantifying finger fold patterns and length along with joint diameters on hand photographs as a potential metrical biomarker for joint swelling in RA.
Methods: A semantic segmentation deep neural network was trained on detecting dorsal finger folds of the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints. Computer vision techniques were used to calculate diameter and pixel length of finger folds. The finger fold index (FFI) was defined as ratio between pixel length of diameter and mean recognized finger folds on PIP 2-4. The FFI was analysed for 327 PIP joints in 109 pictures of 70 RA patients in 129 visits with 30 of whom had ≥ 2 visits. The swelling biomarker is evaluated among patients in different disease activity stage, at the PIP joint level, per hand (mean of FFI of PIP 2-4) and patient characteristics.
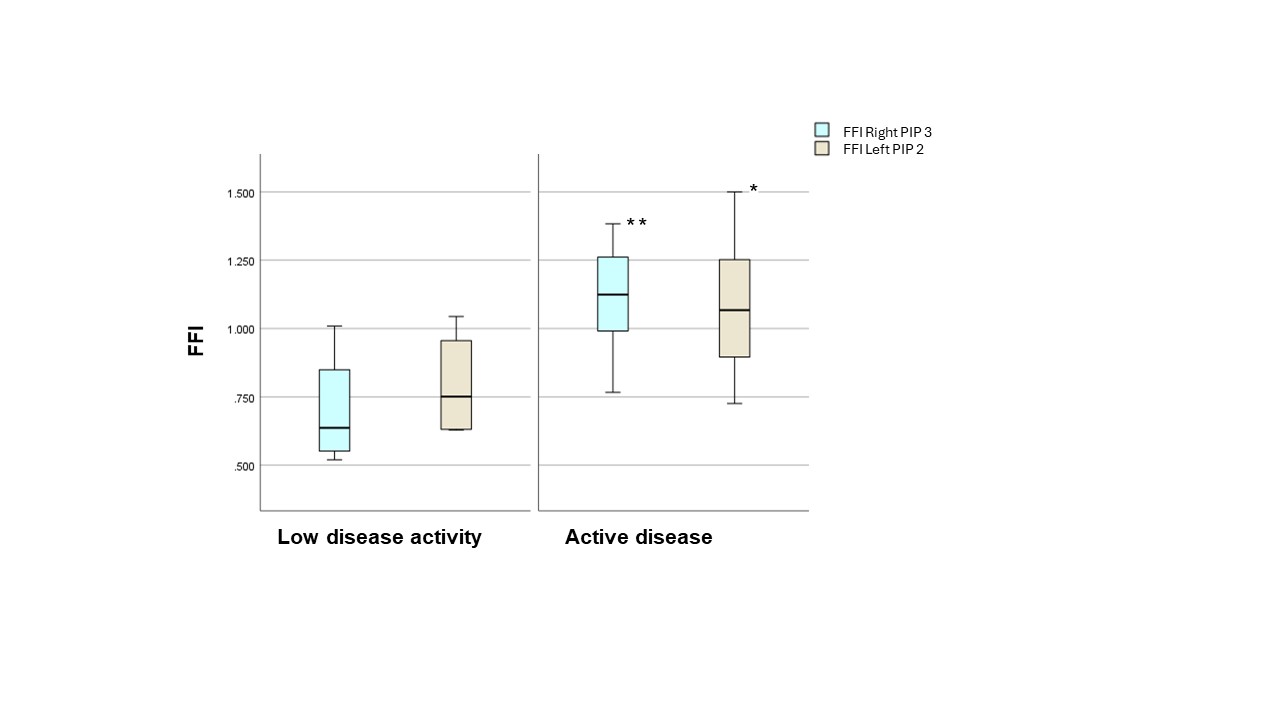
Results: The mean age was 64 years (range 34 – 96years) with 80% identifying as female. Over all visits 41 % of patients were in active disease state (DAS28-CRP ≥ 3.2). There was no significant difference in the mean of the FFI (PIP 2-4) between the left and the right hand (1.01 ± 0.16 SD; 0.98 ± 0.21 SD). The FFI did not show any difference for age or sex. At the joint level, there was a significant difference between the active and low disease activity groups in the mean of the left PIP joint 2 (1.07 vs. 0.69, p = 0.01) and the right PIP joint 3 (1.08 vs. 0.71, p < 0.001) (Fig.1). The mean FFI (left and right) differed between patients in active disease (left: 1.11, right; 1.01) versus in low disease activity state (left: 0.79, right: 0.91) but not significantly.
Conclusion: Joint extracted measurements (FFI) of PIP 2 and 3 joints on hand photographs were able to predict disease activity stage in RA patients. More research is needed to norm the metrical swelling biomarker and explore the integration of FFI into routine clinical practice for enhanced disease monitoring and personalized treatment strategies in RA.
References:
Hügle T, Caratsch L, Caorsi M, Maglione J, Dan D, Dumusc A, et al. Dorsal Finger Fold Recognition by Convolutional Neural Networks for the Detection and Monitoring of Joint Swelling in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Digit Biomark. 2022 May-Aug;6(2):31-5. PMID: 35949225. doi: 10.1159/000525061.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Koller C, Blanchard M, Maglione J, Hermann P, Huegle T. An Algorithm Pipeline for Automated Metrical Analysis of Joint Swelling in Rheumatoid Arthritis via Smartphone Hand Photographs [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-algorithm-pipeline-for-automated-metrical-analysis-of-joint-swelling-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-via-smartphone-hand-photographs/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-algorithm-pipeline-for-automated-metrical-analysis-of-joint-swelling-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-via-smartphone-hand-photographs/