Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: So far few studies explored ultrasound (US) as a tool to assess vascular subcutaneous involvement in patients affected by systemic sclerosis (SSc). We aim to evaluate the acute vascular effects of intravenous iloprost (ILO) infusion by power Doppler US (PDUS) examination at periungual (PU) and finger pulp (FP) subcutaneous areas in a consecutive series of SSc patients.
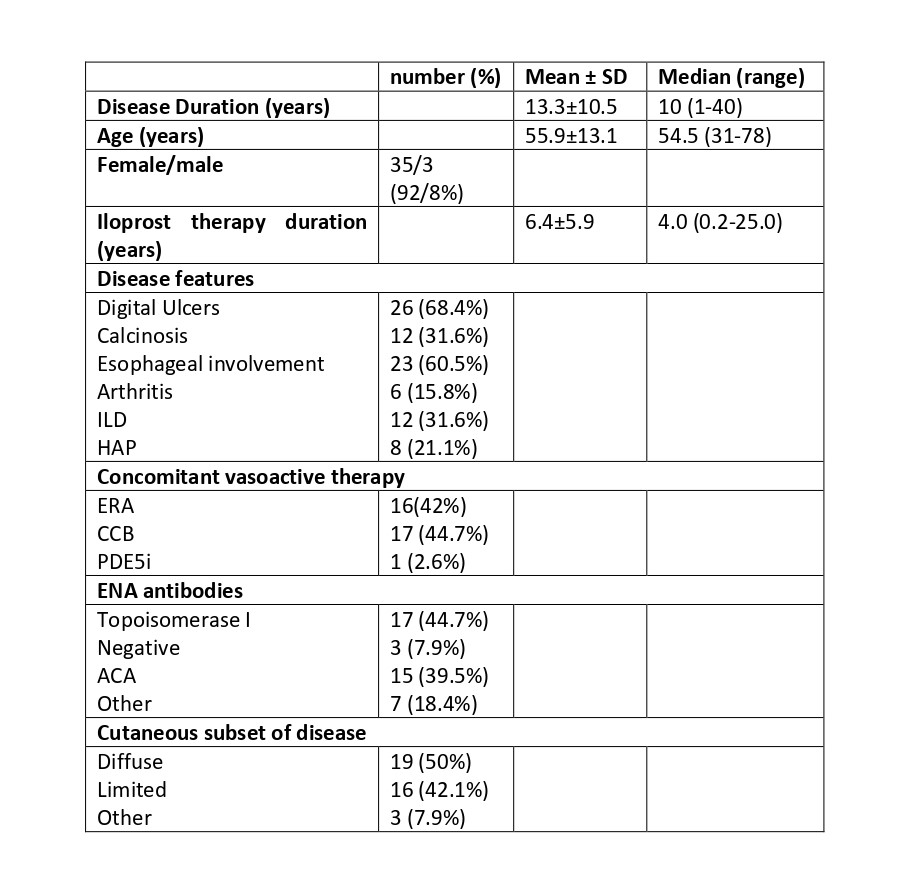
Methods: Seventy-seven consecutive observations were done in 38 SSc patients (ACR/EULAR criteria). FP and PU vascularization of the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd finger of the dominant hand were evaluated before and after ILO infusion (dosage 0.5-2.0 ng/kg/min for 4-6 hours) using an Esaote MylabClassC, (Genoa, Italy) machine equipped with a 22-8 Mhz multifrequency linear probe. The image with the highest presence of PD signal at PU and FP for each finger was scored according to a semiquantitative 0-5 scale (0 = no signal, 5 = signal of healthy controls) and summed up to obtain a total patient PD score (TotS). Single finger PU PD scores were summed to obtain total PU PD score (TotPU). Single finger FP PD scores were summed to obtain total FP PD score (TotFP). Values before and after ILO treatment were compared by T-test for paired samples. No improvement in TotS was defined as a difference between T1 and T0 observation ≤ 0; improvement if the difference between T1 and T0 was 1. Clinical demographic and US data entered in a multivariate logistic regression analysis to evaluate factors predictive of TotS improvement.
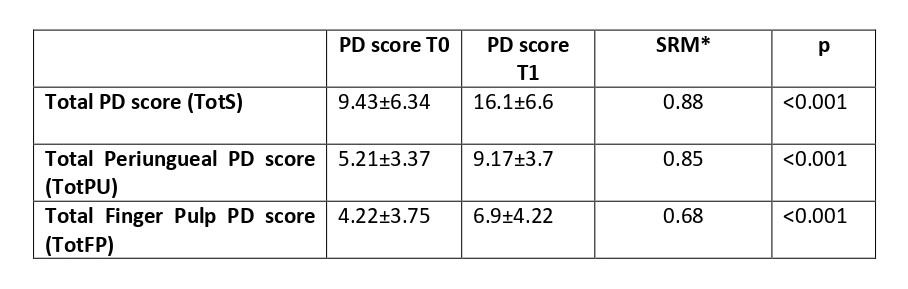
Results: Clinical and laboratory features of the enrolled patients are reported in Table 1. The effects of ILO infusion on total PD scores are reported in Table 2. TotS was 9.43±6.34 at T0 and increased to 16.1±6.6 after treatment (p= < 0.001). TotS improved in 60 observations, while in 17 there was no variation or worsening. TotPU was 5.21±3.37 at T0 and increased to 9.17±3.7 after treatment (p= < 0.001). TotFP was 4.22±3.75 at T0 and increased to 6.9±4.22 at T1 (p= < 0.001). At multivariate logistic regression analysis concomitant therapy with calcium channel blockers (CCB) was predictive of PD total score improvement > 0 (OR 4.53; 95% CI 1.14-18.1 p=0.032) and concomitant pulmonary arterial hypertension (HAP) was associated to lack of response (OR 0.27; 95% CI 0.08-0.94 p=0.04).
Conclusion: PDUS examination of the PU and FP area can demonstrate an ILO acute vascular effect in SSc patients. Therapy with CCB and presence of HAP impact on PD score improvement.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Testoni S, Magnani L, Tomassini C, Laneri A, Salvarani C, MACCHIONI P. Acute Effects of Intravenous Iloprost on Finger Power Doppler Ultrasound in Scleroderma Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/acute-effects-of-intravenous-iloprost-on-finger-power-doppler-ultrasound-in-scleroderma-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/acute-effects-of-intravenous-iloprost-on-finger-power-doppler-ultrasound-in-scleroderma-patients/