Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Contemporary pharmacological management of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is set within a treat-to-target framework. This requires quantitative, longitudinal assessments of disease activity with a view to treatment adjustment where necessary. There are many composite scores of RA disease activity and methods to assess response, including improvement in CDAI based on its minimum clinically important difference (MCID) and EULAR response criteria based on the DAS28-CRP. These response measures were employed in the PRIMA-102 (NCT05936970) study supporting development of a novel blood-based assay to predict response to biologic and targeted synthetic DMARDs. The objective of the study is to investigate the agreement between the CDAI MCID and EULAR response criteria and identify correlates of discordance.
Methods: An interim analysis was performed on 636 participants treated with ≥ 1 prior cs/b/tsDMARD who initiated a new b/tsDMARD, TNFi (n=187), JAKi (n=178), Anti T-Cell (n=171), Anti IL-6R (n=77), Anti B-Cell (n=23), contributing data to a prospective, multi-center, observational cohort requiring baseline (BL) blood collection and clinical outcome measures at BL and week 12. Agreement between the two clinical response measures was computed using kappa (𝜅) coefficients and correlates of discordance were assessed using analysis of variance (continuous variables) or chi-square variance (categorical variables) and Hedges’ g values were computed to estimate the magnitude of the difference between the groups, with positive values indicating a higher mean in the MCID-only subgroup and negative values corresponding to a higher mean in the EULAR-only subgroup.
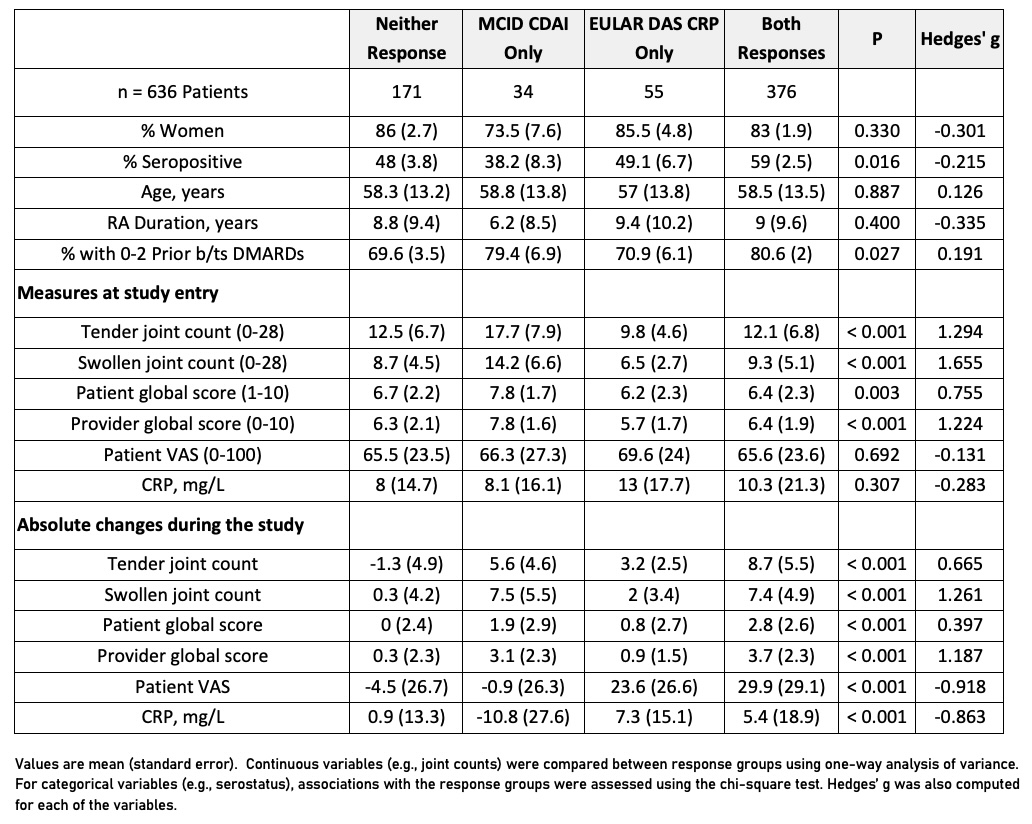
Results: 410 participants (64%) had a CDAI MCID response, and 431 participants (68%) had moderate or good DAS28-CRP EULAR response (Table 1). 34 participants (5.3%) were responders per CDAI MCID only, and 55 participants (8.6%) were responders per EULAR response criteria only. Agreement between the two measures was substantial and did not differ by MOA (overall 𝜅=0.69, 95% CI [0.63-0.75], TNFi 𝜅=0.68, JAKi 𝜅=0.67, Anti T-Cell 𝜅=0.69, Anti IL-6R 𝜅=0.72, Anti B-Cell 𝜅=0.68). Baseline characteristics and RA disease activity measures associated with discordance included serostatus, line of therapy, joint counts, and patient/provider global assessment; changes from baseline that were associated with discordance with large relative effect sizes included swollen joint count, provider global assessment, patient VAS, and CRP (Table 2).
Conclusion: There was generally good agreement between CDAI MCID and EULAR Response criteria, suggesting that either method could support development of a precision medicine test to predict treatment response. However, the higher percentage of positive responses unique to the DAS28-CRP EULAR criteria suggests that EULAR response based on DAS28-CRP may introduce bias when assigning response status for drug classes (e.g., IL-6R) that directly modulate CRP levels.
Table 1: Agreement Between Response Measures for Each Drug Class
.jpg) Table 2: Correlates of Discordance Between MCID CDAI and EULAR DAS CRP Response Labels in the PRIMA-102 Study Population
Table 2: Correlates of Discordance Between MCID CDAI and EULAR DAS CRP Response Labels in the PRIMA-102 Study Population
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Taylor P, Carlson J, Vu S, Fransen S, Abdueva D, Curtis J. Agreement Between Two Rheumatoid Arthritis Response Measures Across b/ts DMARD Treatment Classes in a Large, Prospective Observational Study Supporting the Development and Clinical Validation of a Novel Blood-based Precision Medicine Test [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/agreement-between-two-rheumatoid-arthritis-response-measures-across-b-ts-dmard-treatment-classes-in-a-large-prospective-observational-study-supporting-the-development-and-clinical-validation-of-a-nov/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/agreement-between-two-rheumatoid-arthritis-response-measures-across-b-ts-dmard-treatment-classes-in-a-large-prospective-observational-study-supporting-the-development-and-clinical-validation-of-a-nov/