Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: Abstracts: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical II (0879–0884)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-11:15AM
Background/Purpose: The course of interstitial lung disease (ILD) in systemic sclerosis (SSc) is highly variable and difficult to predict using clinical variables alone. Therefore, there is a need for reliable biomarkers to improve prognostication. The Scleroderma Lung Study (SLS) II showed that Krebs von den Lungen 6 (KL-6), CCL18, IFNγ-inducible 10-kDa protein (IP-10), and monokine induced by IFNγ (MIG) were significant predictors of ILD progression. In this study, we aimed to validate these findings and build a multivariable model to predict the course of ILD in SSc based on longitudinal data in a US-based multicenter observational cohort.
Methods: Patients with SSc enrolled in the CONQUER cohort were included in this analysis. Enrollment in CONQUER required fulfillment of the 2013 ACR/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria and disease duration of less than five years from the onset of the first non-Raynaud’s symptom. For the current study, we included only those patients who had interstitial lung disease (ILD) confirmed by high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) and who were treated with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) between the baseline and 12-month visits. The study visits were scheduled every 6 months. Blood samples were collected at baseline. Sixty-two proteins were measured as part of a multiplex assay. We used linear mixed-effects models to evaluate the predictive significance of individual cytokines for ILD progression. Follow-up FVC% was the outcome, with baseline cytokine levels, MMF treatment status, baseline FVC%, and time as fixed effects. Random intercepts and slopes accounted for between-patient variability in baseline FVC% and its change over time. A Bayesian regularized linear mixed-effects model was used to develop a prediction model that included clinical variables and serum protein levels.
Results: A total of 122 patients were included, of whom 100 (82%) were female, with a median age of 52 years and a mean disease duration of 2.7 years. Higher baseline levels of IP-10 (b = 0.0020, P = 0.013) and MIG (b = 0.0007, P = 0.023) were associated with higher FVC% over time, indicating a better ILD course. In contrast, higher KL-6 levels (b = –0.0020, P = 0.015) predicted lower FVC% over time. CCL18 was not significantly associated with the FVC% trajectory. In the exploratory analysis, α2-macroglobulin (α2M, b = -3.29, P < 0.001) and serum amyloid P component (SAP, b = -0.49, P = 0.007) also showed predictive significance. In the multivariable Bayesian model, baseline FVC% had the highest estimate among clinical variables (β = 14.03), while α2-macroglobulin had the highest among protein predictors (β = –1.39). The R2 of the model, including clinical predictors and a selected number of serum proteins, was 0.765.
Conclusion: This study confirmed the predictive significance of IP-10, MIG, and KL-6 for the course of SSc-ILD and identified α2M and SAP as potential biomarkers. We also built a multivariable model including clinical and protein variables to predict the SSc-ILD course.
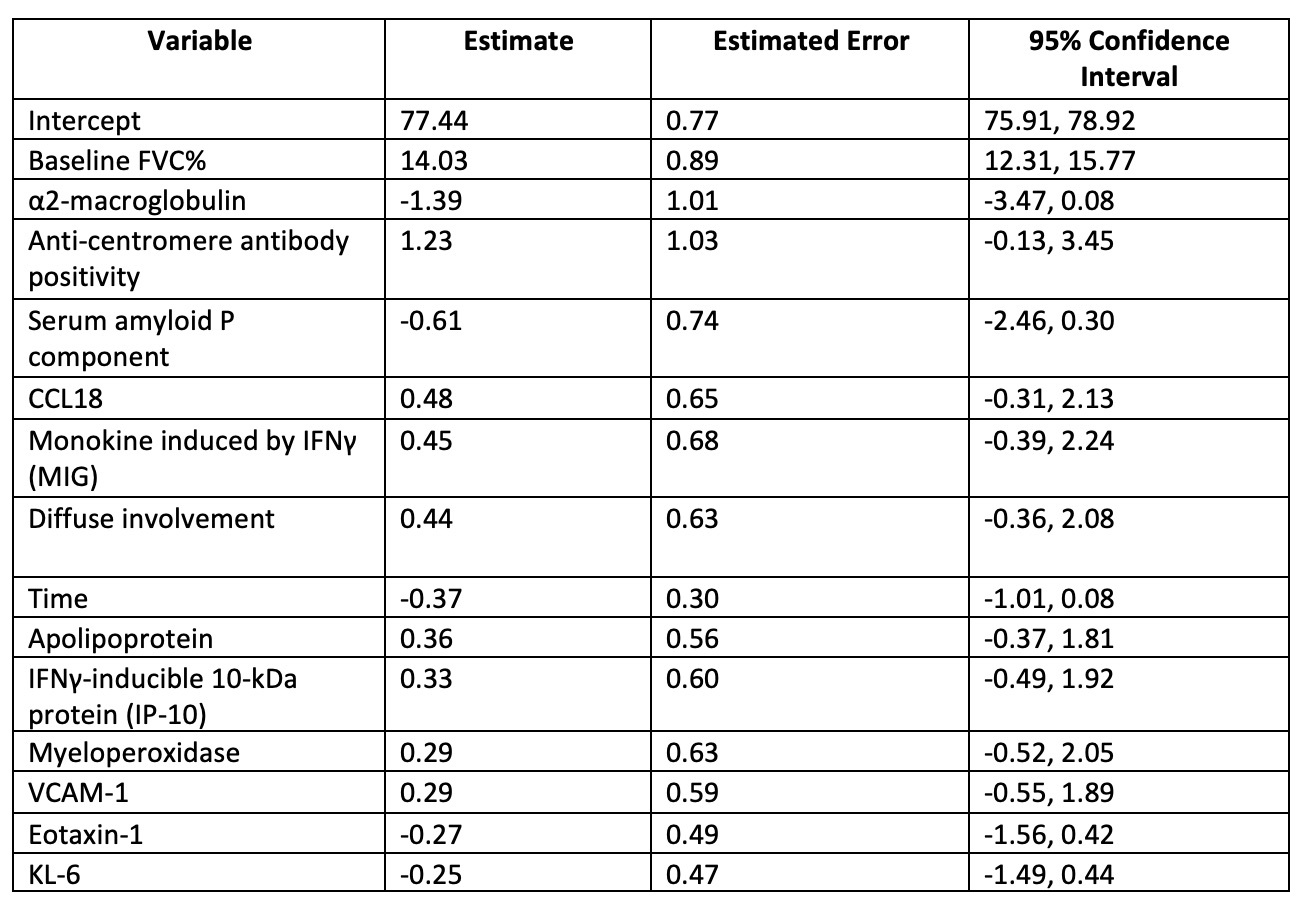 Table 1. Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of study participants
Table 1. Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of study participants
.jpg) Table 2. Predictive significance of the proteins identified by the SLS II for the FVC% course
Table 2. Predictive significance of the proteins identified by the SLS II for the FVC% course
.jpg) Table 3. A Bayesian regularized linear mixed-effects model to predict FVC% course
Table 3. A Bayesian regularized linear mixed-effects model to predict FVC% course
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ayla A, Huang C, Pedroza C, Zhang M, VanBuren J, Castelino F, Chung L, Evnin L, Frech T, Gordon J, Hant F, Hummers L, Khanna D, Lakin K, Lebiedz-Odrobina D, Luo Y, Makol A, Mayes M, McMahan Z, Molitor J, Moore D, Richardson C, Sandorfi N, Shah A, Shah A, Shanmugam V, Skaug B, Steen V, Volkmann E, Zahn C, Zheng W, Bernstein E, Assassi S. Predictive Significance of Serum Proteins for the Course of Systemic Sclerosis-Related Interstitial Lung Disease in the Multicenter CONQUER Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictive-significance-of-serum-proteins-for-the-course-of-systemic-sclerosis-related-interstitial-lung-disease-in-the-multicenter-conquer-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictive-significance-of-serum-proteins-for-the-course-of-systemic-sclerosis-related-interstitial-lung-disease-in-the-multicenter-conquer-cohort/
