Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0001–0018) B Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapies targeting CD19 or B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) have shown unprecedented effects in treatment-resistant autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and others. However, the limitations in patient populations for CAR-T arise from significant safety concerns, complex logistical hurdles and unsuccessful retreatment. Recently, bispecific antibodies (e.g. Blinatumomab and Teclistamab), which may offer an alternative approach to CART with similarly effective B cell depletion but off-the-shelf convenience, have been approved in B cell malignancies and showed impressive efficacy in patients with autoimmune indications in case reports. Furthermore, in some patients, disease may be anchored in the long-lived plasma cells that express BCMA but not CD19. Therefore, the aim is to develop a first-in-class tri-specific antibody targeting CD19/BCMA/CD3 to achieve a rapid and deep B cell depletion with a differentiated safety profile, potentially beneficial for the treatment of autoimmune disorders across multiple therapeutic areas.
Methods: KT501 is a novel IgG-like trispecific T cell engager, designed to bind CD3, CD19, BCMA with high affinity, thereby targeting a broad range of B cell populations. Utilizing an innovative molecular design aimed at maximizing potency while minimizing cytokine release by a unique CD3 masking platform, KT501 has demonstrated robust B cell cytotoxicity and reduced cytokine production in vitro and in non-human primate (NHP) due to its cross activity in NHP.
Results: In vitro, KT501 is more potent in B cell killing and results in lower cytokine release compared with Blinatumomab. In preclinical studies using cynomolgus monkeys, KT501 induced rapid and profound B cell depletion following a single 1 mg/kg intravenous (IV) dose in peripheral blood, bone marrow, spleen and lymph nodes (Figure 1), with minimal cytokine release. Furthermore, a single subcutaneous (SC) administration of 1mg/kg led to reduction from baseline for serum IgA, IgG and IgM levels by 67%%, 44% and 39%, respectively at day 26. In the ongoing repeated dose cyno toxicology study with a wide range of doses (0.01 to 10 mg/kg) by SC injection, KT501 was well tolerated with no fever and other clinical signs/symptoms observed at all dose levels. As presented in Figure 2, after the initial SC administration, peripheral CD20+ B cells were depleted within 24 hrs at the lowest dose of 0.01 mg/kg. Cytokine release syndrome relevant cytokines were transiently increased but all back to the levels similar to pre-dose level within 24 hrs, with no increased cytokines at the subsequent doses.
Conclusion: These findings in preclinical studies strongly support the clinical development of KT501 as a first-in-class trispecific TCE that is potentially effective and convenient therapy with a differentiated safety profile for many autoimmune diseases. A Phase I first-in-human clinical trial is anticipated to begin in Q1 2026.
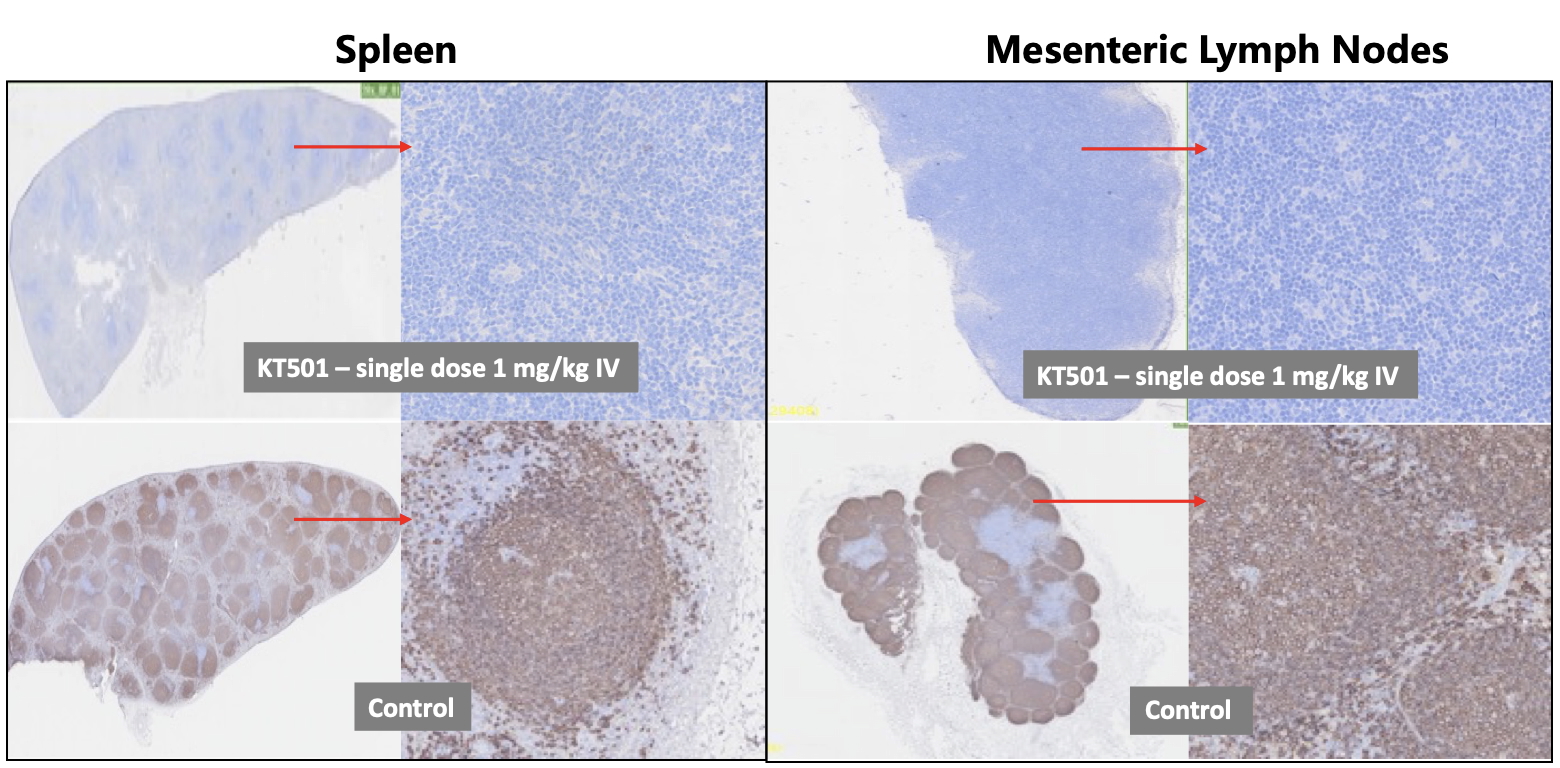 Figure 1: B cell Depletion in Spleen and Lymph Nodes in NHP (CD20 Immunohistochemistry Staining)
Figure 1: B cell Depletion in Spleen and Lymph Nodes in NHP (CD20 Immunohistochemistry Staining)
.jpg) Figure 2: Peripheral Blood B cell Depletion and Cytokines After Initial SC Dose in NHP (0.01, 1, 5 and 10 mg/kg)
Figure 2: Peripheral Blood B cell Depletion and Cytokines After Initial SC Dose in NHP (0.01, 1, 5 and 10 mg/kg)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bao M, Wang J, Zhao J, Xu W. KT501, a CD19/BCMA/CD3 trispecific antibody, leads to rapid and deep B-cell depletion with well-tolerated safety [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/kt501-a-cd19-bcma-cd3-trispecific-antibody-leads-to-rapid-and-deep-b-cell-depletion-with-well-tolerated-safety/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/kt501-a-cd19-bcma-cd3-trispecific-antibody-leads-to-rapid-and-deep-b-cell-depletion-with-well-tolerated-safety/
