Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Plenary II
Session Type: Plenary Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Achieving an NIH Activity Index of < 2 upon treatment is associated with less LN flare and thus better long-term kidney survival. Here, we developed and validated a panel of urinary biomarkers to predict an NIH Activity Index > 2.
Methods: A panel of 1,200 proteins (Kiloplex, RayBiotech) was measured in urine samples collected within 3 weeks of kidney biopsy and at weeks 12, 24 and 52 in LN patients by the Accelerating Medicines Partnership in RA/SLE (publicly available). The classifier was trained to identify proliferative LN with an NIH Activity Index > 2. A series of machine learning classifiers were tested to identify the performing model in terms of AUC and LogLoss by cross validation in 80% of the data. Model performance was validated in a distinct 20% partition of the data. Renal response was defined at one year from biopsy in patients with baseline UPCR > 1: Complete = UPCR < 0.5, serum creatinine < 125% of baseline, prednisone < 10 mg/d; Partial = UPCR < 50% from baseline but > 0.5, serum creatine < 125% of baseline, but prednisone up to 15 mg/d; Non-responders did not meet prior definitions.
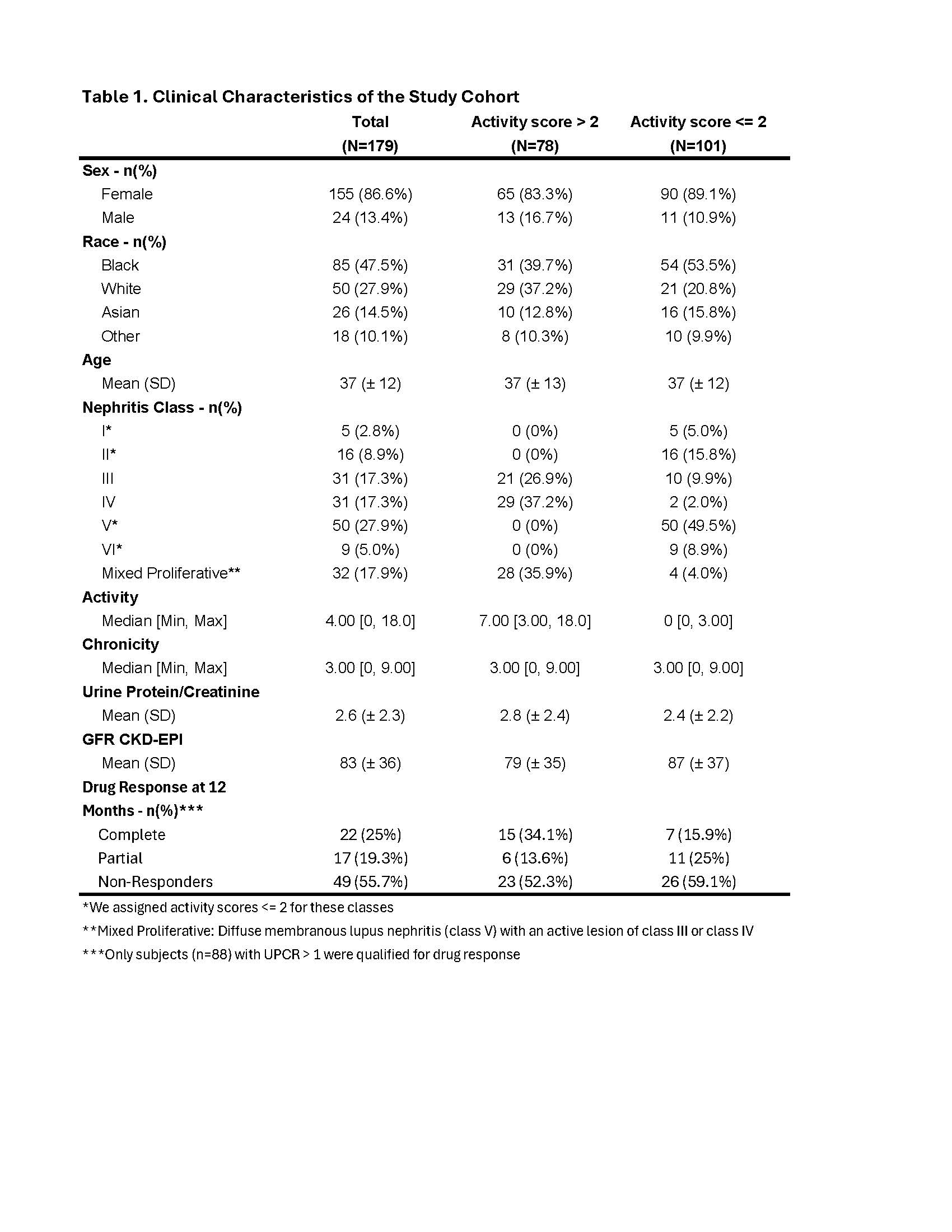
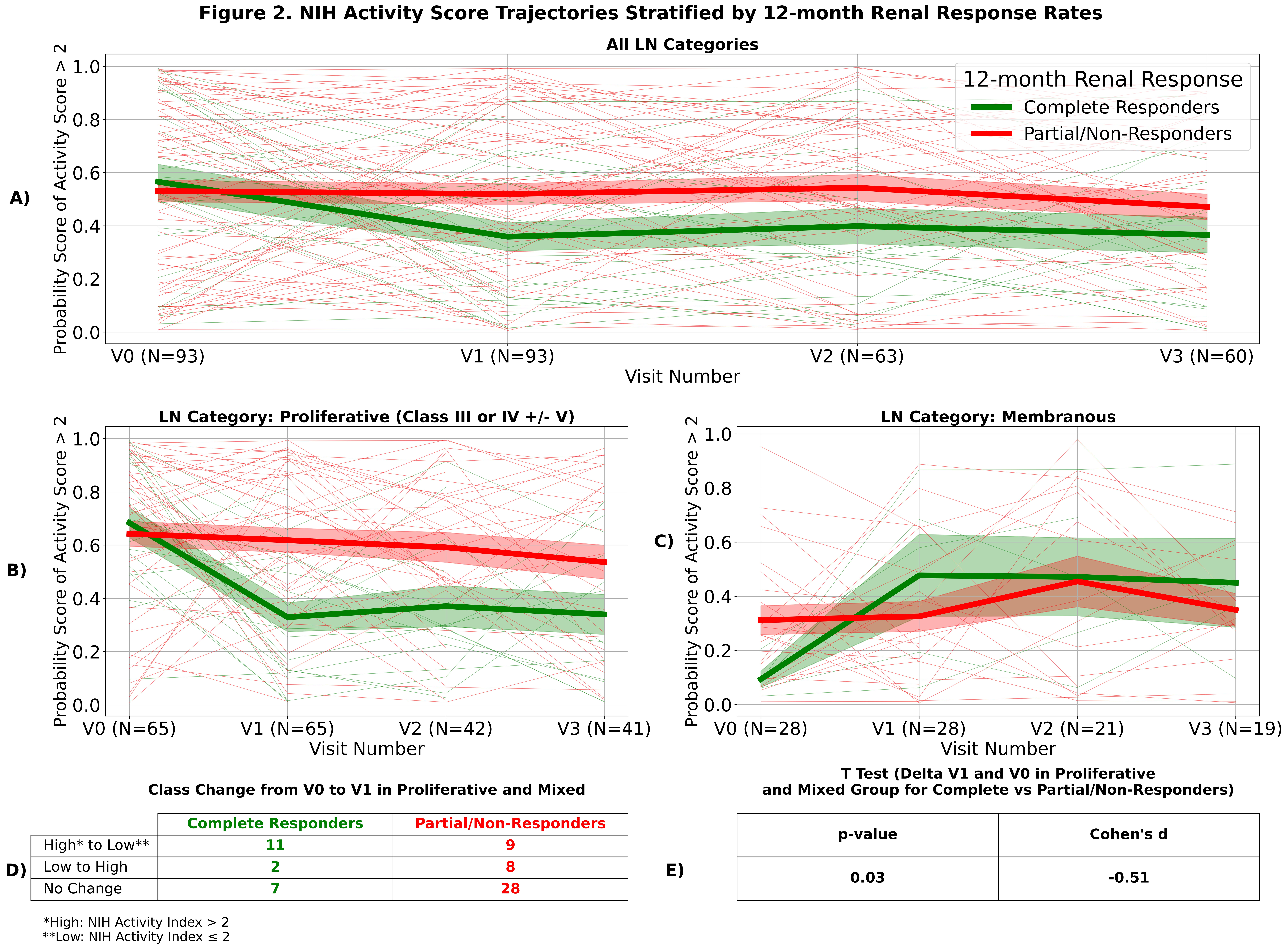
Results: A cohort of 179 subjects were included: 94 (53%) with proliferative LN (class III or IV +/- V), 50 (27.9%) with pure membranous LN, 21 (11.7%) with class I or II LN, and 9 (5%) with class VI LN (Table 1). We identified a panel of 12 urinary proteins that maximized the performance to robustly predict an NIH Activity Index > 2 (AUC 90%) while minimizing the number of biomarkers (Fig. 1A). This light gradient boosting machine (GBM) model predicted an NIH Activity Index > 2 with an AUC of 90% outperforming clinically available biomarkers such as C3 (73%), C4 (67%), anti-dsDNA (60%) and UPCR (59%) (Fig. 1A). We validated the model in a testing set confirming its accuracy (AUC 86%) and improved performance over the clinical biomarkers (Fig. 1B). The top 3 features in terms of relative importance were interferon gamma receptor 1 (IFN gamma R1), CD163 and CEACAM-1 (Fig. 1C). Because the rapid resolution of histological activity is critical to prevent irreversible kidney damage in LN, we studied the trajectories of the biomarker panel as a means to noninvasively track changes in histological activity in response to treatment. Patients who ultimately were classified as complete responders at 1 year displayed a different trajectory of the activity score predictions (Fig. 2A). At the 3-month follow up visit (V1) compared to baseline (V0), proliferative LN complete responders had a lower probability of an activity score > 2 compared to partial/non-responders (Cohen’s d: -0.51, p = 0.03) indicating a lower probability of an activity score > 2 (Fig. 2B).
Conclusion: We identified a noninvasive urinary biomarker panel that robustly predicts meaningful and actionable histological findings (active proliferative LN). It outperformed currently clinical available biomarkers. In contrast to proteinuria, which nonspecifically reflects renal disease, this panel for histological activity includes a set of 12 proteins linked to intrarenal inflammation. An improvement in the biomarker panel at 3 months predicted a clinical response at 1 year. Upon further validation, this biomarker panel could aid in the diagnosis of LN and longitudinally guide treatment decisions in LN.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fava A, Concoff A, O'Malley T, Taghavi S, Warsi T, Kumar S, Schleif C, Petri M. A Urinary Biomarker Panel to Predict the Probability of Histologically Active Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-urinary-biomarker-panel-to-predict-the-probability-of-histologically-active-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-urinary-biomarker-panel-to-predict-the-probability-of-histologically-active-lupus-nephritis/