Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Neddylation, NEDD8 conjugating process, is a post-translational modification that plays a crucial role in regulating ubiquitination by targeting cullin (CUL)-ring E3 ubiquitin ligases. Our previous research indicated that neddylation is dysregulated in RA FLS, and that its inhibition can reduce arthritis severity in the K/BxN serum transfer model. However, the dysregulation of neddylation in SKG mice remains largely unexplored. This study aims to investigate whether neddylation is dysregulated in arthritic SKG mice and to evaluate its potential as a therapeutic target for arthritis.
Methods: Arthritis was induced in SKG mice through intraperitoneal injection of zymosan. The neddylation status of CUL1 and CUL5, and the relative gene expression of Nub1 and Csn1 in joint tissue were compared between arthritic and naïve SKG mice using Western blotting, and RT-qPCR, respectively. In vitro, we assessed the effects of the selective neddylation inhibitor TAS4464 on the induction and maturation of bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDCs), on T cell proliferation, as well as on co-culture T cells with TAS4464-treated BMDCs.
Results: We first investigated the neddylation status in arthritic SKG mice and discovered that the neddylation of CUL1 and CUL5 was upregulated in the joints of arthritic SKG mice (Figure a). Gene expressions of nub1 and csn1, negative regulators of neddylation, were decreased in arthritic SKG mice (Nub1: 1.03 ± 0.76 and 0.28 ± 0.12; p=0.019, Csn1: 1.06 ± 0.59 and 0.50 ± 0.34; p=0.029 for naïve mice and arthritic mice, respectively), which indicated that neddylation systems were dysregulated in the arthritic joints. Subsequently, we assessed the effects of neddylation inhibition on DC differentiation, maturation, and T cell proliferation. The neddylation inhibitor promoted the differentiation of PD-L1-positive DCs (78.7 ± 8.2 % and 91.1 ± 4.7 % for DMSO and TAS4464, respectively; p=0.021), reduced the maturation of MHC II-positive DCs (60.7 ± 10.3 % and 36.9 ± 10.6 % for DMSO and TAS4464, respectively; p=0.008) without altering PD-L1 expression, and had a trend to suppress T cell proliferation (37.8 ± 10.3 % and 13.6 ± 5.5 % for DMSO and TAS4464, respectively; p=0.058). Finally, we assessed the efficacy of neddylation inhibition on arthritis, and revealed the neddylation inhibitor alleviated arthritis severity in SKG mice (Figure b).
Conclusion: Upregulated neddylation in inflamed joints could be a novel therapeutic target in autoimmune arthritis.
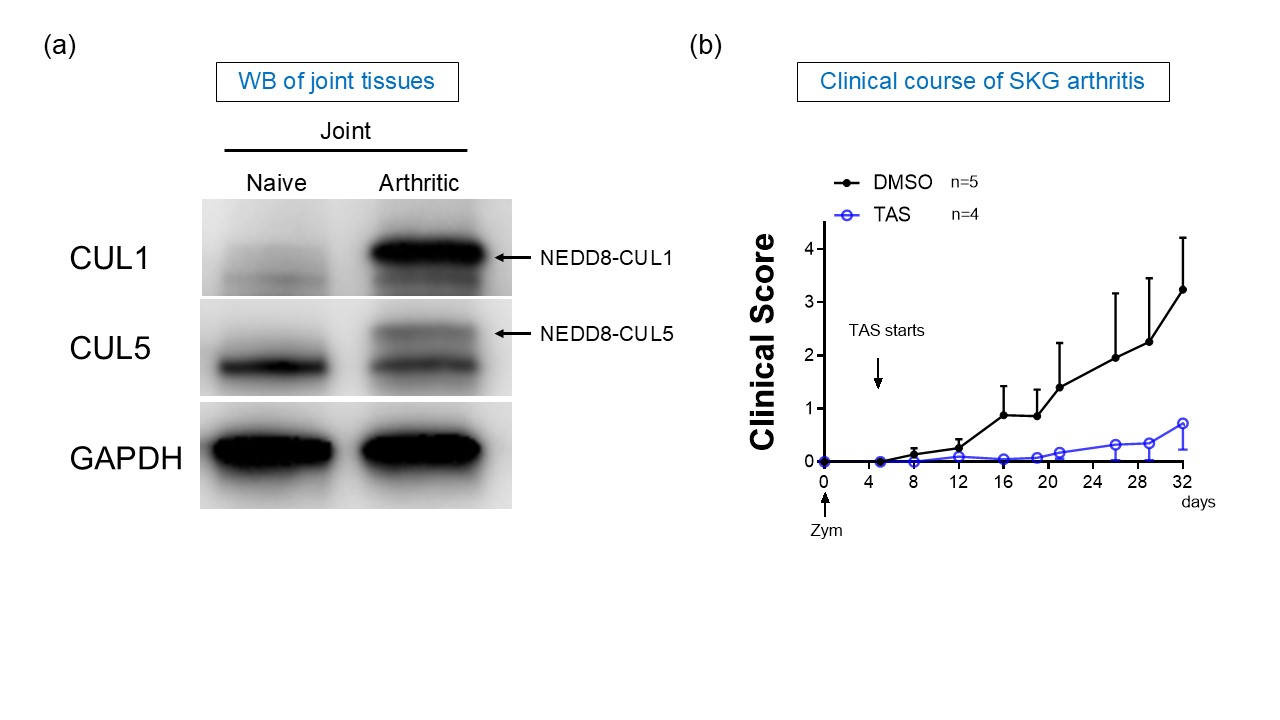 (a) Representative images of western blotting of CUL1, CUL5 and GAPDH in the joints of naive and arthiritic SKG mice. (b) Clinical scores of zymosan injected SKG mice treated with TAS4464 or DMSO.
(a) Representative images of western blotting of CUL1, CUL5 and GAPDH in the joints of naive and arthiritic SKG mice. (b) Clinical scores of zymosan injected SKG mice treated with TAS4464 or DMSO.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sendo S, Fanjul A, Nishisaka K, Yamada H, Okano T, Nishimura K, Ueda Y, Saegusa J. Neddylation as a Therapeutic Target in Autoimmune Arthritis: Evidence from SKG Mice [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/neddylation-as-a-therapeutic-target-in-autoimmune-arthritis-evidence-from-skg-mice/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/neddylation-as-a-therapeutic-target-in-autoimmune-arthritis-evidence-from-skg-mice/
