Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 10:00AM-10:50AM
Background/Purpose: National health authorities reported a prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection around 7% of the general population in Barcelona county (1). A recent report focused on autoimmune and immune-mediated inflammatory disease (AI/IMID) in Spain reported a slightly higher prevalence than in general population, especially in patients under targeted therapies and patients with systemic disease (2). Our aim was to analyze clinical characteristics and outcomes in a multidisciplinary cohort of patients with AI/IMID and symptomatic COVID-19 infection in a single tertiary center.
Methods: We included confirmed cases with RT-PCR SARS-CoV-2 test positive after nasopharyngeal swab according to Microbiology registry from Hospital Clinic of Barcelona from the 1st of March until May 29th, 2020. Data was matched with our registry of AI/IMID diseases. Additionally, patients under clinical follow-up for AI/IMID underwent a telephone survey to establish probable cases according CDC classification. We evaluated clinical characteristics and COVID-19 outcomes including clinical complications, need for ICU admission, and death as well as markers of systemic inflammatory response.
Results: From a total of 1,709 patients who gave positive for RT-PCR SARS-CoV-2, we identified 1,448 single patients. Around 5.000 patients with AI/IMID are under follow-up in our center. Thirty-one patients (23 female) with AI/IMID were identified, with a median age of 53 (IQR 25) years. Twenty-six cases were confirmed by PCR and 5 were diagnosed as probable cases. Main comorbidities included hypertension in 32% of cases and chronic pulmonary disease in 16%. Rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease were the most common diseases in 29% and 22%, respectively. Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients with AI/IMID are summarized in Table 1. Nine (29%) out of 31 patients were under glucocorticoid treatment (mean dose 7.0 ± 5.5 mg/d), 4 (12.9%) under hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), 9 under methotrexate (29%), and 8 (25.8%) under targeted synthetic/biologic DMARDs (mainly TNF inhibitors). A total of 16 (51%) patients had pneumonia and required admission. There were no differences between admission rates according to age, gender, underlying diagnosis, or baseline treatment. Most patients (87%) received the institutional standard treatment for COVID-19 with Lopinavir/ritonavir, HCQ and azithromycin. One patient had renal insufficiency and a pulmonary complication that resolved before discharge. Only 1 patient required ICU admission and another patient died due to COVID-19 infection. Characteristics and clinical outcomes of patients admitted due to COVID-19 are summarized in Table 2. During admission, immunosuppressive therapies were stopped in 7 (43%) cases and ts/bDMARDs in 3 (18%) cases. Four patients presented a clinical flare.
Conclusion: In our center, less than 1% of patients with AI/IMID had symptomatic COVID-19 infection. Most patients had a satisfactory outcome; including patients under ts/bDMARDs and clinical fares during admission and follow-up were uncommon. We are running comparative analysis with other populations and evaluating the prevalence of asymptomatic COVID-19 infection in patients AI/IMID.
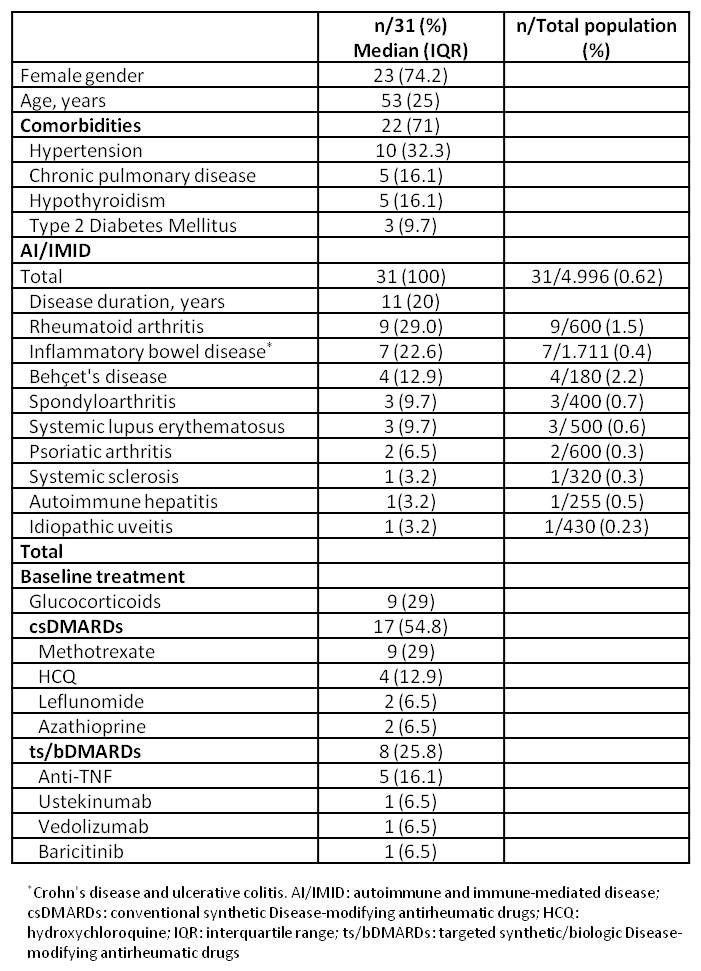 Table 1. General characteristics of symptomatic COVID-19 patients with AI/IMID
Table 1. General characteristics of symptomatic COVID-19 patients with AI/IMID
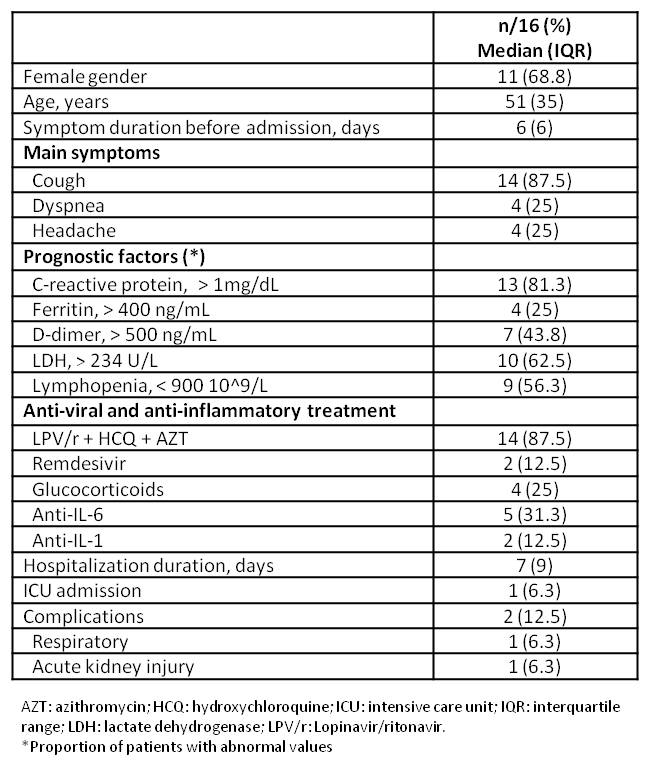 Table 2. Characteristics and clinical outcomes of patients admitted due to COVID-19
Table 2. Characteristics and clinical outcomes of patients admitted due to COVID-19
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sarmiento-Monroy J, Espinosa G, Meira F, Caballol B, Londoño M, Llufriu S, Moll A, Quintana Porras L, Ramirez Garcia F, Inciarte-Mundo J, Solana E, Blanco Y, Martinez E, Llorens V, Prieto-González S, Espigol G, Milisenda J, Cid M, Giavedoni P, Mascaró J, Blanco I, Barbera J, Sibila O, Gratacos-Gines J, Adan A, Agustí A, Sanmartí R, Panés J, Cervera R, Vila J, Soriano A, Gómez-Puerta J, INMUNOCOVID CLINIC O. A Multidisciplinary Registry of Patients with Autoinmune and Immune-Mediated Diseases with Symptomatic COVID-19 Infection from a Single Center [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-multidisciplinary-registry-of-patients-with-autoinmune-and-immune-mediated-diseases-with-symptomatic-covid-19-infection-from-a-single-center/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-multidisciplinary-registry-of-patients-with-autoinmune-and-immune-mediated-diseases-with-symptomatic-covid-19-infection-from-a-single-center/
