Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: Plenary I (0772–0776)
Session Type: Plenary Session
Session Time: 10:00AM-10:15AM
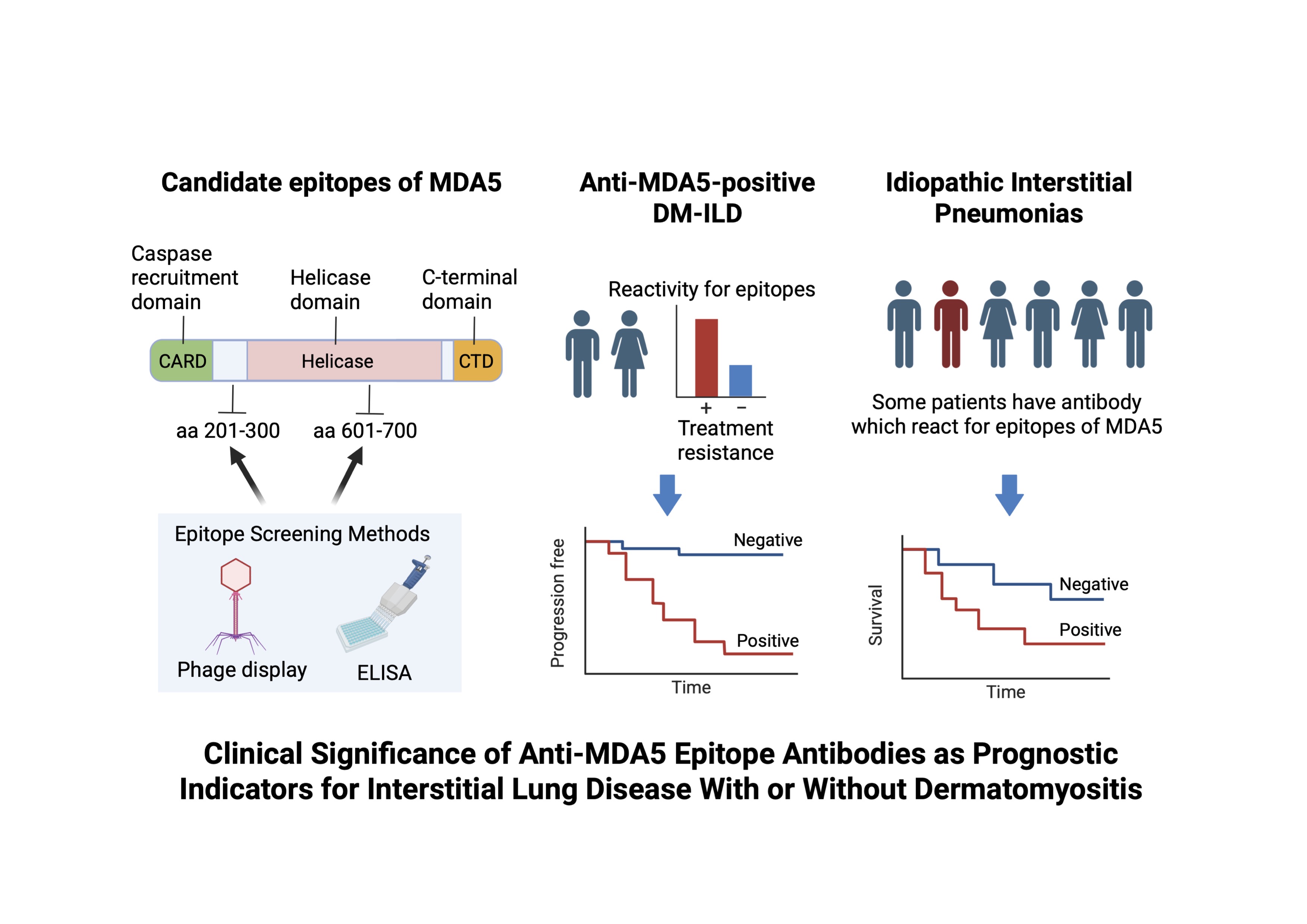
Background/Purpose: Melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5) is a cytoplasmic RNA sensor and activates the innate immune response. Autoantibodies against MDA5 are associated with rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease (ILD) in dermatomyositis (DM). Moreover, MDA5 protein expression is upregulated in the lungs of patients with MDA5-positive-ILD and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. We hypothesized that specific antibody reactivity against certain MDA5 epitope peptides correlates with severe ILD phenotypes and could serve as biomarkers not only in anti-MDA5-positive DM-ILD but also in idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIPs).
Methods: We screened sera from patients with anti-MDA5-positive DM-ILD to identify epitopes using T7 phage display and ELISA with recombinant MDA5 fragments. Two candidate regions, MDA5 (amino acids 201–300) and MDA5 (amino acids 601–700), were identified (Figure 1). We retrospectively analyzed 30 anti-MDA5-positive DM-ILD patients treated with unified therapy (discovery cohort) and validated findings in 54 patients from a multicenter cohort (validation cohort). Resistance to initial triple therapy (glucocorticoid, calcineurin inhibitor, cyclophosphamide) was defined as the need for additional therapy or death within 6 months. Moreover, we examined 288 IIP patients for reactivity to MDA5 (201-300 and 601-700) and assessed their clinical significance in predicting survival outcomes.
Results: In the discovery cohort, high reactivity to MDA5 (201-300) and MDA5 (601-700) was significantly associated with resistance to initial therapy. ROC analysis showed strong predictive ability (sensitivity and specificity were 88% and 71% in MDA5 (201-300), and 63% and 93% in MDA5 (601-700), respectively). In the validation cohort, MDA5 (201-300) positivity was significantly associated with lower 6-month progression-free survival (43% vs. 74%, p< 0.05, Figure 2). Reactivity to MDA5 (601-700) trended toward poorer outcomes but was not statistically significant. Among IIP patients, MDA5 (201-300) and MDA5 (601-700) positivity were significantly more frequent in non-survivors. Patients positive for MDA5 (201-300) or MDA5 (601-700) had lower 5-year survival rates (34% vs. 66%, p< 0.01; 42% vs. 67%, p< 0.01, respectively, Figure 3).
Conclusion: We identified two MDA5 epitope regions—MDA5 (201-300) and MDA5 (601-700)—that are strongly associated with treatment resistance and poor prognosis in anti-MDA5-positive DM-ILD. Furthermore, reactivity to these epitopes also predicted poor outcomes in IIPs. Epitope-specific reactivity may reflect underlying pathogenic mechanisms and serve as novel biomarkers for risk stratification and treatment decision-making in ILD with or without obvious autoimmune disease background.
.jpg) Figure 2. Progression free survival rates of anti-MDA5-positive DM-ILD
Figure 2. Progression free survival rates of anti-MDA5-positive DM-ILD
.jpg) Figure 3. Overall survival rates of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias
Figure 3. Overall survival rates of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sasai T, Nakashima R, Nonaka M, Nomura N, Ogawa A, Nohda Y, Shirakashi M, Hiwa R, Tsuji H, Yoshifuji H, Matsuda S, Katsushima M, Ishitoku M, Yoshida Y, Todoroki Y, Kubo S, Handa T, Tomioka H, Tachikawa R, Tomii K, Tanizawa K, Arai T, Kotani T, Hashimoto M, Hirata S, Tanaka Y, Mimori T, Morinobu A. Clinical Significance of Anti-MDA5 Epitope Antibodies as Prognostic Indicators for Interstitial Lung Disease With or Without Dermatomyositis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-significance-of-anti-mda5-epitope-antibodies-as-prognostic-indicators-for-interstitial-lung-disease-with-or-without-dermatomyositis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-significance-of-anti-mda5-epitope-antibodies-as-prognostic-indicators-for-interstitial-lung-disease-with-or-without-dermatomyositis/