Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Treatments depleting CD19-expressing B cells have shown benefit in a range of autoimmune diseases. T cell engagers (TCE) offer off-the-shelf convenience, the predictable pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic properties of monoclonal antibodies, and the potential to achieve deep target cell depletion as seen with chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy. CLN-978 is a T cell engager comprised of tandemly arranged CD19- and CD3-specific single-chain fragment variable domains and a single-domain albumin binder for serum half-life extension. CLN-978 has high affinity for CD19 and moderate affinity for CD3 (Meetze K, et al. J Immunother Cancer 2023;11:e007398) and is administered via subcutaneous (SC) injection. In a phase 1, first-in-human study (NCT05879744), patients with B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (B-NHL) were treated with the starting dose of 30 micrograms (mcg) SC weekly of CLN-978, which demonstrated a favorable safety profile and a complete metabolic response in 1 of 3 treated patients. We report preclinical and translational studies in autoimmune diseases.
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) derived from healthy donors and patients with Sjögren’s disease (SjD), SLE, or RA, were cultured in the presence of CLN-978 for 48 hours. In a mouse model of SLE, NOD scid gamma (NCG) mice engrafted with PBMC from a patient with SLE were treated with CLN-978 weekly for 3 weeks. Cynomolgus monkeys were administered single and up to 4 weekly SC doses of CLN-978 at dose levels ranging from 2 to 100 mcg/kg. Peripheral blood and tissues (lymph nodes, spleen, and bone marrow) were assessed for B cell depletion by flow cytometry and quantitative immunohistochemistry (QIHC), respectively.
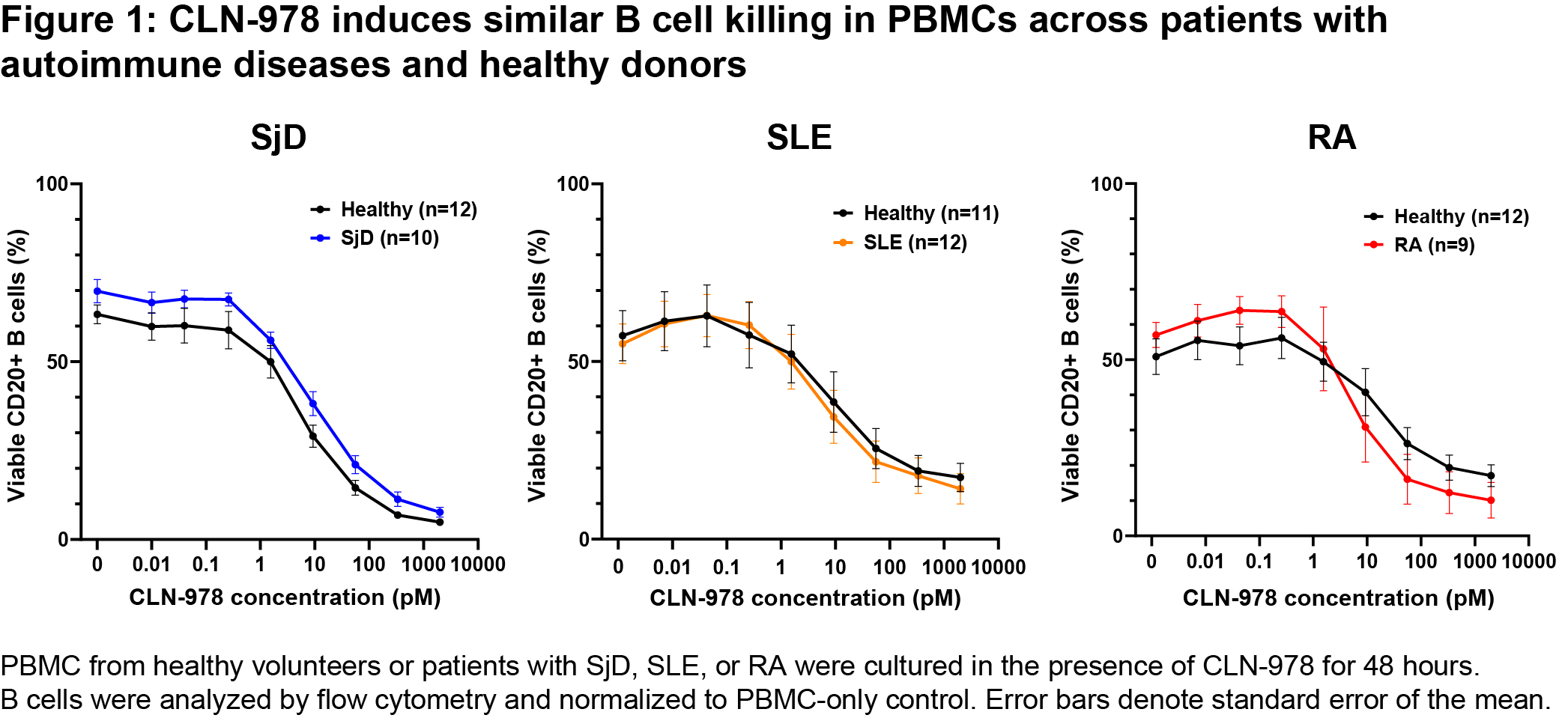
Results: In vitro, CLN-978 induced similar B cell killing (Figure 1) and T cell activation in PBMCs from healthy donors and in patients with SjD, SLE, or RA. In mice engrafted with human SLE PBMC, CLN-978 treatment depleted human B cell populations in blood and spleen, reduced human IgG and anti-dsDNA IgG blood levels, and abrogated human IgG deposition in kidney glomeruli compared with controls (Figure 2). In cynomolgus monkeys, a dose-related B cell depletion was observed in peripheral blood following administration of a single priming dose +/- a single target dose of CLN-978 (Figure 3A). Dose-related B cell depletion was also observed in lymphoid tissues, spleen, and bone marrow following administration of 4 weekly SC doses (Figure 3B). CLN-978 was well tolerated in monkeys following multiple weekly SC doses up to 100 mcg/kg.
Conclusion: CLN-978 is a highly potent, SC-administered, CD19-directed TCE. Preclinical in vitro and in vivo data including deep B cell depletion in both peripheral blood and tissue, along with existing clinical data in B-NHL patients, support broad development across autoimmune diseases. Phase 1b studies of CLN-978 are currently being conducted in patients with CLN-978 in SjD, SLE, and RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ioffe E, Sauer K, Shearer T, Michaelson J, Jones J, Zhang Y, Wax S, Sreih A. CLN-978, a CD19 x CD3-Directed T Cell Engager, Leads to Rapid and Deep B Cell Depletion In Vitro and In Vivo, Supporting Clinical Development Across Multiple Autoimmune Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cln-978-a-cd19-x-cd3-directed-t-cell-engager-leads-to-rapid-and-deep-b-cell-depletion-in-vitro-and-in-vivo-supporting-clinical-development-across-multiple-autoimmune-diseases/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cln-978-a-cd19-x-cd3-directed-t-cell-engager-leads-to-rapid-and-deep-b-cell-depletion-in-vitro-and-in-vivo-supporting-clinical-development-across-multiple-autoimmune-diseases/

.jpg)
.jpg)