Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: T Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease (2043–2047)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 10:00AM-10:50AM
Background/Purpose: The cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) autoantibody is a highly specific and predictive marker for the clinical diagnosis of RA. Elevation in CCP titers can be detected several years before patients develop clinical arthritis and is also a predictive biomarker for RA risk. CCP+ RA is associated with increased levels of distinct synovial and circulating T cell immunophenotypes, including the expansion of PD-1hi CXCR5- T peripheral helper (Tph) cells. However, whether these and other immune cell populations are altered in the peripheral blood of CCP+ individuals without RA is unknown.
Methods: We employed time of flight mass cytometry (CyTOF) with a panel of 39 surface markers to characterize T cells in cryopreserved peripheral blood mononuclear cells from a cohort of CCP- controls (n=23), CCP- first-degree relatives (FDRs) of patients with classified RA (n=27), CCP+ individuals at-risk of future RA (n=30), and active CCP+ early RA patients (diagnosis within 1 year, n=20). RA patients fulfilled the 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria. We used CITRUS to define and quantify the clusters of PD-1hi cells based on their multi-dimensional features. Expanded cell populations were confirmed by biaxial gating, and the statistical significance was determined by Mann-Whitney U test.
Results: Global T cell phenotypes were generally similar in CCP- groups, CCP+ at risk, and CCP+ early RA, including frequencies of naïve and memory CD4 and CD8 T cells and Tregs. By biaxial gating, both Tph cells and Tfh cells (PD-1hi CXCR5+) were increased in this CCP+ early RA cohort (Figure 1). The number of Tph cells in CCP+ at-risk individuals was increased compared to CCP- controls, although not statistically significant. For a broader assessment of PD-1hi T cells, we used CITRUS to cluster gated PD-1hi cells, including both CD4 and CD8 T cells. Among PD-1hi T cells, 2 specific subpopulations were identified as significantly expanded in CCP+ early RA patients (Figure 2A). Phenotypic assessment highlighted increased CD39 expression on the expanded subclusters. Biaxial gating confirmed the significant expansion of PD-1hi CD39hi CD4 memory T cells in CCP+ early RA patients compared to all the other groups (Figure 2B). In addition, the CD39hi subset of Tfh or Tph cells, but not total Tph and Tfh cells, were significantly higher in CCP+ RA compared to CCP+ at-risk group. The frequency of CD39hi Tph cells was not increased in CCP+ at-risk individuals compared to CCP- controls; however, the expression of PD-1 on these cells was increased in CCP+ at-risk compared to controls (p=0.003, 1.25-fold change), a finding also seen in CCP+ early RA patients (Figure 3). The mean expression intensity of PD-1 on CD39hi Tph cells was significantly correlated with CCP titer across all donors (r=0.376, p< 0.0001).
Conclusion: Detailed immunophenotyping analyses highlighted a robust expansion of CD39hi Tph cells in CCP+ early RA patients. In CCP+ individuals at risk of future RA, CD39hi Tph cells were not clearly increased in frequency, but expressed higher levels of PD-1 compared to CCP- controls and PD-1 levels were correlated with CCP titer. These results suggest that alterations in T cell phenotypes may be detectable not only early in RA but even preceding clinical onset after CCP elevation.
 Figure 1. Tph cells and Tfh cells were expanded in CCP+ early RA cohort.
Figure 1. Tph cells and Tfh cells were expanded in CCP+ early RA cohort.
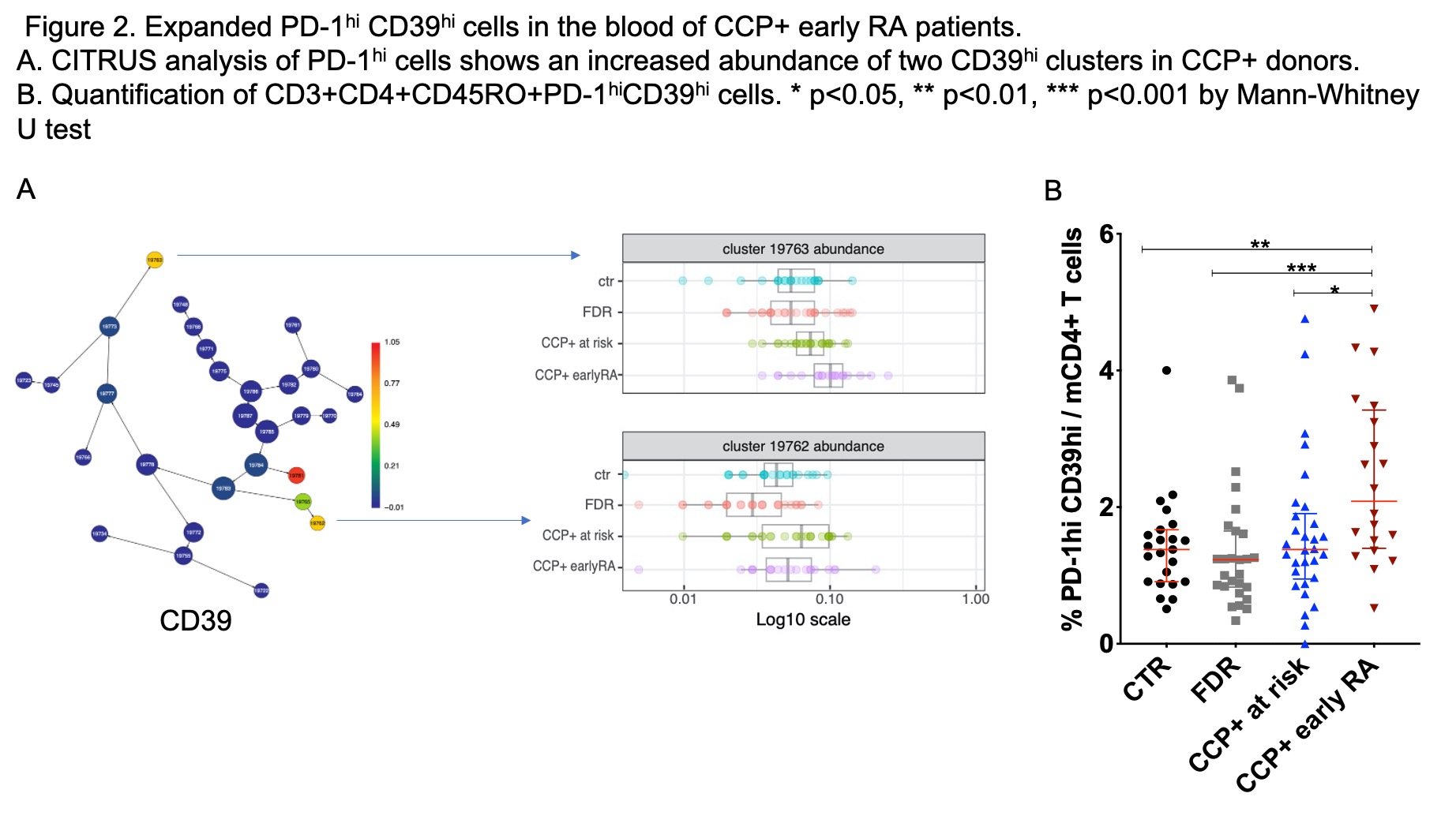 Figure 2. Expanded PD-1hi CD39hi cells in the blood of CCP+ early RA patients.
Figure 2. Expanded PD-1hi CD39hi cells in the blood of CCP+ early RA patients.
 Figure 3. Increased PD-1 expression of CD39hi Tph cells in CCP+ at-risk individuals.
Figure 3. Increased PD-1 expression of CD39hi Tph cells in CCP+ at-risk individuals.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cao Y, Keegan J, Zaccardelli A, Keras G, Seifert J, Bemis E, Feser M, Demoruelle M, D. Deane K, Norris J, Brenner M, Lederer J, Holers V, Sparks J, Rao D. Alterations in Circulating CD4+ T Cell Phenotypes in CCP+ Early RA and CCP+ At-risk Individuals by Mass Cytometry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/alterations-in-circulating-cd4-t-cell-phenotypes-in-ccp-early-ra-and-ccp-at-risk-individuals-by-mass-cytometry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/alterations-in-circulating-cd4-t-cell-phenotypes-in-ccp-early-ra-and-ccp-at-risk-individuals-by-mass-cytometry/
