Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1088–1122) Immunological Complications of Medical Therapy Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: IL-17 is primarily secreted by Th17 cells. The IL-17 family has 6 related cytokines (IL-17A to IL17F); IL-17A and IL-17F, being key proinflammatory mediators. IL-17A is known for its critical role in neutrophil-mediated immune defense. Notably, dual blockade of IL-17A/F has been associated with a higher risk of candidal infections compared to IL-17A inhibition alone. The objective of this study is to investigate the reason for increased risk of candidiasis linked to dual IL-17A/F blockade. Both IL-17A and IL-17F signal through IL-17RA/IL-17RC. This shared pathway suggests a synergistic role in neutrophil-mediated innate immunity; thus, inhibiting both may increase susceptibility to infections. Here we determined synergistic effects of IL-17A/IL-17F on (i) neutrophil chemotaxis and (ii) candidal killing.
Methods: Blood was collected from psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and osteoarthritis (OA) patients (n=12/each). Neutrophils were isolated using density gradient centrifugation; 1×10*6 cells were seeded into 5 µm pore Transwell inserts (upper chamber) in a 24-well plate. In the lower chambers rIL-17A, rIL-17F, with or without anti-IL-17A/F mab antibodies were added (100 ng/ml each, ThermoScientific). After 12 hours, the inserts were removed, and neutrophil migration was quantified by measuring the number of neutrophils in the lower chamber by MTT assay (optical density (OD) at 450nm, Millipore Sigma). To assess neutrophil phagocytic killing of candida, 0.25×10*6 Candida with the same cytokine/antibody conditions as above were added in the lower chamber and 1×10*6 neutrophils in the upper chamber. After 12 hours, migrated neutrophils in the lower chamber were lysed with pH11 H2O; rest of the living cells (Candida)were measured by MTT assay. Results are expressed in OD (Mean±SEM) of lower chamber cells.
Results: Neutrophils treated with rIL-17A (OD: 0.149±0.006), rIL-17F (OD: 0.362±0.007), and rIL-17A+rIL-17F (OD: 0.474±0.018) showed significantly higher chemotaxis (p< 0.001) compared to media only in PsA patients. Chemotaxis was also significantly higher with rIL-17A vs. rIL-17A+anti-IL17A mab (OD: 0.161±0.008, p< 0.001) and rIL-17F vs. rIL-17F+anti-IL-17F mab (OD: 0.160±0.019, p< 0.01). Notably, rIL-17A+rIL-17F induced greater chemotaxis compared to rIL-17A or rIL-17F (p< 0.001) and which could be effectively blocked by anti-IL17A/F (Fig-1). rIL-17A+rIL-17F driven neutrophil chemotaxis effectively killed and significantly reduced candida population (OD: 0.363±0.014) compared to rIL-17A (OD: 0.410±0.005) or rIL-17F (OD: 0.435±0.25)[p< 0.004; Fig-2].
Conclusion: This study reports a unique innate immune function of IL-17A and IL-17F, a synergistic enhancement of neutrophil chemotaxis, which could be effectively blocked by anti-IL17A and anti-IL17F mabs (Fig-1). Furthermore, IL-17A+IL-17F significantly reduced Candida survival by inducing neutrophil chemotaxis, which was neutralized by IL-17A/IL-17F mAbs, leading to increased survival of candida (Fig-2). These findings suggest that dual IL-17A/IL-17F blockade may increase the risk of candidal infections, highlighting the need for close monitoring for mucosal and systemic candidiasis in patients with these therapies.
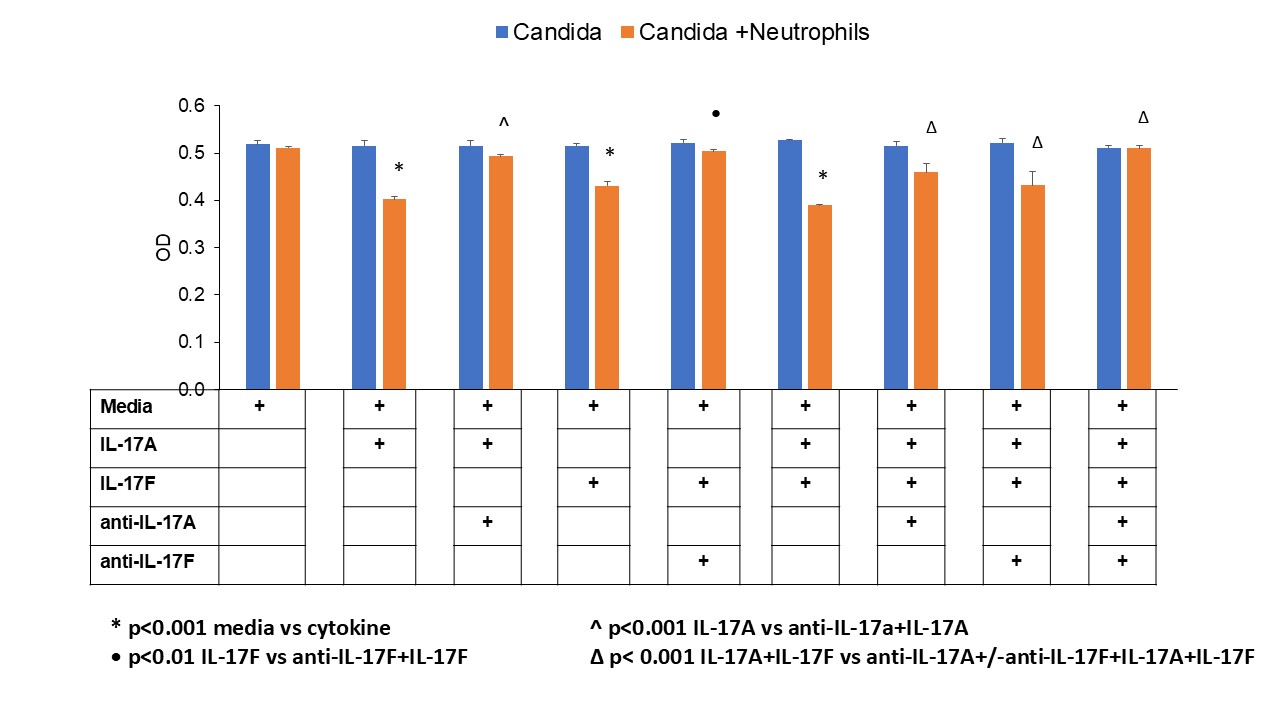 Figure 1: Comparison of neutrophil chemotaxis induced by rIL17A, rIL17F and anti rIL17A + rIL-17F. Both rIL17-A and rIL-17F induced chemotaxis of neutrophils; however combined rIL-17A + rIL-17F showed significantly higher neutrophil chemotaxis. Another intriguing observation was increased chemotaxis with rIL-17A/rIL17F on the neutrophils of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) compared to osteoarthritis (OA).
Figure 1: Comparison of neutrophil chemotaxis induced by rIL17A, rIL17F and anti rIL17A + rIL-17F. Both rIL17-A and rIL-17F induced chemotaxis of neutrophils; however combined rIL-17A + rIL-17F showed significantly higher neutrophil chemotaxis. Another intriguing observation was increased chemotaxis with rIL-17A/rIL17F on the neutrophils of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) compared to osteoarthritis (OA).
.jpg) Figure 2: Reduction of candida population as a result of significant neutrophil chemotaxis induced by rIL-17A + rIL-17F. The IL-17A/ILF mabs significantly reduced neutrophil chemotaxis (Fig-1A) resulting in higher candida survival.
Figure 2: Reduction of candida population as a result of significant neutrophil chemotaxis induced by rIL-17A + rIL-17F. The IL-17A/ILF mabs significantly reduced neutrophil chemotaxis (Fig-1A) resulting in higher candida survival.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Raychaudhuri S, Chakraborty D, Abria C, Raychaudhuri S. Synergistic Effects of IL-17F and IL-17A on Neutrophil Chemotaxis: Increased Risk of Candidiasis with Dual Blockade of IL-17A and IL17-F [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/synergistic-effects-of-il-17f-and-il-17a-on-neutrophil-chemotaxis-increased-risk-of-candidiasis-with-dual-blockade-of-il-17a-and-il17-f/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/synergistic-effects-of-il-17f-and-il-17a-on-neutrophil-chemotaxis-increased-risk-of-candidiasis-with-dual-blockade-of-il-17a-and-il17-f/
