Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Effusion-synovitis (ES) is often seen in knee osteoarthritis (KOA), and MRI-detected ES may serve as a potential imaging biomarker of disease activity, progression, and treatment response. However, reproducible and scalable fully quantitative methods to assess ES remain limited. We developed a multiplanar, semi-automated system for trained non-expert readers to segment ES using two non-contrast enhanced (NCE) 3 T MRI sequences simultaneously and assessed its reliability and validity as an efficient method of quantifying ES in KOA patients.
Methods: OAI participants with radiographic KOA (Kellgren-Lawrence grades 2-3) at baseline were randomly selected (n=80 knees; 1 knee per participant). Following a validated single-slice ES method, a three-monitor setup was employed featuring custom post-processing algorithms to standardize homologous ES on axial DESS and sagittal TSE NCE-MRI images (Figure 1). Variable grayscale thresholding, 3D visualization/localization, and rapid refinement was facilitated by a multi-button mouse (Figure 2). Measurement was performed on both views in parallel with real-time quantification to achieve sub-millimeter volume differences across planes or simultaneously via cross-plane projective segmentation. Fifty knees were segmented in parallel by an MSK radiologist. One non-expert reader was trained using the first 20 scans and then made repeated measurements on the following 30 knees (“validity set”). Three non-experts repeated the parallel approach on 30 different knees (“reliability set”). We evaluated agreement using mean absolute difference (MAD), and intra- and inter-reader reliability using intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) from a linear mixed model with random effects for knee, reader, and interaction between knee and reader.
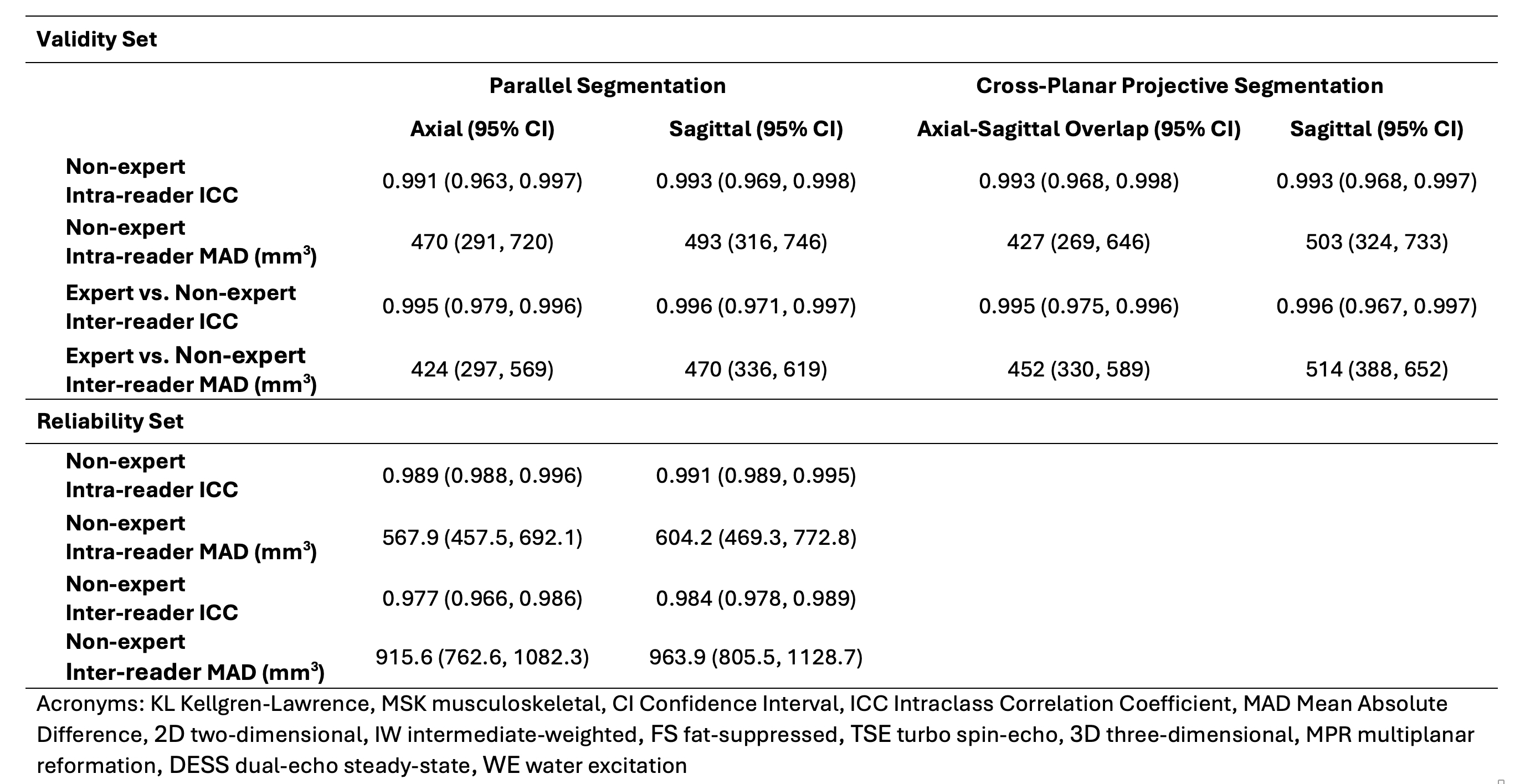
Results: Scan reading times averaged < 5 minutes for simultaneous ES segmentation. ES volumes averaged between 7683 mm³ and 8911 mm³ across comparison groups. In the validity set, the multiplanar (axial, sagittal) inter-reader ICCs were 0.995, 0.996 (MADs: 424 mm³, 470 mm³) and intra-reader ICCs were 0.991, 0.993 (470 mm³, 493 mm³) (Figure 3). When measuring both views simultaneously via projection, the multiplanar inter-reader ICCs were 0.995, 0.996 (452 mm3, 514 mm3) and intra-reader ICCs were 0.993, 0.993 (427 mm3, 503 mm3). In the reliability set, the multiplanar inter-reader ICCs were 0.977, 0.984 (916 mm3, 964 mm3) and intra-reader ICCs were 0.989, 0.991 (568 mm3, 604 mm3).
Conclusion: By employing a system with custom artifact correction, tissue standardization and hardware and software tools, non-expert readers were able to be trained to segment ES. They demonstrated high reliability and concurrent validity with excellent agreement with an expert MSK radiologist’s measurements for both multi-view ES measurement methods. Our method allows for expedited simultaneous segmentation to produce rapid, detailed assessment of ES large knee MRI datasets, and facilitate the development of objective, critical measures of joint inflammation.
.jpg) Figure 3. Reader performance in our study. The “validity set” composed of 29 KL grade 2 and 3 (19 and 10, respectively) knees segmented in parallel by an expert MSK radiologist on sagittal 2D IW FS TSE and axial 3D MPR DESS WE images. One non-expert reader made repeated measurements on the set using parallel and cross-planar projective segmentation to assess non-expert intra-reader and inter-reader reliability and validity using both approaches. Three additional non-experts repeated parallel measurements of 29 different KL 2 and 3 knees (16 and 13, respectively, “reliability set”) to assess non-expert inter- and intra-reader reliability.
Figure 3. Reader performance in our study. The “validity set” composed of 29 KL grade 2 and 3 (19 and 10, respectively) knees segmented in parallel by an expert MSK radiologist on sagittal 2D IW FS TSE and axial 3D MPR DESS WE images. One non-expert reader made repeated measurements on the set using parallel and cross-planar projective segmentation to assess non-expert intra-reader and inter-reader reliability and validity using both approaches. Three additional non-experts repeated parallel measurements of 29 different KL 2 and 3 knees (16 and 13, respectively, “reliability set”) to assess non-expert inter- and intra-reader reliability.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gilles G, Robles D, Grawer L, Christiansen N, Jayyusi K, Shaikh A, Tang R, Taljanovic M, Duryea J, Bedrick E, Kwoh C. Multiplanar MRI Quantification of Effusion-Synovitis: Reliability and Potential Investigative Utility for Inflammation-Mediated Knee Conditions [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/multiplanar-mri-quantification-of-effusion-synovitis-reliability-and-potential-investigative-utility-for-inflammation-mediated-knee-conditions/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/multiplanar-mri-quantification-of-effusion-synovitis-reliability-and-potential-investigative-utility-for-inflammation-mediated-knee-conditions/

.jpg)