Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1306–1346) Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is the first oral targeted synthetic disease-modify anti-rheumatic drug for patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis 1. This study aimed to identify the factors associated with the discontinuation of tofacitinib in patients with RA in clinical practice.
Methods: RA patients who received tofacitinib between 2015 and 2020 were included in this observational cohort study. The patients were followed for at least one year, ending on December 31, 2022. A tofacitinib non-responder was defined as a patient who required discontinuation or switch to another bDMARD. Conversely, tofacitinib responders were defined as those who could continue to receive tofacitinib without experiencing a loss of efficacy or severe adverse events. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses and Kaplan–Meier survival curve analysis were used to investigate the factors associated with the discontinuation of tofacitinib.
Results: A total of 266 patients were enrolled. The average age of the patients was 57.07 ± 12.07 years, and 99 (37.2%) were tofacitinib non-responders. Univariate analysis revealed that the non-responders had a lower rate of concomitant hydroxychloroquine treatment, and higher rates of leflunomide, biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARD), and tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) treatment compared to the responders. Cox regression adjusted analysis indicated that prior bDMARD treatment (hazard ratio (HR) = 1.423, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.024, 1.976, p = 0.036), prior TNFi treatment (HR = 1.605, 95% CI = 1.165, 2.212, p = 0.004), and prior non-TNFi treatment (HR = 1.326, 95% CI = 1.012, 2.075, p = 0.048) were associated with a higher non-response rate. Moreover, Kaplan–Meier survival curve analysis revealed that the patients with prior bDMARD treatment had a higher non-response rate.
Conclusion: The RA patients who received tofacitinib in this study had a good response rate, and the average non-response rate was around 37% after two years of treatment. The main factor associated with an inadequate response to tofacitinib was prior bDMARD treatment. Prior TNFi treatment was the strongest factor associated with a non-response to tofacitinib. Patients with a non-response to tofacitinib may consider bDMARDs with other mechanisms if previous treatment with TNFis was unsuccessful.
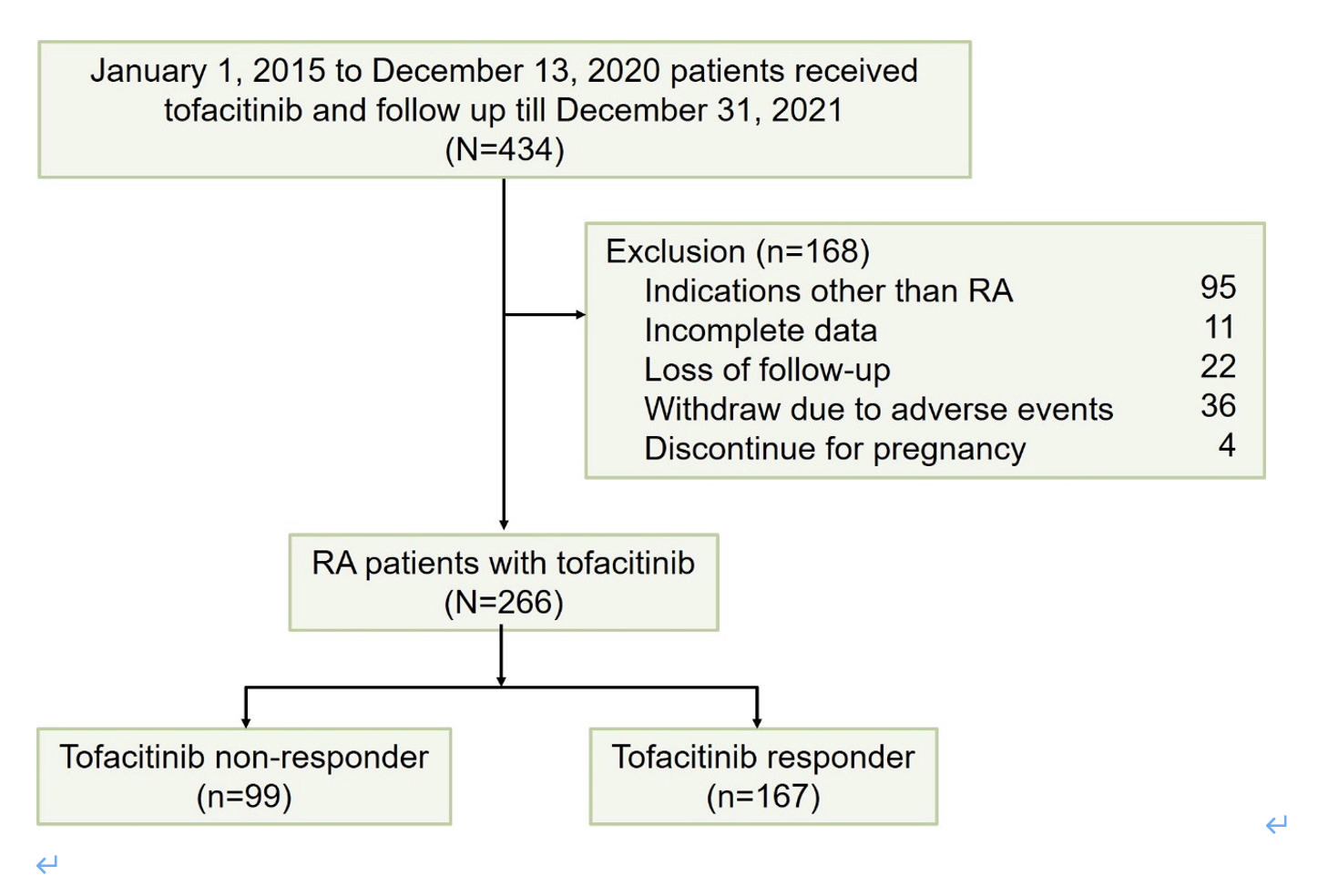 Figure 1 Flowchart for identifying rheumatoid arthritis patients with tofacitinib in Chang Gung memorial hospital. RA, rheumatoid arthritis.
Figure 1 Flowchart for identifying rheumatoid arthritis patients with tofacitinib in Chang Gung memorial hospital. RA, rheumatoid arthritis.
.jpg) Table 2. Multivariate Cox regression analysis: adjusted hazard ratio of the factors for tofacitinib in RA patients
Table 2. Multivariate Cox regression analysis: adjusted hazard ratio of the factors for tofacitinib in RA patients
.jpg) Figure 2. A) Drug survival curve for comparing RA patients with bDMARDs-näive and bDMARDs-experienced (B) Drug survival curve of comparing RA with prior TNFis, prior non-TNFis and bDMARDs näive.
Figure 2. A) Drug survival curve for comparing RA patients with bDMARDs-näive and bDMARDs-experienced (B) Drug survival curve of comparing RA with prior TNFis, prior non-TNFis and bDMARDs näive.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
fang y, Tsai P, CHEN y. Exploring the Factors Associated with the Discontinuation of Tofacitinib in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Retrospective Cohort Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploring-the-factors-associated-with-the-discontinuation-of-tofacitinib-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-retrospective-cohort-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploring-the-factors-associated-with-the-discontinuation-of-tofacitinib-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-retrospective-cohort-study/
