Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0210–0232) Measures & Measurement of Healthcare Quality Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The presence of the HLA-B5801 allele increases the risk of life-threatening allopurinol hypersensitivity syndrome (AHS). The 2020 ACR gout management guidelines conditionally recommend HLA-B5801 testing before starting allopurinol in populations more likely to have this allele, including African Americans and individuals of Southeast Asian descent (FitzGerald et al, Arthritis Care Res 2020). While intended to reduce harm, these guidelines could result in delayed or untreated gout in these high-risk populations if appropriate systems are not in place. This project aims to identify beliefs, practices, and consequences of HLA-B5801 testing to inform future strategies that ensure prompt urate-lowering therapy (ULT) initiation for all individuals.
Methods: Data collection included a chart review and provider survey. The chart review was conducted at two academic rheumatology clinics from October 1, 2023 to September 30, 2024. All new patients and hospital discharge visits with a diagnostic code for gout (M10.XX, M1A.XX) during this period were reviewed. Manual chart review collected self-identified race as listed in the electronic health record, consideration of ULT, length of allopurinol treatment, HLA-B5801 testing, and ULT prescribing/dispensing details. A local survey of rheumatology providers assessed HLA-B5801 testing practices, perceived testing frequency, barriers, and future testing intentions. The chart review and survey results informed the creation of a fishbone diagram to identify targets for quality improvement interventions (Figure 1).
Results: We identified 78 patients who fit our criteria (Table 1). Of those, 47% of Black patients (n=14) and 75% of Asian patients (n=3) had HLA ordered (Table 2). Among Black and Asian patients who started allopurinol, HLA-B5801 testing was ordered for 50% (n=7) of patients on allopurinol for ≤6 months and for 57% (n=8) who had never received allopurinol. Of the patients who had never received allopurinol, 25% (n=2) started low dose allopurinol the same day HLA-B5801 testing was ordered while the remainder waited for results. Of the 20 survey responses, 100% reported awareness of ACR guidelines; 60% reported consistently ordering HLA-B5801 testing. The majority (85%) felt comfortable discussing race/ancestory to guide testing. Among the 8 providers who did not routinely order testing, there were concerns about delaying ULT initiation, thought that testing would not impact management, and challenges with ordering the test.
Conclusion: Providers demonstrated variable practices and beliefs surrounding HLA-B5801 testing. This may reflect uncertainty about implementing a race- or ancestry-based recommendation in clinical practice. Future goals for our quality improvement project are to reduce barriers for HLA-B5801 ordering so high-risk populations for the HLA-B5801 allele may be promptly and safely started on appropriate ULT.
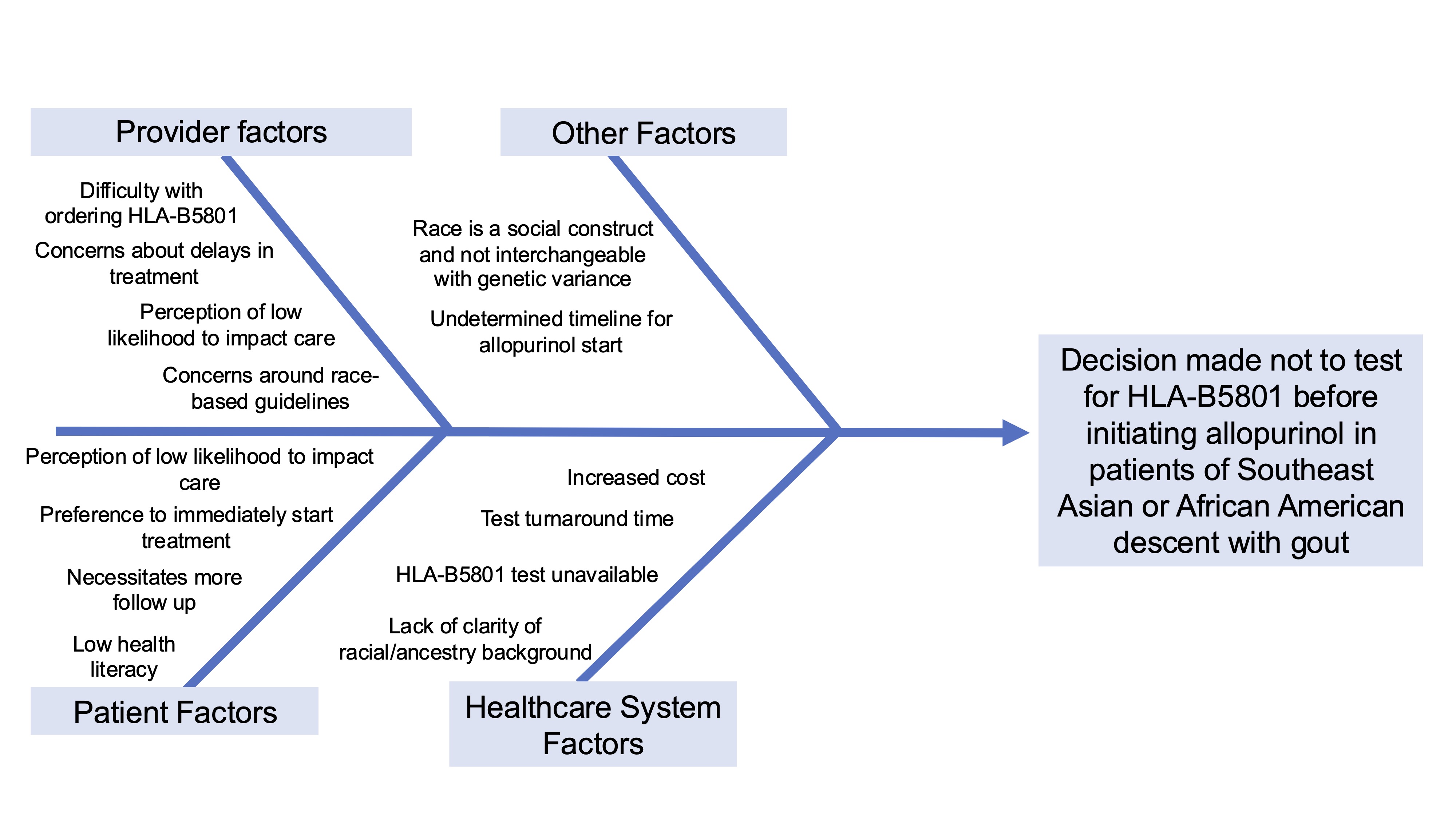 Fishbone diagram examining barriers to testing HLA-B5801
Fishbone diagram examining barriers to testing HLA-B5801
.jpg) Baseline Patient Characteristics
Baseline Patient Characteristics
.jpg) Assessment of HLA-B5801 testing in high-risk populations as defined by the ACR gout guidelines by self-identified race
Assessment of HLA-B5801 testing in high-risk populations as defined by the ACR gout guidelines by self-identified race
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Anstett S, Coburn B, Garcia-Gonzalez C, Krall M, Gupta A, Madan R, Lee S, Aguila T, Mayer A, Breed E, Thomas P, Sandorfi N, Shahane A, Dayno R. A Quality Improvement Project to Explore the Implications of the 2020 ACR Gout Guideline Recommendations for HLA-B5801 Testing [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-quality-improvement-project-to-explore-the-implications-of-the-2020-acr-gout-guideline-recommendations-for-hla-b5801-testing/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-quality-improvement-project-to-explore-the-implications-of-the-2020-acr-gout-guideline-recommendations-for-hla-b5801-testing/
