Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (0978–1006) T Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Current therapies inadequately restore immune homeostasis due to incomplete pathogenic cell clearance and limited multi-lineage targeting. UTAA91 integrates: 1) PD-1 agonist-targeted cytotoxicity: The PD-1 nanoantibody module directs Vδ1T cells to selectively eliminate PD-1+ pathogenic T cells via their potent killing capacity: includng follicular helper T cells (Tfh), peripheral helper T cells (Tph) and effectors; 2) CD19-targeted B-cell clearance: Concurrent CD19 nanoantibody-mediated B-cell depletion disrupts T-B cell collaboration; 3) Vδ1T cells for deep tissue penetration.
Methods: Manufacturing: Vδ1T cells from donor PBMCs were enriched via MACS, engineered with CD19/PD1-CAR (Chimeric antigen receptor), and Fas-knockout via CRISPR-Cas9 to mitigate HvGR; In vitro: PD-1+ T-cell/B-cell depletion quantified in SLE/RA/SS patient PBMCs; In vivo: Humanized NPG mice with CD19+ tumors assessed for HvGR suppression, PD1+ T-cell clearance, tumor inhibition (flow cytometry/IVIS), and safety.
Results: The cGMP-compliant manufacturing process for UTAA91 demonstrates exceptional industrial feasibility, achieving the following critical quality attributes: Vδ1T cell purity >90%, stable CAR molecule expression rate >30%, Fas gene-specific knockout efficiency >90%, expansion capability exceeding 10,000-fold, Tnaive subset proportion >90%, and sustained high expression of NKG2D/DNAM1 and chemokine receptors, establishing a robust cellular foundation for long-term immune regulation. In vitro functional validation confirmed UTAA91’s dual-targeted cytotoxicity against CD19+ and PD1+ cells, maintaining >90% specific killing efficiency through multiple rounds of antigen stimulation, which highlights its superior functional persistence. In humanized mouse models, UTAA91 effectively overcame allogeneic therapy barriers by significantly suppressing host-versus-graft reaction (HvGR), clearing peripheral PD1+ T cells, and inhibiting tumor growth, with no treatment-related toxicity observed. Of significant translational value, UTAA91 exhibited precise and potent depletion of pathogenic cells in PBMCs derived from autoimmune disease patients (including SLE, RA, and SS), specifically eliminating CD19+ B cells and Tfh/Tph populations while selectively removing hyperactivated CD4+PD1+and CD8+PD1+T cells. Notably, functional PD1-T cell subsets were preserved post-treatment. This marks the first preclinical demonstration of UTAA91’s unique capability to simultaneously target bidirectional T-B cell pathogenic pathways, offering a transformative therapeutic strategy for autoimmune diseases.
Conclusion: UTAA91, the first dual-targeting allogeneic UCAR-Vδ1T therapy, pioneers a “dual depletion” mechanism to eliminate B and Tfh/Tph cells, overcoming T-B interaction limitations and offering a groundbreaking solution for autoimmune diseases.
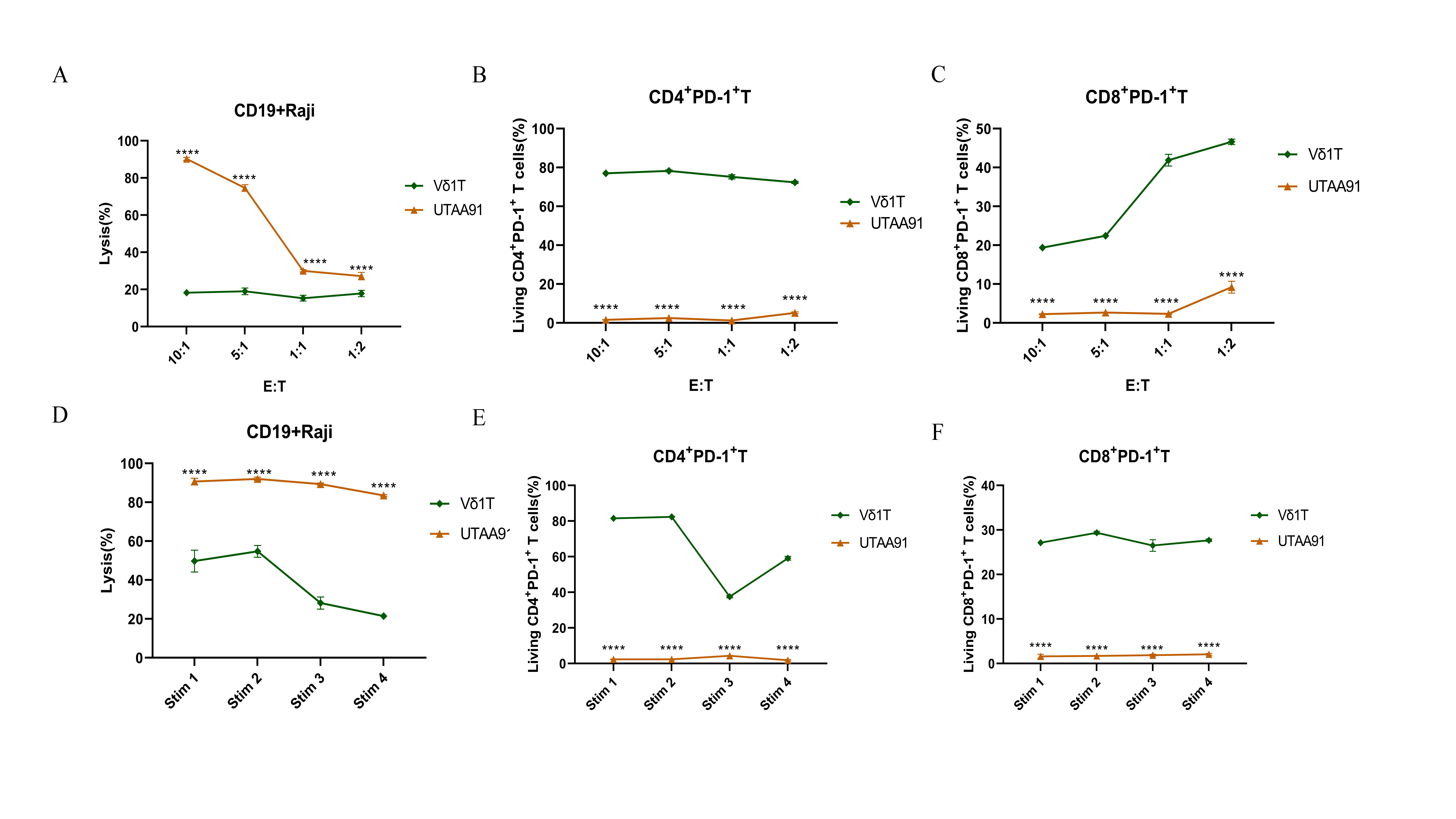 Figure 1: In vitro validation of dual-target specificity and functional persistence of UTAA91. (A) Targeted cytotoxicity of UTAA91 against CD19⁺ Raji cells in vitro; (B) Targeted cytotoxicity of UTAA91 against CD4⁺PD1⁺ T cells in vitro; (C) Targeted cytotoxicity of UTAA91 against CD8⁺PD1⁺ T cells in vitro; (D) Persistent cytotoxicity of UTAA91 against CD19⁺ Raji cells in vitro; (E) Persistent clearance capacity of UTAA91 against CD4⁺PD1⁺ T cells in vitro; (F) Persistent clearance capacity of UTAA91 against CD8⁺PD1⁺ T cells in vitro.
Figure 1: In vitro validation of dual-target specificity and functional persistence of UTAA91. (A) Targeted cytotoxicity of UTAA91 against CD19⁺ Raji cells in vitro; (B) Targeted cytotoxicity of UTAA91 against CD4⁺PD1⁺ T cells in vitro; (C) Targeted cytotoxicity of UTAA91 against CD8⁺PD1⁺ T cells in vitro; (D) Persistent cytotoxicity of UTAA91 against CD19⁺ Raji cells in vitro; (E) Persistent clearance capacity of UTAA91 against CD4⁺PD1⁺ T cells in vitro; (F) Persistent clearance capacity of UTAA91 against CD8⁺PD1⁺ T cells in vitro.
.jpg) Figure 2: In vitro cytotoxicity of UTAA91 against peripheral PBMCs from autoimmune patients with various indications. (A) Clearance capacity against CD19⁺ B cells; (B) Clearance capacity against PD1⁺ CD4⁺ T cells; (C) Clearance capacity against PD1⁺ CD8⁺ T cells; (D) Clearance capacity against Tfh cells in peripheral blood; (E) Clearance capacity against Tph cells in peripheral blood; (F) Raw flow cytometry data from one donor (RA). Notes: n=6, including patients with SLE, SSc, SS, RA, psoriasis, etc.
Figure 2: In vitro cytotoxicity of UTAA91 against peripheral PBMCs from autoimmune patients with various indications. (A) Clearance capacity against CD19⁺ B cells; (B) Clearance capacity against PD1⁺ CD4⁺ T cells; (C) Clearance capacity against PD1⁺ CD8⁺ T cells; (D) Clearance capacity against Tfh cells in peripheral blood; (E) Clearance capacity against Tph cells in peripheral blood; (F) Raw flow cytometry data from one donor (RA). Notes: n=6, including patients with SLE, SSc, SS, RA, psoriasis, etc.
.jpg) Figure 3: In vivo efficacy of UTAA91 in humanized tumor-bearing mice. (A) Preclinical in vivo experimental protocol; (B) Time-dependent monitoring of the proportion of Vδ1T/CAR-VδT cells in total CD3⁺ T cells in peripheral blood; (C) Time-dependent monitoring of the proportion of host T cells in total CD3⁺ T cells in peripheral blood; (D) Depletion of PD-1+ host T cell across experimental groups; (E) Pharmacokinetics of UTAA91 in peripheral blood; (F) Body weight monitoring across experimental groups; (G) Fluorescence imaging of tumor burden in mice.
Figure 3: In vivo efficacy of UTAA91 in humanized tumor-bearing mice. (A) Preclinical in vivo experimental protocol; (B) Time-dependent monitoring of the proportion of Vδ1T/CAR-VδT cells in total CD3⁺ T cells in peripheral blood; (C) Time-dependent monitoring of the proportion of host T cells in total CD3⁺ T cells in peripheral blood; (D) Depletion of PD-1+ host T cell across experimental groups; (E) Pharmacokinetics of UTAA91 in peripheral blood; (F) Body weight monitoring across experimental groups; (G) Fluorescence imaging of tumor burden in mice.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jiang L, you F, Yan K, Yao J, Wu H, Wu J, Chang X, Peng C, Meng H, Wang M, Zhang P, Zhang B, Yang L. UTAA91: An Off-the-Shelf Allogeneic CAR-Vδ1T Therapy Leveraging CD19 Nanoantibody for B-cell Depletion and PD-1 Agonist Nanoantibody for Pathogenic T-cell Elimination in Refractory Autoimmune Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/utaa91-an-off-the-shelf-allogeneic-car-v%ce%b41t-therapy-leveraging-cd19-nanoantibody-for-b-cell-depletion-and-pd-1-agonist-nanoantibody-for-pathogenic-t-cell-elimination-in-refractory-autoimmune-dis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/utaa91-an-off-the-shelf-allogeneic-car-v%ce%b41t-therapy-leveraging-cd19-nanoantibody-for-b-cell-depletion-and-pd-1-agonist-nanoantibody-for-pathogenic-t-cell-elimination-in-refractory-autoimmune-dis/
