Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0506–0521) Sjögren’s Disease – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I: Etiology, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Clinical tests for Sjögren’s disease (SjD) often overlook Ro-seronegative (RoNeg) cases, leading to delayed or missed diagnoses. Identifying additional serum autoantibodies could improve diagnostic accuracy and enhance disease management. Proteome-wide autoantibody screening in RoNeg SjD cases was previously reported using HuProt 3.2 arrays (CDI Labs) with 19,500 proteins1. This expanded study utilizes HuProt 4.0 arrays with >21,000 human proteins. The aim of the study was to identify 24 autoantibody specificities that best discriminate RoNeg SjD (n=86; 30% ESSDAI≥5) from healthy control (HC, n=24) and other rheumatic disease (OD, n=44; 45% SLE, 39% RA, 9% SSc, 7% other) groups for further development of a multiplex Luminex assay.
Methods: Arrays were probed as per the manufacturer except serum incubations were for 18h at 5ºC. IgG (635 nm), and IgA (532 nm) signals were collected using anti-human, heavy chain-specific IgG and IgA secondary antibodies. After assisted alignment of signals with array templates using a novel algorithm-based alignment tool, data were quantile-normalized, and positive thresholds (avg + 3*SD of HCs) for antibody binding to each protein established. Fisher’s exact tests (p < 0.1) identified specificities bound more commonly in the RoNeg group compared to HC and OD groups. Protein specificity enrichments were explored using STRING. A machine learning pipeline (2/3 training, 1/3 testing) incorporating chi-square selection, random forest-based feature selection, and logistic regression was used for classification.
Results: Fisher’s analysis revealed 27 specificities bound by IgG more commonly in RoNeg SjD (14-22%) vs HC (0-4%), with a subset of 4 (CBX3, CBX5, NAV3, NUSAP1) also bound more commonly by IgG from RoNeg SjD vs OD, and significant enrichment in specificities located in pericentric heterochromatin by STRING analysis. The RoPos SjD group bound 57 proteins more commonly than HC, with a subset of 14 recognized more commonly than in the OD group, and STRING enrichment in RNA and miRNA regulation. Common specificities overlapping between RoNeg and RoPos groups included ATAT1, CBX3, PAIP1, PNPLA1, PTK6 and SLC19A1. Machine learning was applied to RoNeg SjD, OD and HC groups. IgG binding to 121 proteins discriminated the RoNeg group with ROC AUC=0.88. IgA and combined IgG + IgA specificities yielded lower ROC AUC values. A panel of 24 IgG specificities selected from one end of the distribution of logistic regression coefficients yielded ROC AUC=0.83. Replacement of 6 specificities with others showing high prevalence among RoNeg SjD by manual analysis yielded a ROC AUC=0.95 for distinguishing RoNeg SjD cases from HC and OD groups (Table 1; Figure 1).
Conclusion: Using proteome arrays, a novel array alignment algorithm, and machine learning pipelines, we developed an advanced approach for autoantibody biomarker discovery in RoNeg SjD, defining a curated panel of 24 autoantibodies with potential diagnostic significance.Reference:1. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023 Sep;82(9):1181-1190.Funding: NIH/NIAMS 3UC2AR081032-04S1; NIH/NIAMS P30AR073750
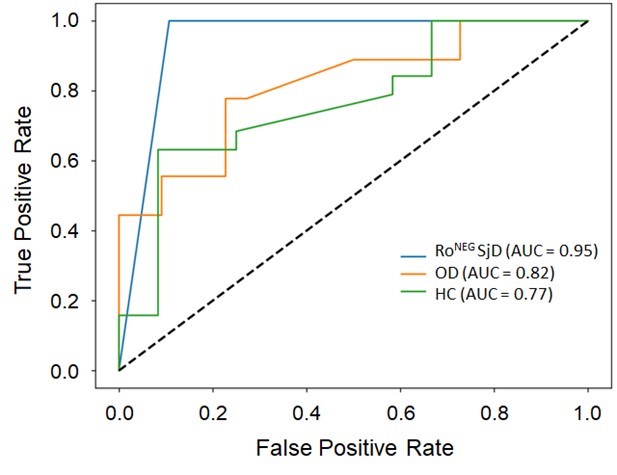 Figure 1. A panel of 24 IgG autoantibody specificities selected by machine learning and manual curation distinguishes Ro seronegative Sjögren’s disease (RoNEG SjD) from healthy control (HC) and other rheumatic disease (OD) groups with ROC AUC = 0.95.
Figure 1. A panel of 24 IgG autoantibody specificities selected by machine learning and manual curation distinguishes Ro seronegative Sjögren’s disease (RoNEG SjD) from healthy control (HC) and other rheumatic disease (OD) groups with ROC AUC = 0.95.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yao S, Lawrence C, Christakos H, Lopez-Davis C, Khatri B, Taylor T, Rasmussen A, Grundahl K, Scofield R, Warner B, James J, Guthridge J, Lessard C, Farris A. Discovery-based Identification of Non-canonical Autoantibody Specificities in Ro Seronegative Sjögren’s Disease Using High-content Human Proteome Arrays [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/discovery-based-identification-of-non-canonical-autoantibody-specificities-in-ro-seronegative-sjogrens-disease-using-high-content-human-proteome-arrays/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/discovery-based-identification-of-non-canonical-autoantibody-specificities-in-ro-seronegative-sjogrens-disease-using-high-content-human-proteome-arrays/

.jpg)