Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is one of the leading cause of mortality in patients with connective tissue diseases (CTDs) [1]. The onset of CTD-ILD is insidious, and the clinical symptoms are atypical and not obvious, therefore ILD is often diagnosed in later stages with severe consequences [1]. Moreover, a confident diagnosis of CTD-ILD can be difficult due to certain similarities with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), the most severe ILD with different prognosis and therapies [2]. Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial to delay fibrosis progression in CTD-ILD, but the limitations of current clinical tools highlight the need to complement them with accessible and non-invasive methods. Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) is the main profibrogenic agent involved in different lung pathologic conditions [3]. Therefore, it is plausible to think that the TGFB expression is differentially altered in CTD-ILD patients. Accordingly, we focused on evaluating the role of TGFB isoforms as new biomarkers with clinical value for the early and accurate diagnosis of ILD in the most affected CTDs for this devastating disease, systemic sclerosis (SSc), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and inflammatory myopathies (IM).
Methods: Peripheral blood was collected from 93 CTD-ILD patients: 33 RA‐ILD, 31 SSc-ILD, and 29 IM-ILD; 48 CTD-nonILD patients: 22 RA‐nonILD, 18 SSc-nonILD, and 8 IM-nonILD; and 148 IPF patients. The relative TGFB1, TGFB2, and TGFB3 mRNA expression was quantified by qPCR.
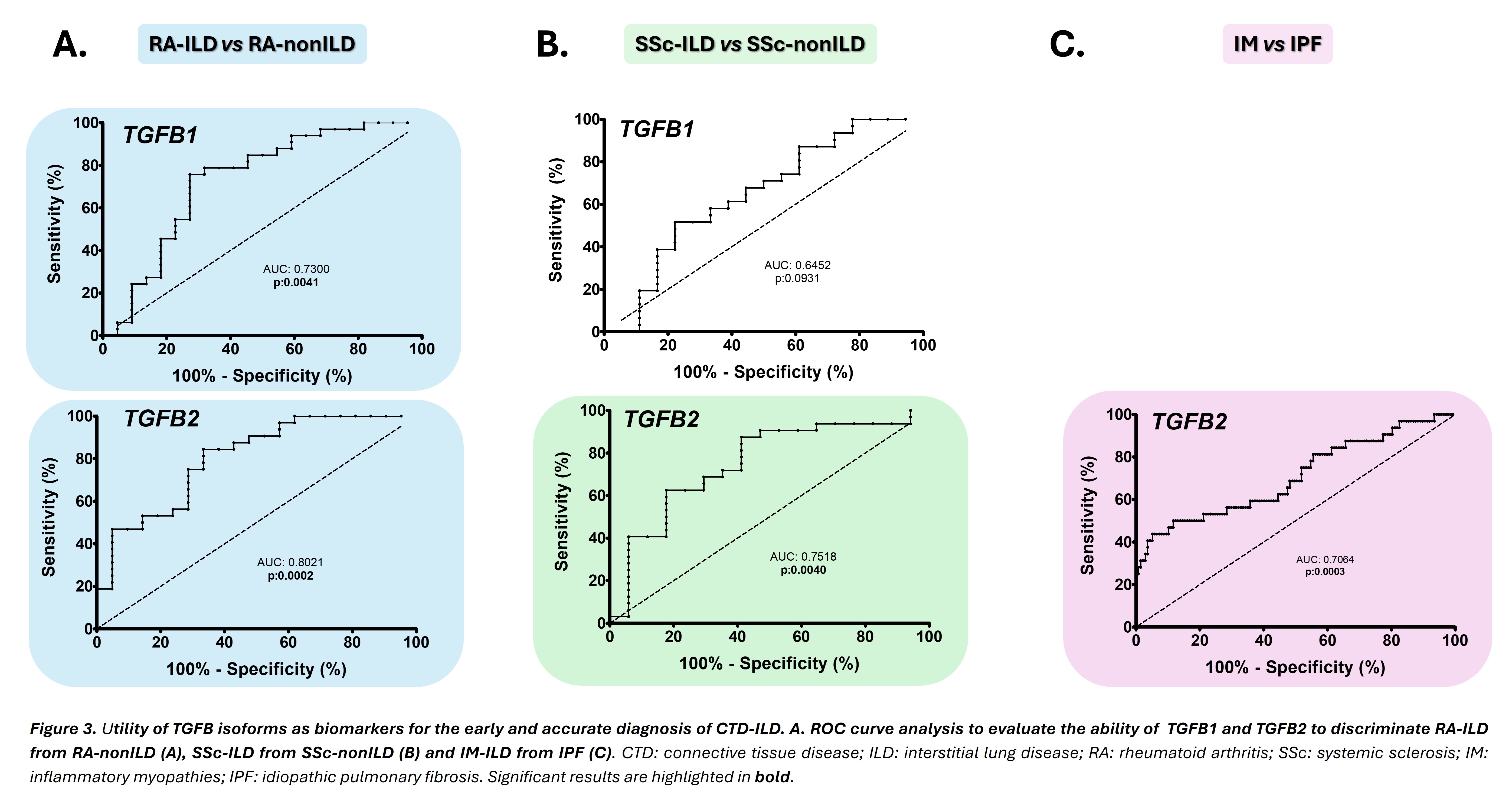
Results: A significant decrease in TGFB1 and TGFB2 expression was observed in RA-ILD and SSc-ILD patients compared to those with RA-nonILD and SSc-nonILD, respectively (TGFB1: p=0.0040, Figure 1A and p=0.0009, Figure 1B, respectively; and TGFB2: p=0.0011, Figure 1A and p=0.0008, Figure 1B, respectively). Interestingly, IM-ILD patients showed an increased TGFB2 expression compared to IPF patients (p=0.0009, respectively, Figure 2C), In a further step, ROC curve analysis confirmed the capacity of TGFB1 and TGFB2 expression to differentiate RA-ILD from RA-nonILD, acting as biomarkers for the early detection of RA-ILD (p=0.0041 and p=0.0002, respectively, Figure 3A) with < 0.3185 for TGFB1 and < 0.001410 for TGFB2 as optimal cut-off values. Furthermore, TGFB2 expression levels also revealed an ability to discriminate SSc-ILD and SSc-nonILD patients, representing an early diagnostic biomarker of SSc-ILD (p=0.0040, Figure 3B) with < 0.001795 as optimal cut-off value. Meanwhile, differences in TGFB2 gene expression were sufficient to differentiate between patients with IM-ILD and those with IPF, acting as a biomarker for the accurate diagnosis of IM-ILD (p=0.0003, Figure 3C) with >0.001547 as optimal cut-off value.
Conclusion: TGFB1 and TGFB2 constitute biomarkers with clinical value for the early detection of ILD in RA and SSc, and the accurate diagnosis of IM-ILD versus IPF, representing promising screening tools for CTD-ILD in clinical practice. References:[1]Autoimmun Rev.2024;23(6):103582.; [2]Respir Investig. 2024;62(3):465-480; [3]J Exp Med. 2020;217(3):e20190103Funding:BoehringerIngelheim;VP-C:NVAL23/02,INNVAL24/10;JCB-L:FI22/00020;RL-:CPII21/00004.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pulito Cueto V, Batista-Liz J, Nieto-Nieto R, Vaquera-Illescas C, San Emeterio-Villar D, Vicente-Mínguez D, Sebastián Mora-Gil M, Atienza-mateo B, Serrano-Combarro A, Iturbe-Fernández D, Mora-Cuesta V, Aguirre-Portilla C, Cifrián J, Blanco R, Lopez Mejias R. Towards an Earlier and Accurate Diagnosis of Connective Tissue Disease-related Interstitial Lung Disease: TGFB Isoform Genes as Upcoming Biomarkers [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/towards-an-earlier-and-accurate-diagnosis-of-connective-tissue-disease-related-interstitial-lung-disease-tgfb-isoform-genes-as-upcoming-biomarkers/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/towards-an-earlier-and-accurate-diagnosis-of-connective-tissue-disease-related-interstitial-lung-disease-tgfb-isoform-genes-as-upcoming-biomarkers/

.jpg)
.jpg)