Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease(CTD-ILD) represents a significant cause of mortality among patients. Presently, research on treatment options for CTD-ILD is limited, with most evidence derived from studies involving patients with systemic sclerosis-associated ILD (SSc-ILD). Each type of CTD possesses unique clinical characteristics, and the concurrent ILD manifestations vary, necessitating tailored treatment strategies. Furthermore, there is a lack of consensus regarding the timing, dosage, duration, and tapering of various medications.
Methods: Patients with severe ILD, characterized by pronounced shortness of breath and an oxygenation index below 300, were treated with a combination of glucocorticoids (GCs), Rituximab (RTX) at a dosage of 375 mg/m² per week for four weeks, and Telitacicept at a dosage of 160 mg per week.Patients with refractory CTD-ILD who do not respond adequately to glucocorticoids (GCs) combined with conventional immunosuppressants, those who struggle to reduce GC dosage, those at high risk of infection, those who refuse high-dose GCs or traditional therapies, and those with additional connective tissue diseases or other systemic damage were treated with Telitacicept 160 mg, administered subcutaneously once a week. Follow up observation for 24 weeks, gradually reducing hormones and immunosuppressant, observing the improvement of CTD and ILD conditions in patients, as well as whether there are adverse reactions such as infection, allergies, organ damage.
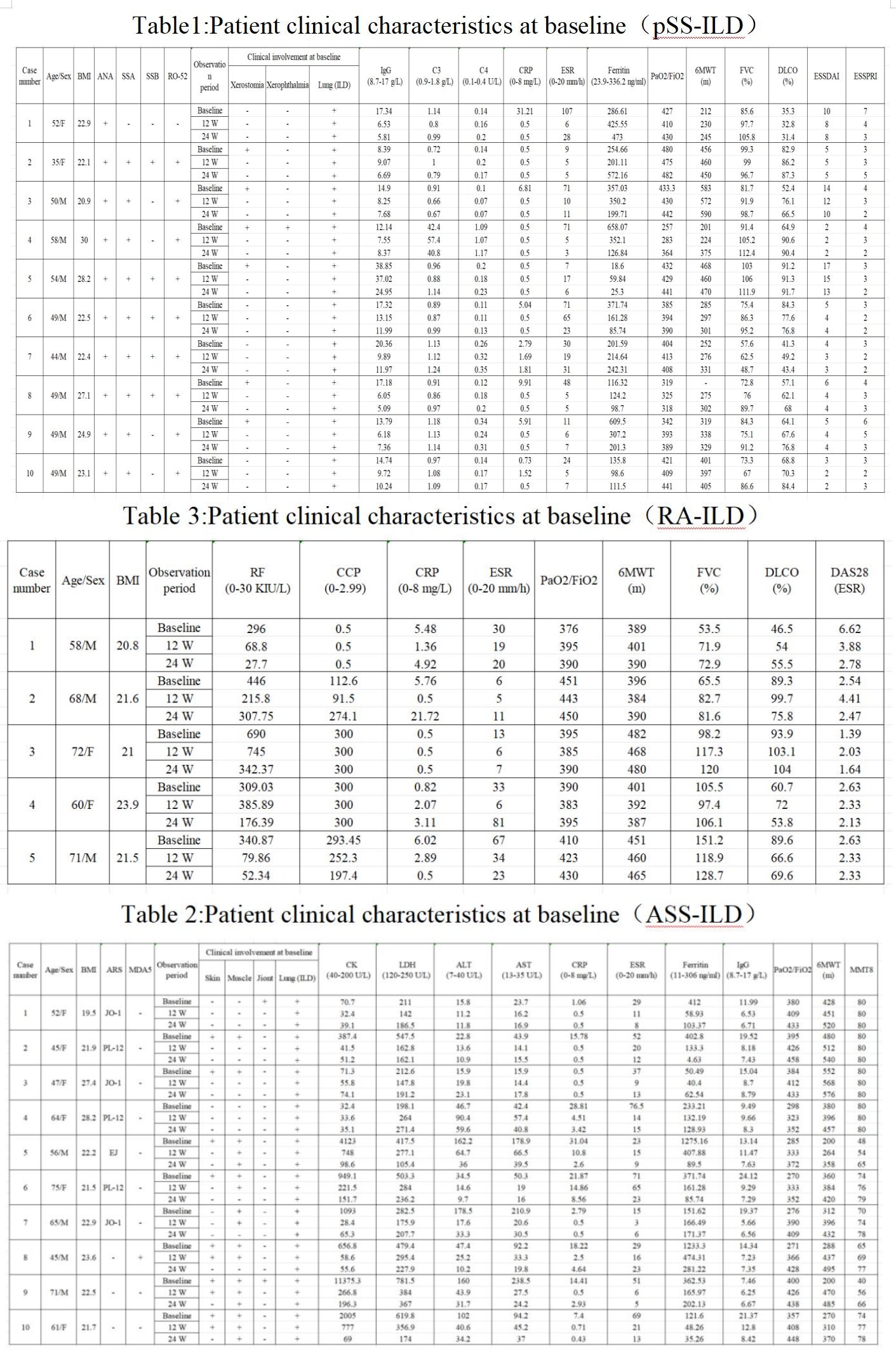
Results: A total of twenty-five patients were included in the study, ten patients with pSS-associated ILD, ten patients with ASS-associated ILD and five patients with RA-ILD. During the treatment process, no adverse reactions were found in all 25 patients. All patients gradually reduced prednisone to 5-7.5 mg/day, while Telitacicept was extended to 160 mg/two weeks. The disease activity has decreased. Chest CT scans revealed varying degrees of reduction in bilateral lung lesions, and lung function demonstrated significant improvement, with FVC% and DLCO% increased, along with the 6MWT elevated.
Conclusion: This is the first clinical trial of the use of Telitacicept for the treatment of CTD-ILD. Our work indicates that the treatment of PSS-ILD, ASS-ILD, RA-ILD by using Telitacicept has achieved good therapeutic effects. Currently, there is insufficient evidence regarding the efficacy of Telitacicept for treating CTD-ILD. This clinical trial suggests that Telitacicept could be a potential option for CTD-ILD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sun M, Chen X, Zhou Y, Yang Y, Xiao F, dai h. Efficacy of Telitacicept in the treatment of Connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease: A Potential therapeutic option [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-telitacicept-in-the-treatment-of-connective-tissue-disease-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-a-potential-therapeutic-option/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-telitacicept-in-the-treatment-of-connective-tissue-disease-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-a-potential-therapeutic-option/

.jpg)