Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Steroids play a key role in treating rheumatic diseases due to their anti-inflammatory effects. However, long-term or high-dose use leads to side effects like steroid-induced hyperglycemia. Clinical trials often fail to tailor glucocorticoid use to individual patients. Machine learning (ML) can aid in personalized medicine. A previous study at our center using supervised ML on real-world data showed a random forest model with 85.6% accuracy in predicting steroid-induced diabetes. Using this modeling, a web app was developed on the same dataset to predict hyperglycemia in individual patients. The aim is to develop and validate a ML-based web app to predict steroid-induced hyperglycemia in rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune rheumatic diseases, using baseline characteristics and expected glucocorticoid doses.
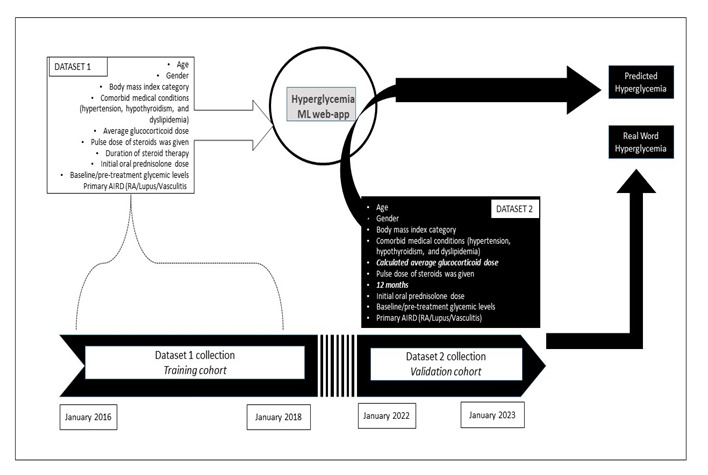
Methods: We developed a random forest classifier-based web app to predict steroid-induced hyperglycemia in patients with autoimmune conditions. Dataset 1 (2016-2018) included patients from a South India tertiary care centre, with data on demographics, comorbidities, and steroid doses. The primary outcome was the development of diabetes following glucocorticoid therapy. The model achieved 88% accuracy and was converted into a web application.
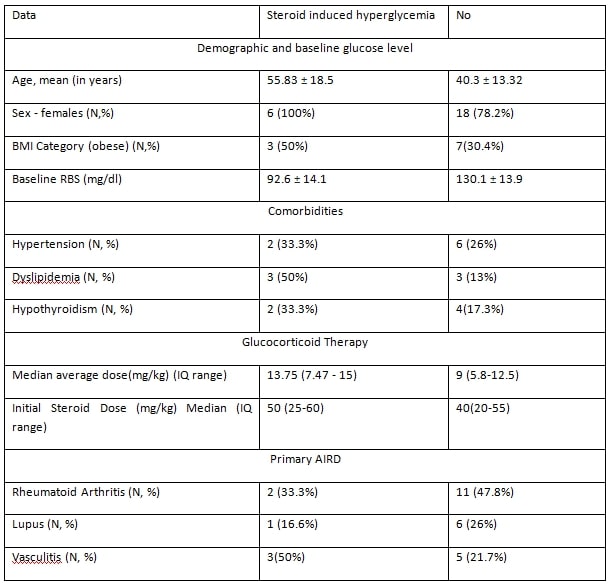
For validation, dataset 2 (2022-2023) included similar patient details, with additional parameters. We used comparable data categories from dataset 1, except for the expected average steroid dose over a 12-month period based on the primary disease. (5.8 mg/day for rheumatoid arthritis, 15 mg/day for lupus, and 11.2 mg/day for vasculitis) The web app’s prediction of hyperglycemia with expected steroid therapy was compared with actual outcome, determining sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values. The study methodology is illustrated in Figure 1.
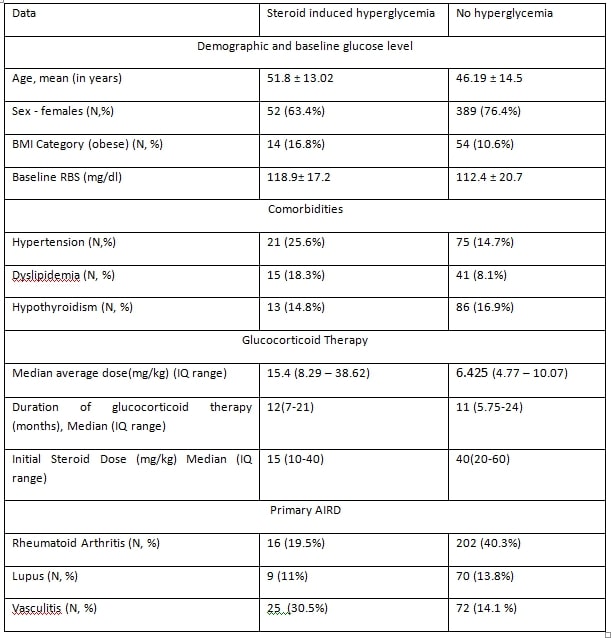
Results: In the training cohort (dataset 1), we included 588 patients, of which 83 (14.1%) developed new-onset hyperglycemia following glucocorticoid therapy. Using this data, we trained a random forest algorithm. The best model achieved 88% accuracy and an 80% area under the ROC curve, with average glucocorticoid dose, BMI, and baseline glucose level being the most important features. We developed a web application and validated it using dataset 2. The web app’s diagnostic performance for hyperglycemia prediction showed a sensitivity of 50% (95% CI: 11.81% to 88.19%) and specificity of 95% (95% CI: 78.05% to 99.89%). The negative predictive value was 88% (95% CI: 76.63% to 94.25%), and the positive predictive value was 75% (95% CI: 27.32% to 95.99%).
Conclusion: Validation of the AI ( Artificial Intelligence) based web app in a real-world cohort demonstrated high specificity, negative predictive value, and positive predictive value. This AI-driven approach to patient data can lead to personalized and accurate treatment strategies. Leveraging large multicenter datasets can further refine these tools, customizing them to match each patient’s unique medical profile for even more precise therapeutics.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Prudhvi Krishna M, Surendran S, CHALAKKARAYIL BHAGAVALDAS M, Sai S, Easwar S, Kumar R, Pradeep M. A Step Towards Personalised Medicine – Development and Efficacy of Machine Learning Based Smart-Web Application for Prediction of Steroid Induced Hyperglycemia in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Other Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-step-towards-personalised-medicine-development-and-efficacy-of-machine-learning-based-smart-web-application-for-prediction-of-steroid-induced-hyperglycemia-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-an/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-step-towards-personalised-medicine-development-and-efficacy-of-machine-learning-based-smart-web-application-for-prediction-of-steroid-induced-hyperglycemia-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-an/