Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0001–0018) B Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapies targeting CD19 have shown unprecedented effects in treatment-resistant autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and others. However, the limitations in patient selection for CAR-T arise from significant safety concerns, complex logistical hurdles, cost and unsuccessful retreatment if flare occurs. Recently, bispecific antibodies (e.g. Blinatumomab), which may offer an alternative approach to CART with similarly effective B cell depletion but off-the-shelf convenience, have been approved in B cell malignancies and showed impressive efficacy in patients with autoimmune indications in case reports. However, the safety profile and treatment options are not optimized. Therefore, the aim is to develop a novel bispecific antibody targeting CD19/CD3 that can achieve a rapid and deep B cell depletion with an optimized safety profile through subcutaneous injection for the beneficial of patients with autoimmune disorders across multiple therapeutic areas.
Methods: KT502 was selected on an innovative molecular design that maximizes B cell cytotoxicity while minimizes cytokine release through a unique CD3 masking technology. KT502 also has cross-activity with non-human primate (NHP), facilitating preclinical safety and efficacy evaluation. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from healthy donors were cultured in the presence of KT502 or blinatumomab for 48 hours. Cynomolgus monkeys were treated with KT502 intravenously (IV) or subcutaneously (SC) in the prove-of-concept toxicology study.
Results: In vitro, KT502 exhibits superior potency in B cell killing but lower cytokine release compared with Blinatumomab. In the preclinical study using cynomolgus monkeys, KT502 induced rapid and profound B cell depletion while cytokine release remained low and transient, highlighting KT502’s a favorable and differentiated safety from CAR-T therapies and other TCEs with similar target. Following three weekly SC injection of 1mg/kg, robust B cell depletion in spleen and lymph nodes were achieved by day 22 (Figure 1) with no fever or other clinical signs/symptoms observed. The cytokine release syndrome relevant biomarkers were generally low after the initial dose; importantly, all were back to the levels similar to pre-dose within 24 hrs (Figure 2). Furthermore, reductions from baseline for serum IgM, IgA and IgG levels were 65%, 54% and 34%, respectively by day 21.
Conclusion: KT502, a novel CD19/CD3 TCE developed through a unique CD3 masking technology, demonstrated a rapid and deep B depletion in vitro and in NHP study with a favorable and differentiated safety profile. These early findings strongly support the clinical development of KT502 as a potential effective treatment with an optimized safety profile that may also provide patient-friendly treatment option for a broad range of autoimmune diseases. A Phase I first-in-human clinical trial is anticipated to begin in Q1 2026.
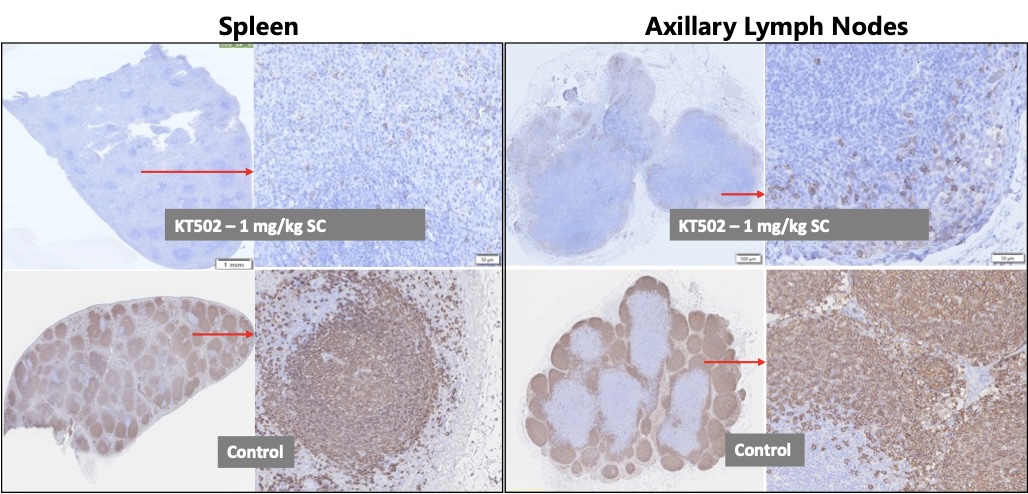 Figure 2: Cytokine Release Following 1 mg/kg SC in NHP (Predose to 24hrs on Day 1)
Figure 2: Cytokine Release Following 1 mg/kg SC in NHP (Predose to 24hrs on Day 1)
.jpg) Figure 1: B cell Depletion in Spleen and Lymph Nodes in NHP (CD20 Immunohistochemistry Staining at Day 22)
Figure 1: B cell Depletion in Spleen and Lymph Nodes in NHP (CD20 Immunohistochemistry Staining at Day 22)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bao M, Wang J, Zhao J, Xu W. KT502, a novel CD19-directed TCE (T-cell engager), leads to rapid and deep B-cell depletion with low cytokine release [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/kt502-a-novel-cd19-directed-tce-t-cell-engager-leads-to-rapid-and-deep-b-cell-depletion-with-low-cytokine-release/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/kt502-a-novel-cd19-directed-tce-t-cell-engager-leads-to-rapid-and-deep-b-cell-depletion-with-low-cytokine-release/
