Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: SpA Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Diagnosis of axial spondyloarthritis (AxSpA) is challenging and often delayed primarily due to the lack of sensitive and specific markers needed for accurate and timely identification. The pathophysiological importance of extracellular 14-3-3η antigen, typically an intracellular protein, and its autoantibodies (AAbs) is well-established in autoimmune rheumatologic disorders. Previous studies have confirmed the diagnostic and prognostic value of 14-3-3η AAbs in RA and AxSpA. This study aims to validate the findings in AxSpa and test whether 14-3-3η levels change over time.
Methods: Sera from a pilot cohort of 49 patients with AxSpA obtained from the Follow Up Research Cohort in Axial Spondyloarthritis (FORCAST) Prognostic Cohort, and from 25 healthy controls (HC), previously tested on the MSD platform, were analyzed using a new Luminex® 14-3-3η AAb assay. Sera from a second test cohort of 114 AxSpA patients at baseline and at year 1 and from 86 presumed healthy individuals were tested for 14-3-3ƞ AAb levels for confirmatory purposes. The diagnostic performance of 14-3-3η AAbs was assessed using regression modeling and ROC analysis, adjusting for covariates. The optimal thresholds were identified through the Youden index, with significance defined as p< 0.05.
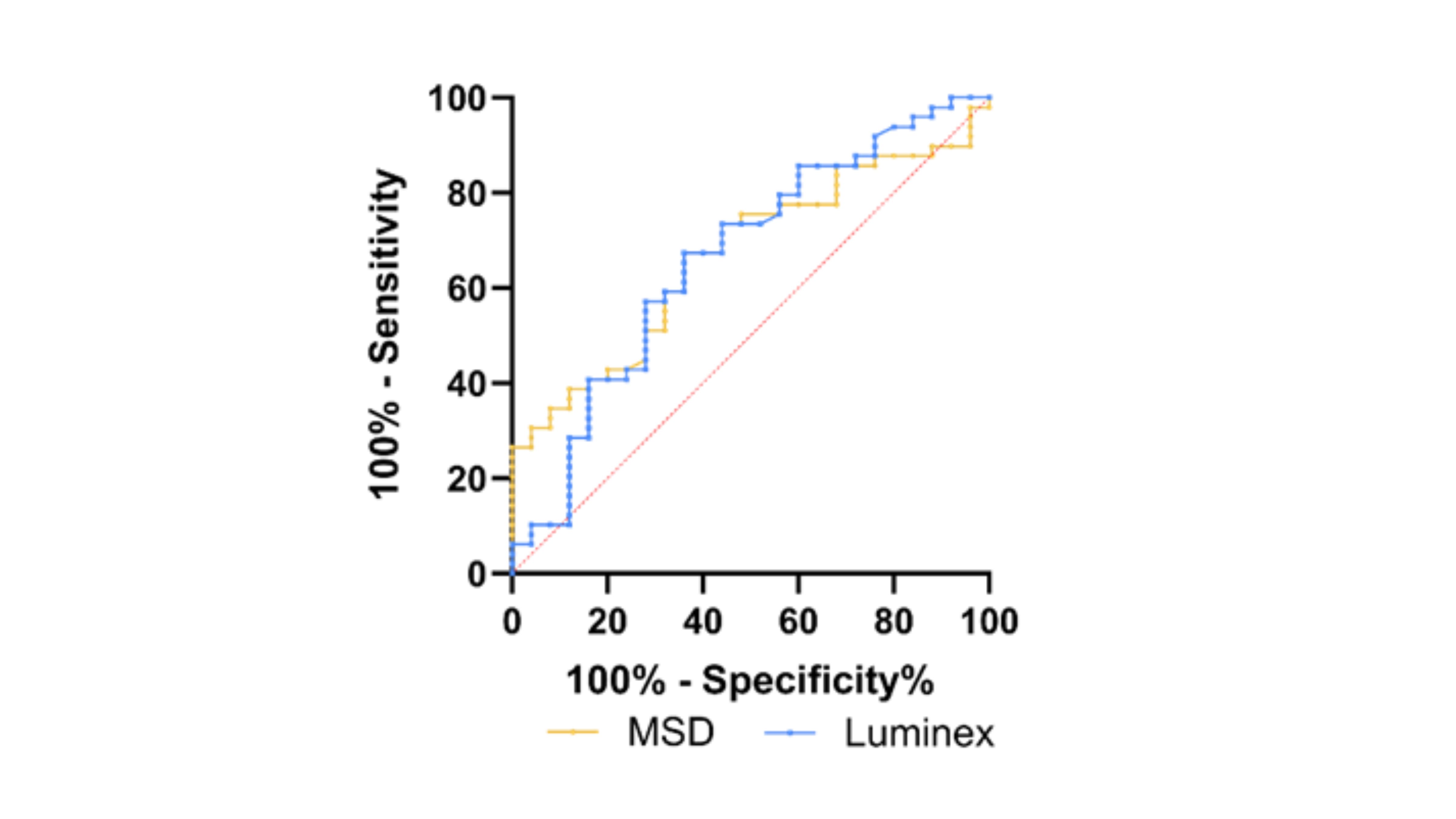
Results: ROC analysis in the pilot cohort yielded an AUC of 0.67 (95% CI, 0.55-0.79) for MSD and 0.66 (95% CI, 0.53-0.80) for Luminex, indicating similar performance across platforms. For AxSpA patients aged ≤45, the Luminex assay showed an AUC of 0.74 (95% CI, 0.61-0.88), p=0.003. Combining 14-3-3η AAbs with CRP identified 90% of AxSpA patients, with no correlation found between the levels of the two markers (r = -0.14, p = 0.38).
In the test cohort, 14-3-3η AAb median baseline levels were significantly higher in AxSpA patients compared to healthy controls, with values of 44.38 (32.0-70.1) versus 35.5 (21.8-46.0), p=0.003. The mean age (SD) for AxSpA patients and healthy cohort was 40.6 (11.3) and 39.7 (11.3) years, respectively. ROC analysis of 14-3-3η AAb, which included age, sex, and CRP, yielded an AUC of 0.82 and a ChiSq of 81.96, p< 0.0001. The optimal threshold value yielded a sensitivity of 76.2% and a specificity of 74.1% identifying 80 TP, 22 FP, 63 TN, and 25 FN. Out of 105 patients assessed for both CRP and 14-3-3η AAb, 60 (57%) were CRP positive, 47 (45%) were AAb positive, and 83 (79%) were positive for either biomarker.
The Wilcoxon matched-pairs test indicated a significant difference in the levels of 14-3-3η AAb from baseline to year 1 (p=0.029). The median change in AAb levels between patients who received TNF treatment and those who did not, was not statistically significant (p=0.71) but was independent of HLA-B27 status (p=0.16).
Conclusion: The Luminex-based 14-3-3η AAb assay demonstrates equivalent effectiveness to the MSD RUO assay in differentiating AxSpA patients from healthy individuals. The combined detection of 14-3-3η AAbs and CRP identified 90% and 79% of AxSpA patients in the two cohorts tested, highlighting the potential of these biomarkers as complementary diagnostic tools. We present findings on the modifiability of 14-3-3η AAbs from baseline to one year in AxSpA and their potential application for prognosis and patient monitoring.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Marotta A, Maksymowych W, Wichuk S, Sidhu N. 14-3-3 Eta (η) Auto-Antibody as a Diagnostic Marker in Axial Spondyloarthritis: A Longitudinal Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/14-3-3-eta-%ce%b7-auto-antibody-as-a-diagnostic-marker-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-longitudinal-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/14-3-3-eta-%ce%b7-auto-antibody-as-a-diagnostic-marker-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-longitudinal-study/