Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1191–1220) Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) are a group of autoimmune disorders characterized by chronic skeletal muscle inflammation leading to muscle weakness and limitations in physical function. Despite the clinical significance of functional impairments in IIM, there are few validated tools of physical function in this population. Even though the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) is widely accepted, data on its validity are limited. Further, its length and complex scoring system make it cumbersome in clinic, requiring development of a more efficient and validated measure of physical function in these patients. The HAQ-II is a shortened version of the HAQ with 10 items validated in RA. In this study, we aim to assess measurement properties of HAQ-II in evaluation of physical function in individuals with IIM.
Methods: Data were from adults enrolled in FORWARD -The National Databank for Rheumatic Disease- between 1999-2023. Participants had a physician diagnosis of IIM and completed the HAQ-II along with other items related to their disease, comorbidities, pain, fatigue, and quality of life. Internal consistency of HAQ-II was assessed using Cronbach’s α. Floor and ceiling effects were calculated by identifying the proportion of minimum and maximum possible HAQ-II scores. Discriminant validity was assessed by comparing differences in baseline HAQ-II scores between relevant subgroups. Construct validity was evaluated by comparing HAQ-II scores and measures of physical health, including SF-36 physical functioning, patient global disease activity, fatigue, and pain using Pearson correlations based on a priori hypotheses derived from the literature. Responsiveness of HAQ-II was assessed using linear mixed models.
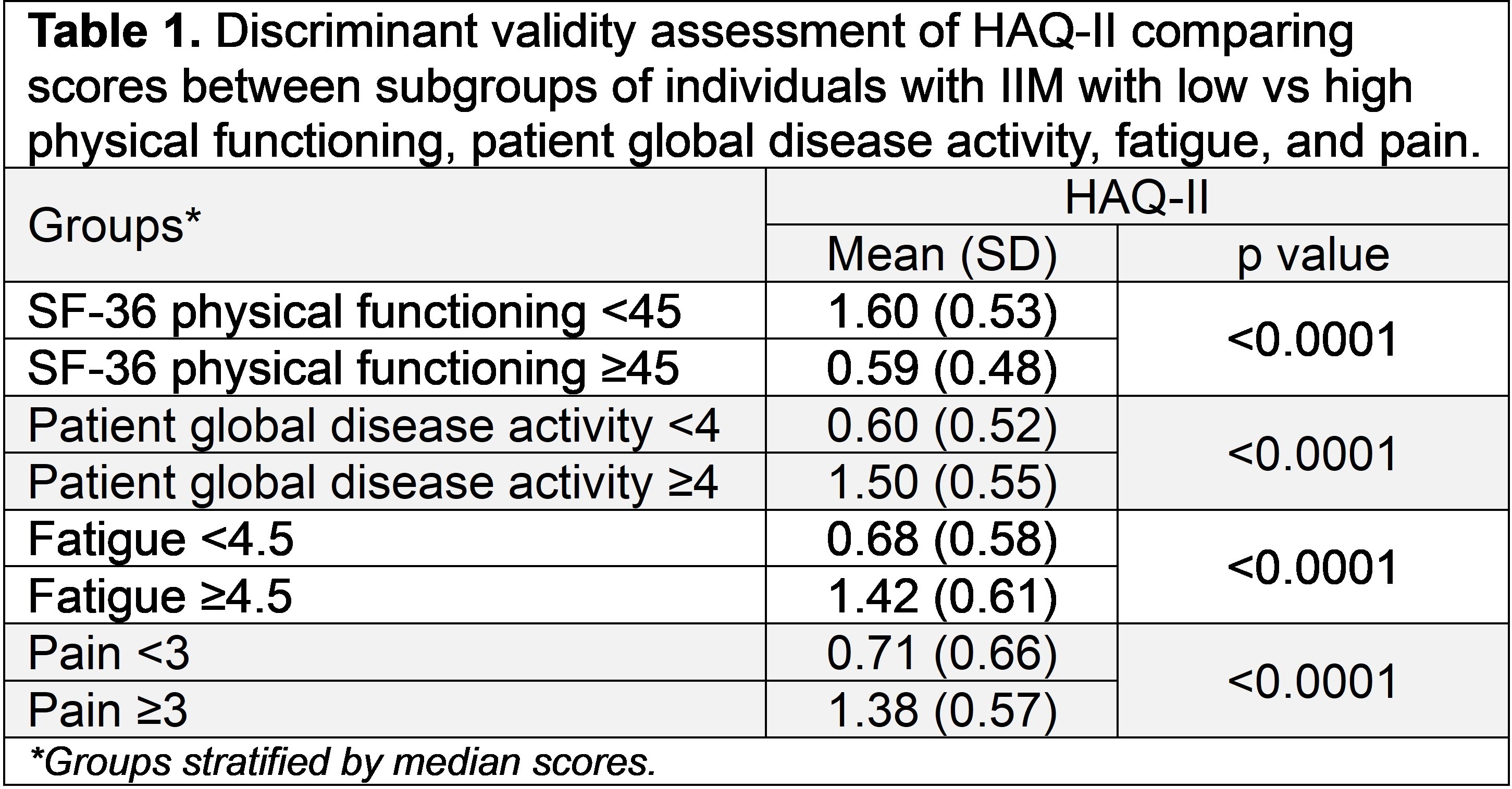
Results: A total of 192 participants with IIM (mean age 54.8 [±13.7]; 79.3% female) who completed the HAQ-II (mean 1.1 [±0.7]) were included in the study. Cronbach’s α of HAQ-II was 0.93. Floor and ceiling effects were negligible with 7.8% and 0%, respectively. All a priori hypotheses for discriminant validity were met with significant differences in HAQ-II scores between participants with low vs high physical functioning, patient global disease activity, fatigue, and pain levels (p < 0.0001) (Table 1). Fifteen out of 17 a priori hypotheses (88.2%) were met for the construct validity of HAQ-II. HAQ-II had weak correlations with symptom duration, age, BMI, Rheumatic Disease Comorbidity Index, SF-36 mental component score, role limitations due to emotional problems and emotional well-being, moderate correlations with pain levels, fatigue levels, health satisfaction, SF-36 general health, and social functioning, and strong correlations with SF-36 physical component score and physical functioning (Table 2). After controlling for age, sex, and obesity, change in HAQ-II was significantly associated with change in pain, fatigue, patient global disease activity, and SF-36 PCS (Table 3).
Conclusion: HAQ-II demonstrated good internal consistency, validity, and responsiveness in assessing physical function in individuals with IIM. Our findings support the HAQ-II as a valid and practical instrument and support its application in both clinical and research settings.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lee S, Wipfler K, Ritz E, Aydemir B, Michaud K, Saygin D. Measurement Properties of a Shorter Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ-II) in Patients with Inflammatory Myopathies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/measurement-properties-of-a-shorter-health-assessment-questionnaire-haq-ii-in-patients-with-inflammatory-myopathies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/measurement-properties-of-a-shorter-health-assessment-questionnaire-haq-ii-in-patients-with-inflammatory-myopathies/

.jpg)
.jpg)