Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Treatments, Outcomes, & Measures
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
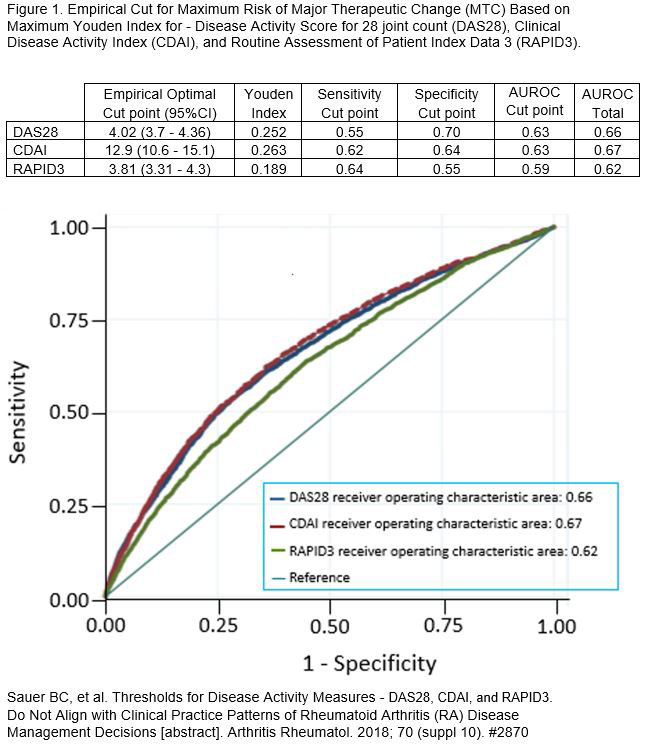
Background/Purpose: Despite ACR recommendations to initiate a major therapeutic change (MTC) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients with moderate/severe disease activity, our recent work has shown that MTC is only implemented in about 50% of these patients and that the decision to initiate MTC occurs most often at higher levels than recommended by ACR guidelines – a Youden-MTC threshold (Figure 1). This analysis evaluated the potential for ACR20 response following MTC above and below the Youden-MTC threshold for MTC and compared ACR response potential across different levels of disease activity as reported by three different Disease Activity Measures (DAMs) – DAS28, CDAI, and RAPID3 – Youden-MTC threshold and DAMs defined in Figure 1.
Methods: The clinic visit was the unit of observation for US Veterans enrolled in the VA Rheumatoid Arthritis (VARA) registry between 1/1/2006 and 9/30/2017. Eligible visits had: 1) DAS28, CDAI, and RAPID3 recorded; 2) all DAMs at two visits 18 months prior to and one visit between 60 and 180 days after the eligible visit; 3) 18 months baseline data. MTC definition (measured from 7 days before to 30 days after visit) included: 1) initiation of new biologic or non-biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) or prednisone; 2) escalation of DMARD dose by ≥25%; or 3) increase in monthly average prednisone dose by 25%; and/or 4) injection of 2 or more joints with corticosteroids. ACR20 response after each eligible visit was determined at the next follow-up visit between 60 and 180 days after the eligible visit date and stratified by disease activity by the different DAMs and the Youden-MTC threshold. The G-computation with Generalized Estimating Equations (GEE) model was fitted using the exchangeable working covariance structure to account for clustering of visits within patients.
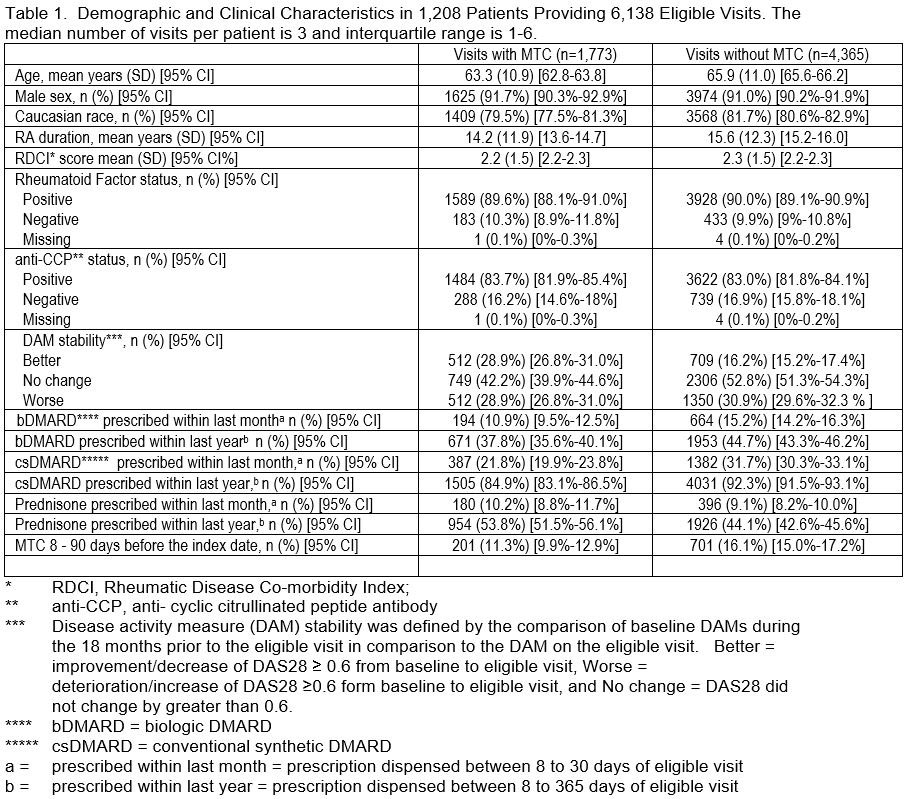
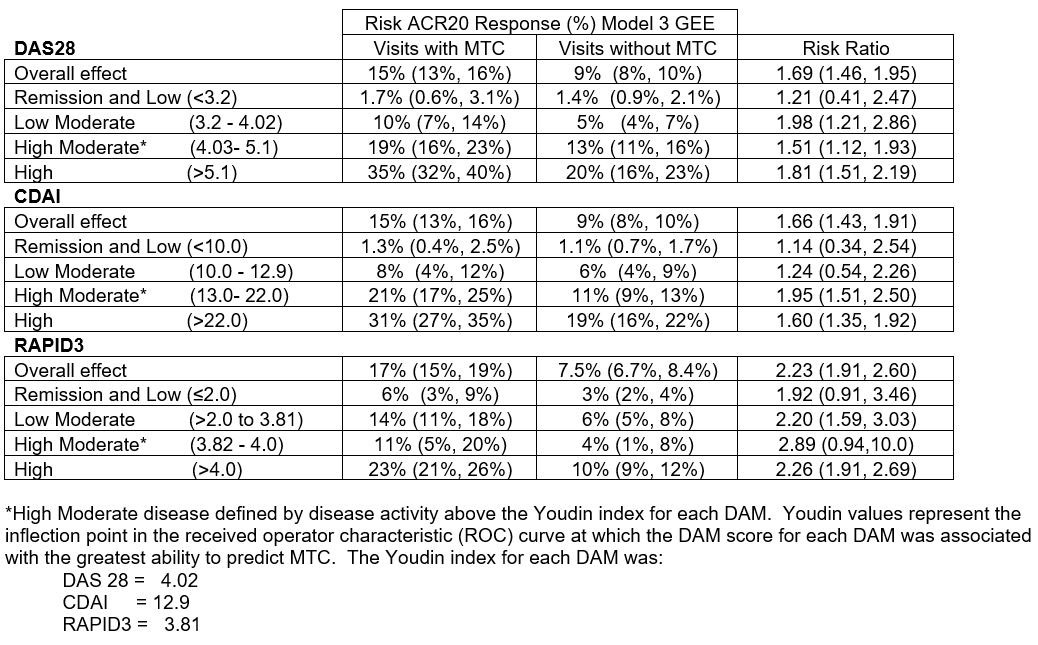
Results: In 1,208 VARA patients, there were 6,138 eligible visits – 1,773 (28.9%) with MTC and 4,365 (71.1%) without MTC. Demographic, clinical, disease stability, and DMARD use are reported in Table 1. Eligible visits with MTC had a higher rate of ACR20 response in comparison to visits without MTC at all levels of disease activity with the percent of patients with ACR response after MTC increasing with higher disease activity level particularly above the Youden threshold (Table 2). While MTC was not common below Youden-MTC threshold, ACR 20 response was still significantly greater for both DAS28 and RAPID3 in the Low Moderate group. ACR20 responses were more common in patients with disease activity above Youden-MTC with DAS28 and CDAI than RAPID3.
Conclusion: Following MTC, the ACR20 response was most likely in patients with disease activity above the Youden-MTC threshold even though the risk ratios were similar across all categories classified as active disease by ACR criteria, including the Low Moderate group. RAPID3 classified more patients at higher disease activity levels which resulted in larger effect estimates (on risk ratio scale) even though the prevalence of ACR20 response was lower. Therefore, DAS28 and CDAI may be preferred DAMs for directing MTC decisions as patients with high disease activity by these DAMs were associated with higher ACR20 response than patients with high disease activity by RAPID3.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cannon G, Chen W, Shen J, Accortt N, Collier D, Sauer B. A Comparison of Clinical Improvement Following a Major Therapeutic Change Utilizing Updated Treatment Thresholds Defined by Three Different Disease Activity Measures [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-comparison-of-clinical-improvement-following-a-major-therapeutic-change-utilizing-updated-treatment-thresholds-defined-by-three-different-disease-activity-measures/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-comparison-of-clinical-improvement-following-a-major-therapeutic-change-utilizing-updated-treatment-thresholds-defined-by-three-different-disease-activity-measures/