Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) is a frequently used composite measure by rheumatologists (MD) in routine care used to guide target-based treatment decisions. During the COVID19 pandemic treatment decisions were made during telemedicine visits relying on patient (pt) reports. Virtual care will likely be used in future. We previously showed high agreement between MD- and PT- CDAI scores and control of disease activity (score ≤10) suggesting the PTCDAI can inform if a pt has achieved RA treatment targets. Our goal here was to determine if change scores in a proposed PTCDAI between 3M and 6M visits were similar to those of the reference MD CDAI, amongst patients with differing changes of disease activity to further assess the validity of a PTCDAI for use in virtual care. We hypothesized that differences between MD and PT CDAI change scores over 3 months will be similar whether or not patients remain in controlled/uncontrolled disease activity or not.
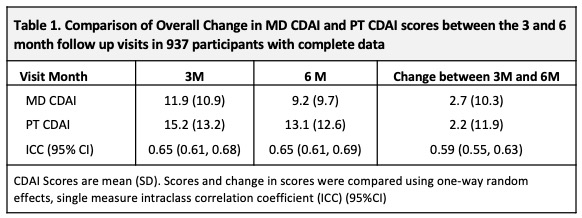
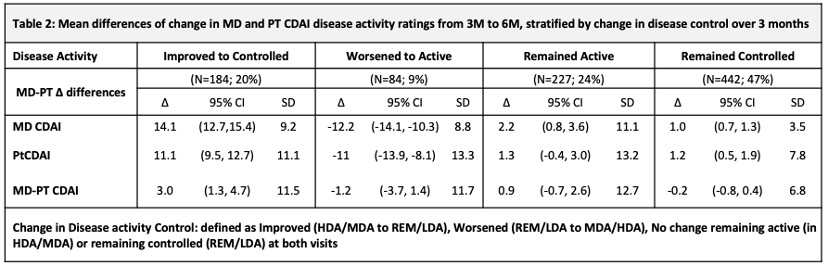
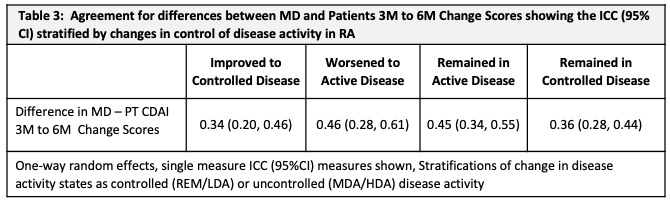
Methods: Data were from 937 pts with new onset inflammatory arthritis (Symptoms < 1 year) meeting criteria or MD diagnosis of RA, enrolled between Nov 2011 and July 2020 into the Canadian early ArThritis CoHort (CATCH) study. Eligible pts were all treated for RA and had complete data at 3- and 6- month (M) visits to calculate both CDAI scores. MDs and PTs independently rated 28-tender/painful and 28-swollen joint counts (TJC28/SJC28) using a homunculus, and provided respective global assessments (GA) (NRS 0-10). The PTCDAI score was the sum of Pt rated TJC28, SJC28, MDGA and PtGA (0-76). Changes in MD-CDAI and PT-CDAI scores were compared between 3M and 6M visits. The MD-CDAI cut point of ≤10 was used to identify pts with controlled [remission/low DA (REM/ LDA)] vs. uncontrolled (active) [high/moderate DA (MDA/HDA)] RA. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize and compare 3M and 6M change measures. A simple kappa or one-way, random effects, single measure ICC was used to assess agreement of change.
Results: At baseline, 937 pts had a mean (SD) age of 56 (15), symptoms of 5.5 (2.9) (mos), comorbidity score 1.2 (1.3); 70% were female, 81% white, 14% smokers, 30% BMI ≥ 30, 80% met RA criteria, 65%/60% ACPA+/RF+. CDAI scores were: MD CDAI 25.0 (14.1), PtCDAI 27.5 (15.9). All were treated with csDMARDs (73% methotrexate). There was high agreement between change in either CDAI (Table1). The change in MD- and PT-CDAI scores from 3M to 6M, stratified by a change or not in disease control were numerically similar and as clinically expected (Table 2). Agreement between MD and Pt CDAI change scores over 3M to 6M was moderate across disease control strata. As disease state improved or worsened, or when disease remained active, ratings of change in MD and PT-CDAI were well aligned but there was more variability in change ratings as disease activity improved, with patients rating less improvement than the MDs (Table 3).
Conclusion: These data provide additional evidence for the reliability of change in PTCDAI scores between 2 visits and warrant evaluation of the PT CDAI in future studies of outcomes for use in virtual care and telemedicine.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bykerk V, Schieir O, Valois M, Hazlewood G, Hitchon C, Boire G, Tin D, Bessette L, Keystone E, Thorne C, Pope J, Bartlett S. A Change in a Patient Informed Clinical Disease Activity Index (PTCDAI) Is Similar to Their Rheumatologists CDAI When Following Patients with Early RA in the Canadian Early Arthritis Cohort (CATCH) Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-change-in-a-patient-informed-clinical-disease-activity-index-ptcdai-is-similar-to-their-rheumatologists-cdai-when-following-patients-with-early-ra-in-the-canadian-early-arthritis-cohort-catch-st/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-change-in-a-patient-informed-clinical-disease-activity-index-ptcdai-is-similar-to-their-rheumatologists-cdai-when-following-patients-with-early-ra-in-the-canadian-early-arthritis-cohort-catch-st/