Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 5:00PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) decrease quality of life due to joint destruction, pain, and decreased function. Multiple joint osteoarthritis (MJOA) can occur in up to 50% of OA cases. The high incidence of MJOA motivates the development of systemic therapies. Although there are successful therapies for RA treatment, many patients do not benefit from them and they can cause systemic side effects. In OA/RA, matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) drive joint degeneration. Small molecule MMP inhibitors were tested clinically, but were dose limited by toxicities caused by lack of MMP selectivity. Short-interfering RNA (siRNA) therapies can be designed to silence “undruggable targets” but are limited due to significant biological barriers such as extra-hepatic targeting. Albumin-based drug delivery is promising due to its high half-life, recycling ability, and its accumulation in diseased joints. Herein, we characterize a chemically stabilized MMP13 siRNA conjugate, siMMP13< (EG18L)2, which spontaneously binds albumin ‘in situ’.
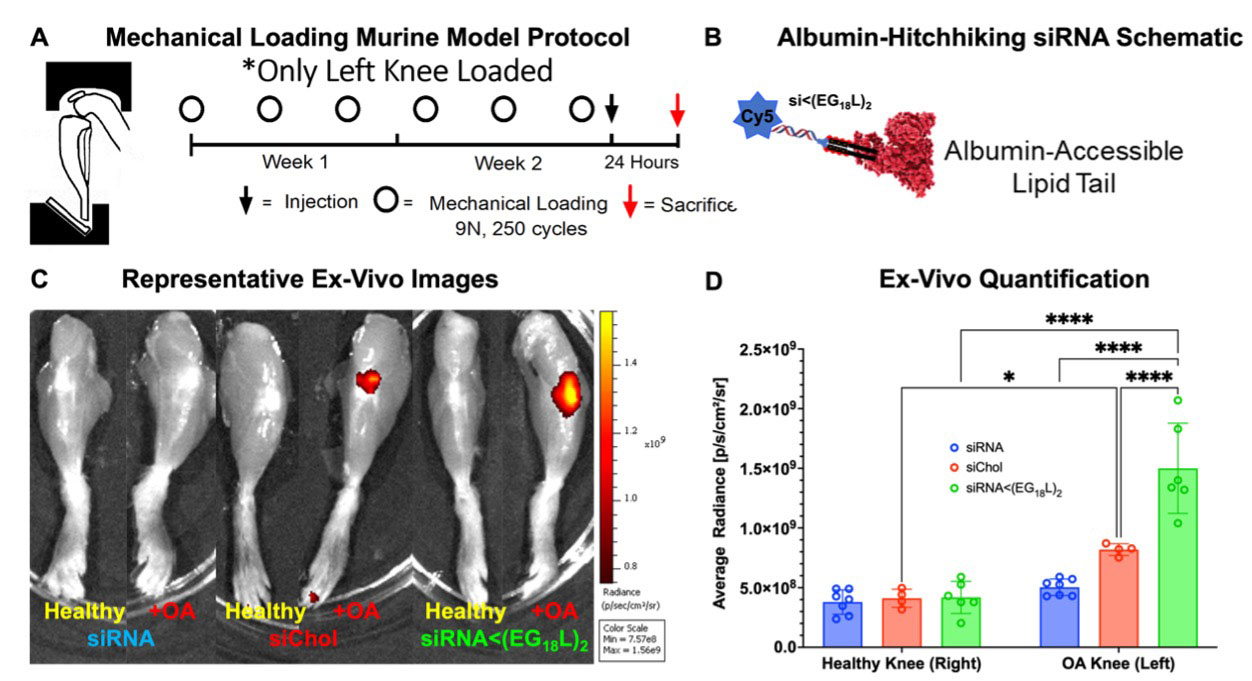
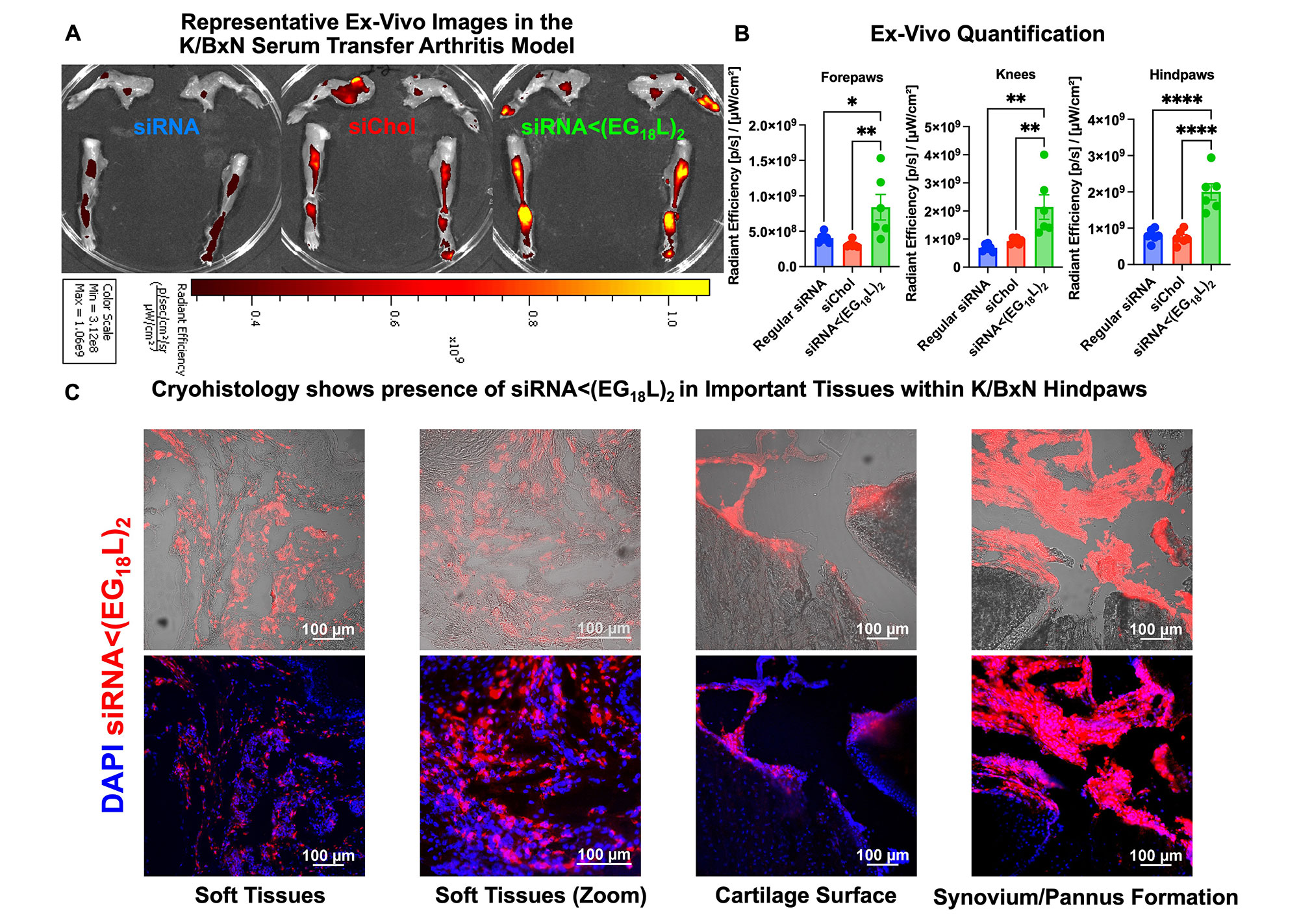
Methods: The siRNA was synthesized with alternating 2′-OMe and 2′-F ribosugar modifications to stabilize against endonucleases and phosphorothiate linkages on the backbone to block exonucleases. For albumin-binding abilities, a splitter phosphoramidite (< ) (to allow for diacyl addition i.e., 2 lipid tails) at the 5ʹ end of the sense strand was added followed by 3 repeats of a hexa-ethylene glycol (EG6) phosphoramidite. Thus, 18 EGs were added prior to each eighteen-carbon (C18) acyl (2x, L2 nomenclature). A Cy5 phosphoramidite was used in fluorescence tracking experiments. An overload-induced osteoarthritis mouse model (9N, 250 cycles, 3x/week) and the K/BxN serum transfer arthritis (STA) mouse model were used for OA and RA studies, respectively.
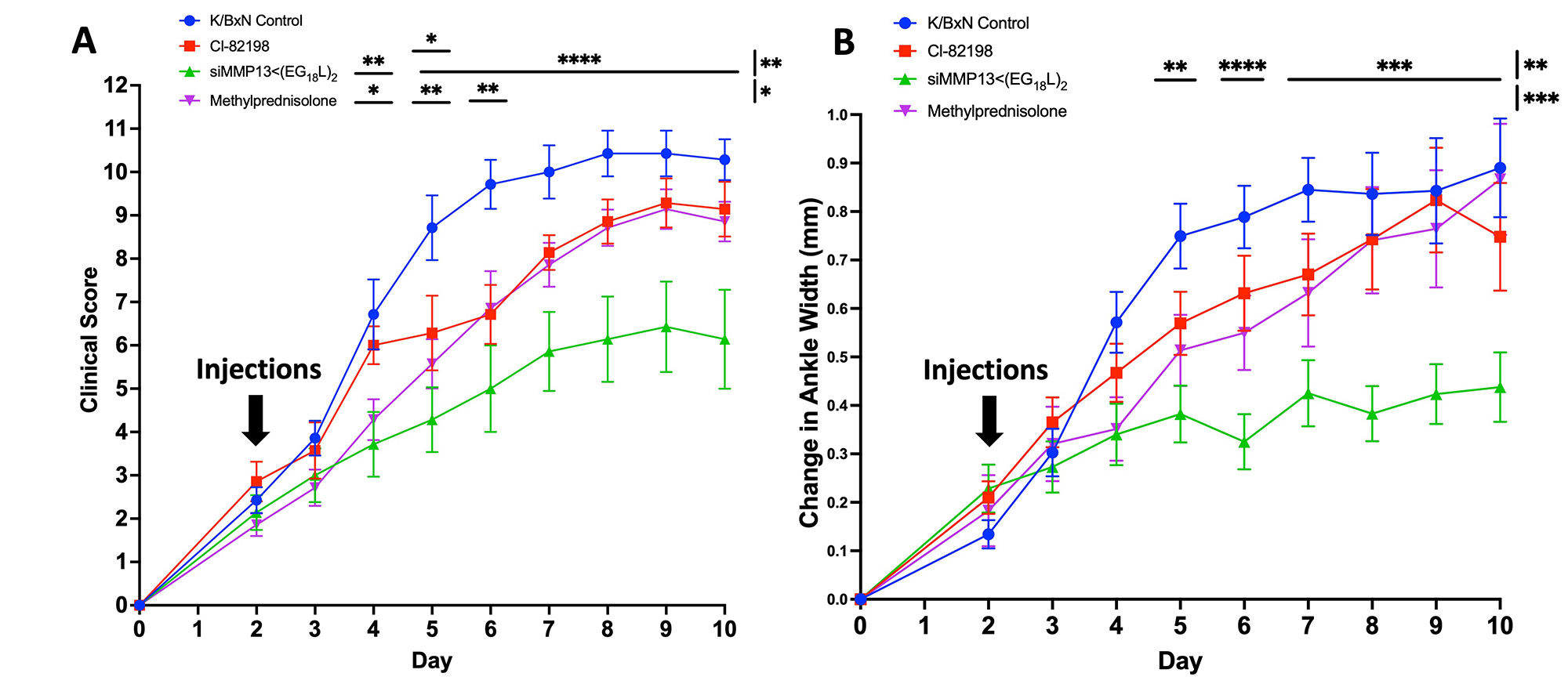
Results: RNA stabilization chemistries increased serum/synovial fluid stability, while maintaining potent MMP13 silencing. Albumin-binding dye Evan’s Blue and fluorescent albumin accumulated more in OA knees/K/BxN hindpaws than healthy knees/hindpaws. siMMP13< (EG18L)2 showed preferential delivery to OA knees/K/BxN hindpaws over healthy knees/hindpaws and demonstrated greater pharmacokinetics than non-end-modified siRNA and cholesterol-conjugated siRNA (Figures 1 and 2). In the K/BxN model, siMMP13< (EG18L)2 reached/treated multiple joints including forepaws, knees, and hindpaws (Figure 3). Overall, siMMP13< (EG18L)2 treatment was safe, provided potent MMP13 mRNA/protein knockdown, provided joint pain benefits, reduced arthritis clinical score, reduced arthritis-related genes, provided joint protection, and performed better than or equal to gold standard clinical controls.
Conclusion: This novel albumin-hitchhiking siRNA shows promise as a platform technology that can be readily adapted for targeting of many rheumatic disease-driver genes. Furthermore, this siRNA technology is modular allowing potential for the engineering of many other chemistries such as targeting moieties, etc. In these studies, siMMP13< (EG18L)2 provided to be therapeutic in pre-clinical animal models of OA and RA, showing the importance of MMP13 in both degenerative and inflammatory arthritis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Colazo J, Hoogenboezem E, Yu F, Shah V, Lo J, Cho H, Hasty K, Crofford L, Duvall C. Albumin-hitchhiking MMP13 siRNA Conjugate (siMMP13< (EG18L)2) for the Treatment of Rheumatic Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/albumin-hitchhiking-mmp13-sirna-conjugate-simmp13-eg18l2-for-the-treatment-of-rheumatic-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/albumin-hitchhiking-mmp13-sirna-conjugate-simmp13-eg18l2-for-the-treatment-of-rheumatic-disease/