Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Abstracts: SpA Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes II
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-4:30PM
Background/Purpose: In a previous study, we reported the discovery and evaluation of a serum protein (22 peptide) signature (RAPsA Dx) which, when using random forest machine learning methods, generated an algorithm that could discriminate PsA from RA patients with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.85. The purpose here was to undertake a large multi-centre study using clinically well-characterised cohorts of patients with PsA or RA to seek to validate the RAPsA Dx signature and associated algorithm as the next important step towards clinical utility.
Methods: Samples of serum from patients with RA or PsA were obtained from 4 centres and 5 separate cohorts. The inclusion criteria were: age between 18-80 years and a diagnosis of recent-onset (symptom duration < 12 months), biologic-Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drug treatment-naive PsA or RA with ongoing active joint inflammation. Patients with RA met the ACR/EULAR classification criteria and those with PsA met the CASPAR criteria. Overall, 623 (58%) patients had PsA and 444 (42%) had RA. All 1067 baseline serum samples and multiple aliquots of a pooled reference serum sample were fractionally randomized across twelve 96-well plates and subjected to trypsin digestion. The digested samples were spiked with a mixture of 22 isotopically labeled peptides corresponding to the 22 RAPsA Dx peptides and used for targeted liquid chromatography (LC) tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) data acquisition by multiple reaction monitoring (MRM).
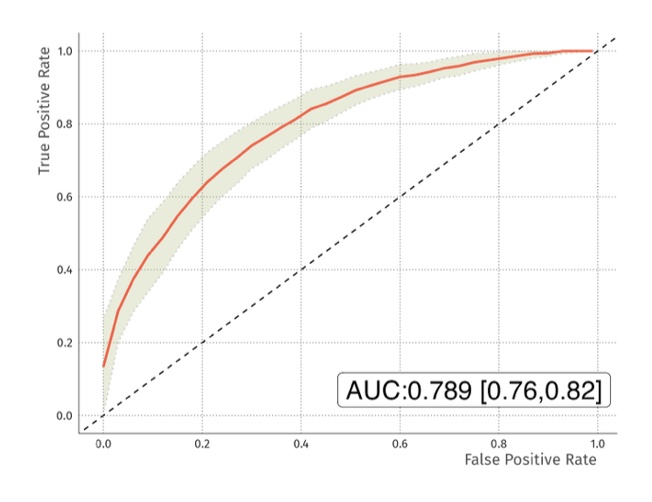
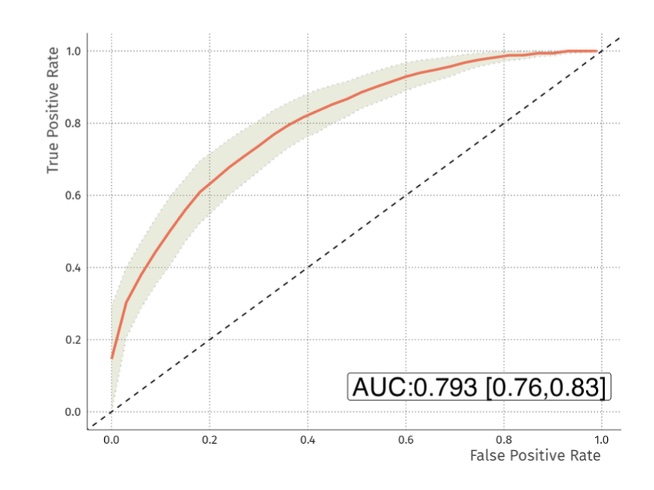
Results: Regularised random forest analysis of the raw MRM data resulted in an average test accuracy of 70.5% [69.7%, 71.4%] with AUC of the receiver operator curve of 0.76 [0.73, 0.79] (Figure 1). The model used 19 of the 22 peptides. The proteins represented by these peptides will be reported. When applied to data from samples (n=50) that were not used to generate the model, it predicted 80% of true observations correctly. The inclusion of 22 isotopically labeled peptides in the samples allowed the data to be normalised for sample loading onto the LC-MS/MS. When data were normalised in this way the test accuracy was 72% [70.8%, 73.1%] with an AUC of 0.793 [0.76, 0.83] (Figure 2). Overall, the data revealed that the RAPsA Dx protein biomarker signature can correctly identify patients with either RA or PsA with an AUC of at least 0.76, a sensitivity of close to 82% and a specificity of 64%. It is important to note that the confidence intervals for the accuracy and AUCs were very narrow revealing the reliability of the data.
Conclusion: Using a large multi-centre cohort of over 1000 patients, we have validated a panel of protein (peptide) biomarkers and associated algorithm that differentiates PsA from RA. We propose that this biomarker signature, RAPsA Dx, will be a useful additional tool to assist rheumatologists and others with clinical decision-making when assessing patients presenting with early inflammatory arthritis and will lead to an earlier definitive diagnosis of PsA. We also suggest that RAPsA Dx may aid in the assessment of patients who are not responding to either standard or novel therapeutic strategies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pennington S, Zhou R, Brady J, Wundervald B, Parnell A, Duffy C, Perryman R, Waddington J, McHugh N, Jadon D, Simon D, Fagni F, Schett G, Morton F, Najm A, Siebert S, Coates L, FitzGerald O. Multi-centre Validation of a Serum Protein Biomarker Signature (RAPsA Dx), Which Discriminates Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) from Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/multi-centre-validation-of-a-serum-protein-biomarker-signature-rapsa-dx-which-discriminates-psoriatic-arthritis-psa-from-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/multi-centre-validation-of-a-serum-protein-biomarker-signature-rapsa-dx-which-discriminates-psoriatic-arthritis-psa-from-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra/