Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Distinguishing seronegative rheumatoid arthritis (RA) from psoriatic arthritis (PsA) sine psoriasis remains challenging, often relying on pathognomonic features (axial involvement, enthesitis) present in only few cases and causing diagnostic changes over time.Generative artificial intelligence (AI) creates synthetic patient profiles to enhance the detection of subtle differences that may elude clinical observation. We applied generative AI for the first time in Rheumatology to evaluate statistical fidelity, privacy preservation, and clinical utility of synthetic data, and to test its potential to differentiate seronegative RA vs PsA sine psoriasis.
Methods: Leveraging data of 105 PsA sine psoriasis and 95 seronegative RA patients, a proprietary synthetic data generation platform was used to implement an optimized Conditional Tabular Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) to produce 200 synthetic patients balanced across diagnostic groups. These were evaluated using Synthetic vAlidation FramEwork (SAFE) (D’Amico S, 2023). MOSAIC framework (D’Amico S, 2024) was employed for classification (PsA vs. RA), using demographic and baseline clinical variables. A Random Forest model was developed and tested on a real validation dataset using 3-fold cross-validation, then was re-evaluated after incorporating synthetic data into the training set to assess any performance enhancement using the same validation set. Model outputs were interpreted with Shapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP).
Results: Generation of 200 synthetic patients had 73% privacy preservation score (nearest neighbor distance ratio; optimal 65-85) and 92% statistical fidelity, indicating that the synthetic cohort mirrored the real one without duplication with similar distributions in principal component analysis (Fig 1).In the real dataset, Random Forest achieved accuracy 85.5% ± 2.3% in distinguishing PsA sine psoriasis from seronegative RA. Random Forest identified family history of psoriasis, monoarthritis, axial disease, enthesitis, fibromyalgia, and high BMI as strong PsA predictors and captured the discrepancy between inflammatory and noninflammatory mechanisms as proper of PsA (higher baseline PhGA, low swollen joint count and CRP). Symmetric arthritis favored classification as RA (Fig 2A).Incorporating synthetic patients, Random Forest accuracy increased to 86.2% ± 2.5%, retained key predictors including typical PsA features (enthesitis, axial and asymmetric involvement), family history of psoriasis, and discrepancy between pain and inflammatory measures (low CRP and swollen joint count, fibromyalgia). Notably, peripheral polyarthritis vs oligoarthritis favored RA and PsA, respectively (Fig 2B).
Conclusion: The first-ever application of generative AI in Rheumatology provided a synthetic data cohort of seronegative RA and PsA sine psoriasis, consistent with real data and privacy-safe. Synthetic data improved classification accuracy. Key variables for intercepting PsA sine psoriasis included family history of PsO, axial/entheseal involvement and mismatch between pain measures and inflammatory markers.
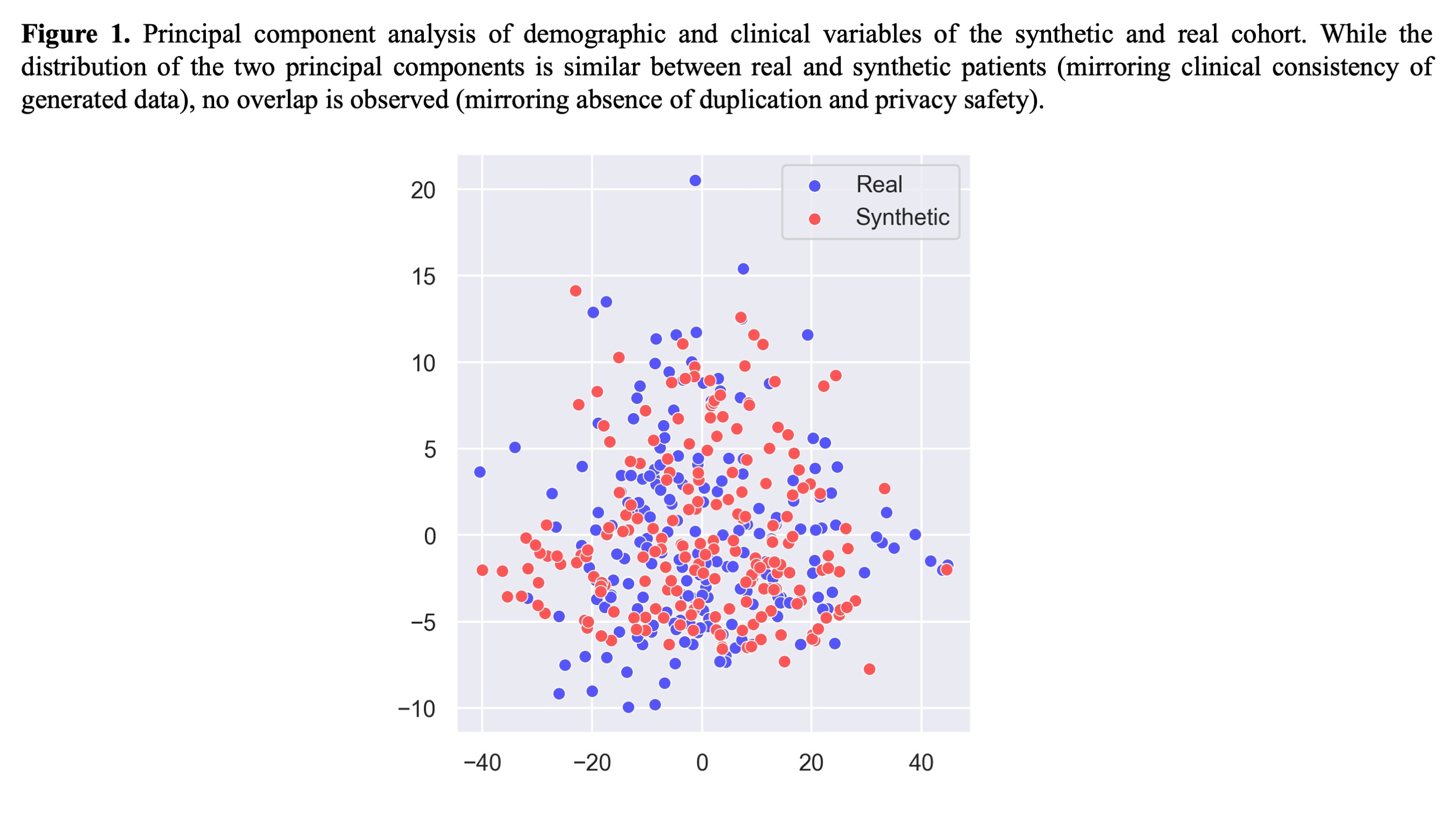 Principal component analysis of demographic and clinical variables of the synthetic and real cohort. While the distribution of the two principal components is similar between real and synthetic patients (mirroring clinical consistency of generated data), no overlap is observed (mirroring absence of duplication and privacy safety).
Principal component analysis of demographic and clinical variables of the synthetic and real cohort. While the distribution of the two principal components is similar between real and synthetic patients (mirroring clinical consistency of generated data), no overlap is observed (mirroring absence of duplication and privacy safety).
.jpg) SHAP summary plot showing the top 10 most influential features for the Random Forest model trained on real (Panel A) and real+synthetic (Panel B) data to distinguish PsA sine PsO (right in the plot) from seronegative RA (left in the plot). Each dot represents a patient; colors indicate feature value (red = high/high frequency, blue = low/low frequency).
SHAP summary plot showing the top 10 most influential features for the Random Forest model trained on real (Panel A) and real+synthetic (Panel B) data to distinguish PsA sine PsO (right in the plot) from seronegative RA (left in the plot). Each dot represents a patient; colors indicate feature value (red = high/high frequency, blue = low/low frequency).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tonutti A, D'Amico S, Morandini P, Faeti C, Barone E, Luciano N, Savevski V, Selmi C. Generative artificial intelligence provides synthetic data to discriminate patients with seronegative rheumatoid arthritis versus psoriatic arthritis sine psoriasis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/generative-artificial-intelligence-provides-synthetic-data-to-discriminate-patients-with-seronegative-rheumatoid-arthritis-versus-psoriatic-arthritis-sine-psoriasis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/generative-artificial-intelligence-provides-synthetic-data-to-discriminate-patients-with-seronegative-rheumatoid-arthritis-versus-psoriatic-arthritis-sine-psoriasis/
