Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1553–1591) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a complex systemic autoimmune disease characterized by vasculopathy, fibrosis, and immune dysregulation. While JAK inhibitors (JAKi) have shown promising immunomodulatory and anti-fibrotic effects in early-phase studies, their real-world impact on SSc patients remains poorly studied. We aimed to assess safety and explore the efficacy in JAKi-treated SSc patients compared to conventional immunosuppressants.
Methods: We conducted a longitudinal retrospective cohort study within the European Scleroderma Trials and Research group (EUSTAR) database. Patients receiving JAK inhibitors (JAKi) were matched 1:5 to patients initiating mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), rituximab (RTX), or methotrexate (MTX) using nearest-neighbour propensity score matching based on age, sex, disease duration, antibody profile, skin subset, presence of digital ulcers (DUs), and baseline lung function.Primary outcomes included adverse events and drug survival (time to permanent discontinuation). Efficacy endpoints were change in FVC% and mRSS at 12 and 24 months, improvement in swollen joint count (SJC) in patients with synovitis, time to new DUs, and a composite disease progression outcome (new PAH, SRC, or ILD progression). Safety events, reasons for discontinuation, and use of vasodilators were also recorded. Time-to-event analyses were performed using Kaplan–Meier and restricted mean survival time (RMST); continuous outcomes were analysed via linear models and paired tests. Follow-up was censored at drug discontinuation for patients without outcome events.
Results: We included 36 JAKi-treated patients (44% baricitinib, 42% tofacitinib, 14% upadacitinib), predominantly female (81%), with a median disease duration of 76 months. Over 98.7 patient-years, 23 adverse events occurred (23.3/100 patient-years), including 12 infections (8 severe, 1 fatal), 7 lab abnormalities, and 3 malignancies. JAKi was permanently discontinued in 14 patients (39%), and transiently interrupted in 7 (19%). At 12 months, FVC remained stable (+1.7%, p=0.530); skin fibrosis improved modestly (−1.1 mRSS, p=0.036), particularly in diffuse cutaneous SSc. Swollen joint count improved in patients with baseline synovitis (median −1, p=0.052). No new calcinosis developed, and two pre-existing cases improved. Time-to-event analyses over 60 months showed comparable risk of recurrent digital ulcers and composite progression events between JAKi and matched MMF, RTX, and MTX arms (RMST differences non-significant; DU log-rank p=0.24). JAKi-treated patients had similar or slightly better RMST for disease progression versus MTX (+3.1 months), though differences did not reach significance.
Conclusion: In this cohort, treatment with JAK inhibitors was not associated with an increased risk of fibrosing or vascular complications compared to conventional immunosuppressive therapies. While these findings suggest a favourable safety profile and potential efficacy of JAKi in SSc, prospective, controlled studies are needed to confirm these results and to explore their potential disease-modifying effects.
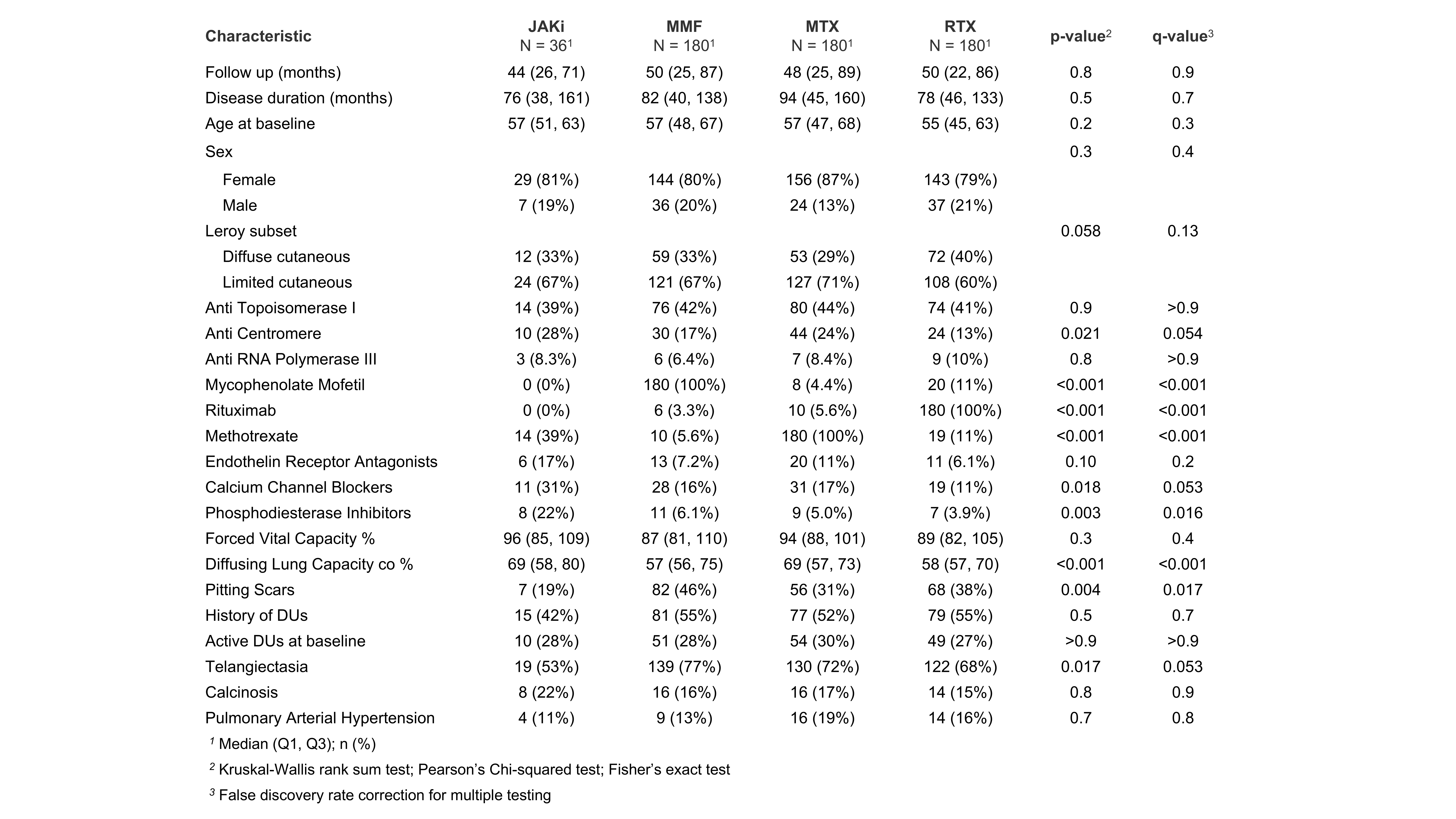 Table 1. Demographic and clinical features of the study cohort stratified by treatment.
Table 1. Demographic and clinical features of the study cohort stratified by treatment.
.jpg) Figure 1. Longitudinal trends of pulmonary function (A) and skin fibrosis (B) in patients treated with JAK inhibitors, stratified by Leroy cutaneous subset.
Figure 1. Longitudinal trends of pulmonary function (A) and skin fibrosis (B) in patients treated with JAK inhibitors, stratified by Leroy cutaneous subset.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Di Donato S, Truchetet M, Minerba M, Distler O, ALEGRE SANCHO J, Braun Moscovici Y, Bergmann C, Sfikakis P, de Vries-Bouwstra J, Baron M, Bellando-Randone S, Dagna L, Denton C, Vonk M, Smith V, Castellvi I, Riemekasten G, Balanescu A, Kuwana M, De Santis M, Solanki K, Batalov A, Mukuchyan V, Matucci-Cerinic M, Allanore Y, Del Galdo F, Hughes M. Real-World Safety and Efficacy of JAK Inhibitors in Systemic Sclerosis: A Propensity-Matched EUSTAR Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-safety-and-efficacy-of-jak-inhibitors-in-systemic-sclerosis-a-propensity-matched-eustar-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-safety-and-efficacy-of-jak-inhibitors-in-systemic-sclerosis-a-propensity-matched-eustar-study/
