Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: CD19 CAR T treatment has demonstrated clinical benefits to patients with severe/refractory systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), possibly due to resetting autoimmunity. A-319, a highly potent T cell engager (TCE), is able to eliminate CD19+ B cells in patients (pts) with hematological malignancies (T1/2: 4-8 hrs). We evaluated if A-319 has the potential to treat and reset autoimmunity in SLE.
Methods: Pts with moderate to severe refractory SLE were treated with A-319. In week (W) 1, pts received A-319 at 0.05μg/kg/day, on days 1, 3 and 5 by 24 hrs IV infusion. In W2-4, pts received A-319 at 0.3μg/kg/day, on days 1, 3 and 5 by 6 hrs IV infusion. Safety, PK and PD parameters including peripheral blood (PB) B cell counts, autoantibodies, and other disease- related biomarkers and efficacy are evaluated for up to 1 year. The study, approved by the local hospital IRB, was registered as NCT06400537.
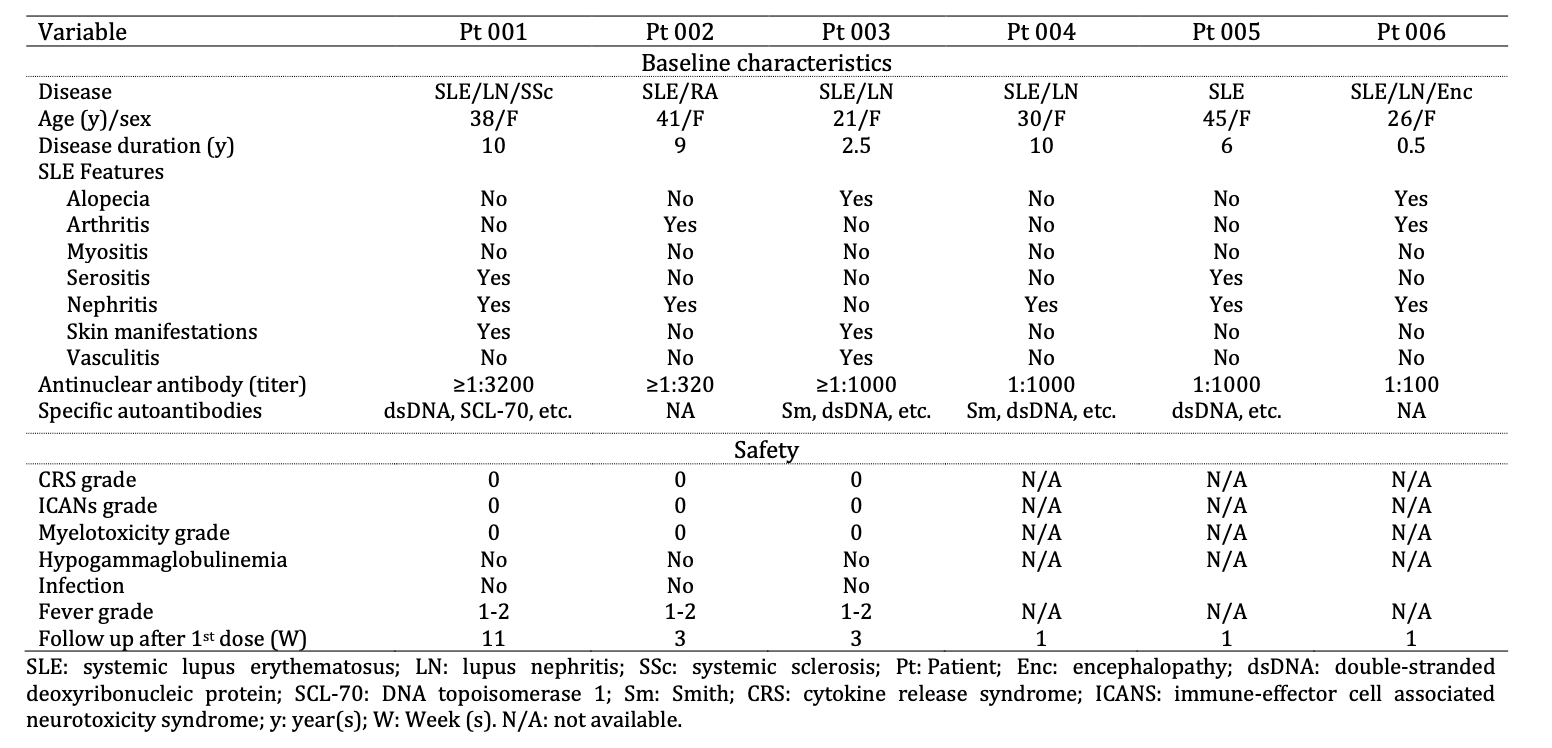
Results: Six pts (SLEDAI-2K: 8-16) received A-319 treatment. Baseline (BL) characteristics are listed in Table 1. Pts had severe/refractory SLE with a median (range) duration of 7.5 (0.5-10) years. Pt 006 had severe SLE with lupus nephritis (LN) and encephalopathy. Two pts had disease overlap with systemic sclerosis (001) and rheumatoid arthritis (002), and five (001, 002, 004, 005 and 006) had concomitant LN. All patients had grade I-II fever (drug-related) during the treatment. No other drug-related adverse events were observed including cytokine release syndrome (CRS), immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome(ICANS), myelotoxicities, hypogammaglobulinemia or infections.
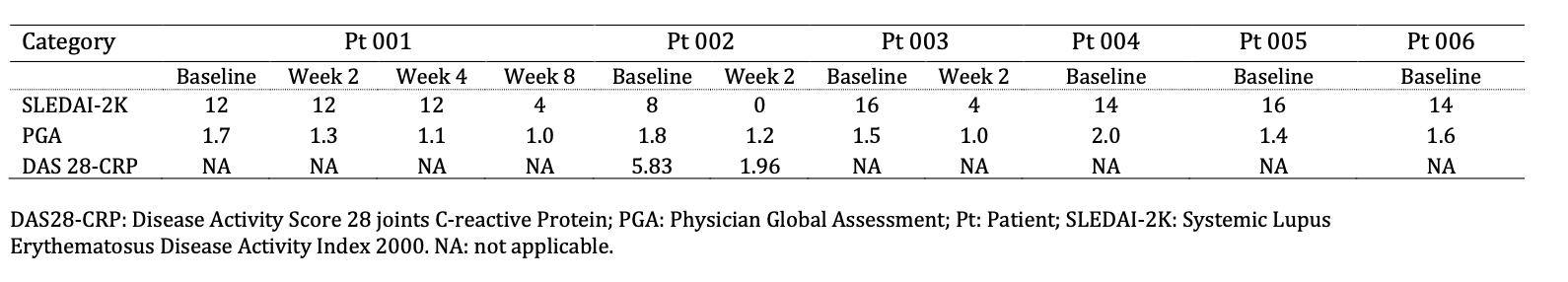
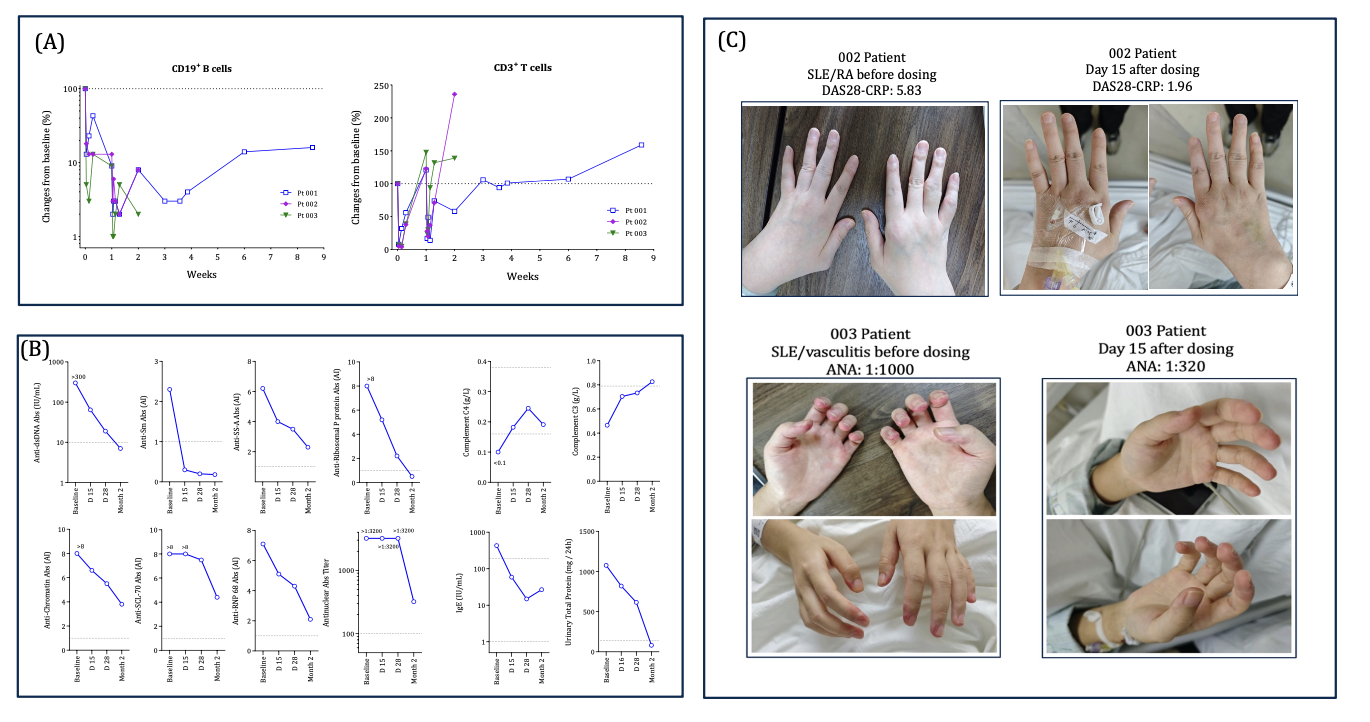
Rapid PB CD19+ B cell depletion was observed during W1. Pt 001 showed CD19+ B cells recovery to >10% of BL at W2 and W4, respectively (Fig 1A). Pt 001 had a marked decrease of autoantibody levels including ANA and anti-dsDNA, Sm, SSA, ribosomal P protein, chromatin, SCL-70, and RNP 68 (Fig. 1B) by W8, with normalization of C4 and IgE levels by Day 15, and C3 and urinary total protein levels by W8. SLEDAI-2K scores improved in Pts 001, 002 and 003, from BL 12 to 4 at W8, 8 to 0 at W2, 16 to 4 at W2, respectively (Table 2). DAS-28 CRP score improved from 5.83 at BL to 1.96 at W2 in Pt 002, while Pt 003 showed improvement of SLE-related vasculitis by W2 (Fig. 1C).
Conclusion: A-319 is well tolerated in severe/refractory SLE pts without evidence of CRS, ICANS or other safety issues commonly seen in T cell-mediated B cell depletion therapies. A-319 (0.05 + 0.3μg/kg) treatment demonstrated rapid B cell depletion, autoantibody reduction, and organ function improvement as early as W2. Evidence of partial B cell recovery was seen by W2. These results suggest that A-319 could rapidly reset autoimmunity with normalization of the B cell repertoire in SLE patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mei C, Guan X, Wu B, Li M, Liu X, Chen X, Song Y, Wang W, Wang C, Mei H, Duan X, Jiang L, Qiu W, Yu L, Liu Y, Zhao X, Zhong X, Xue S, Shen W, Tan Y, Yu G, Tu G, Chen H, Sun A, Yan X, Huang A, Du R, Li Q. A-319, a CD3 X CD19 T Cell Engager (TCE), for the Treatment of Severe/Refractory SLE: Early Evidence of Rapid Reset of Disease-Specific Autoimmunity [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-319-a-cd3-x-cd19-t-cell-engager-tce-for-the-treatment-of-severe-refractory-sle-early-evidence-of-rapid-reset-of-disease-specific-autoimmunity/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-319-a-cd3-x-cd19-t-cell-engager-tce-for-the-treatment-of-severe-refractory-sle-early-evidence-of-rapid-reset-of-disease-specific-autoimmunity/