Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Raynaud’s phenomenon (RP) is characterized as episodic color changes of the digits occurring with exposure to cold environments, sudden temperature decreases, and emotional stress. Patients with RP from connective tissue disease (CTD) can experience attacks in the setting progressive pathologic remodeling of the vasculature, and these patients can be at risk for digital ulcerations. In systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients, surveys have shown that RP is the highest ranked SSc-specific symptom associated with quality-of-life. Anxiety and depression were found to be more common in those with secondary RP compared to primary RP. Mindy-body techniques have been observed to address anxiety, depression, and emotional stress. Guided imagery is a form of meditation that uses internal focused visualization and imaginative content to evoke sensory perceptions to improve wellbeing and reduce anxiety. Thermal biofeedback reduced RP attacks and improved hand warming in a study by Freedman et al; however, guided imagery has not been studied in CTD. Behavioral interventions may provide a low cost, low risk option for individuals with RP, especially in those where the standard medications are contraindicated or not sufficient. The objective of our study was to evaluate the feasibility and efficacy of auditory-guided imagery intervention on CTD-associated RP.
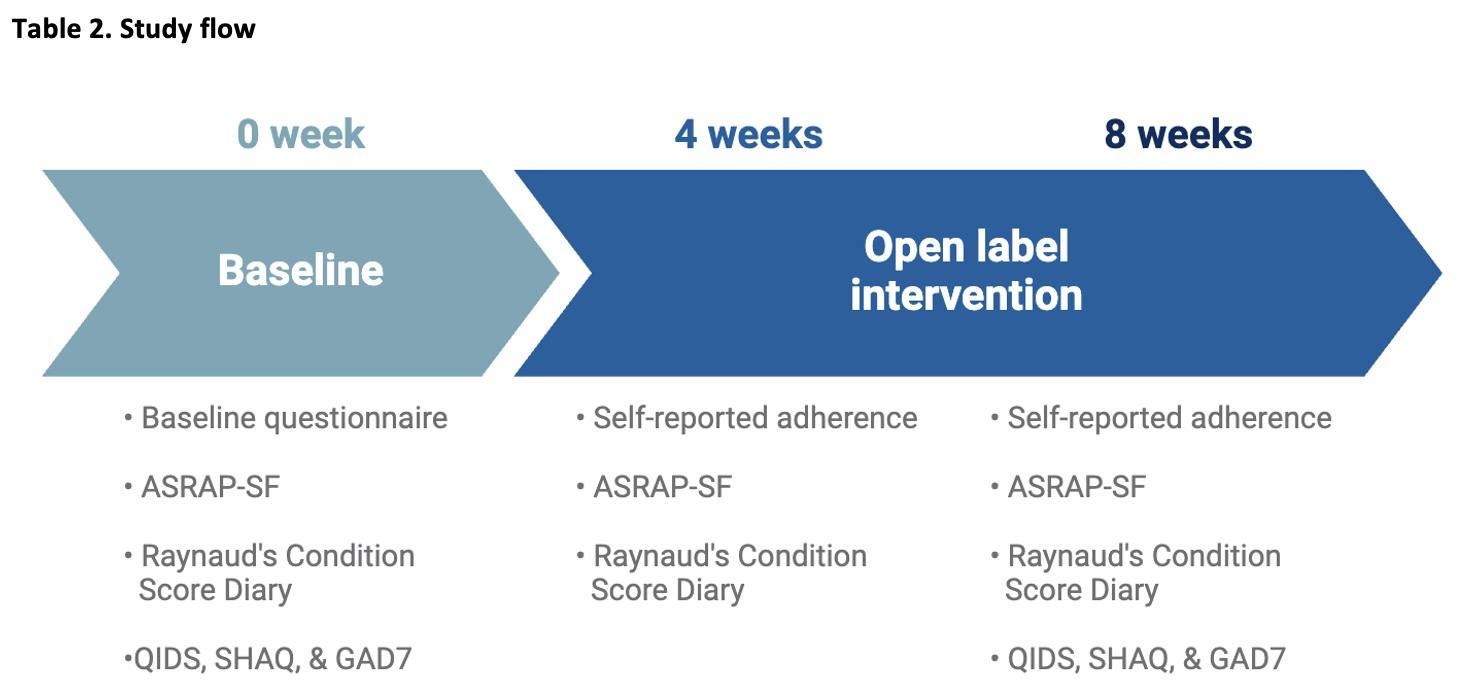
Methods: Eligibility included age 18 or older with CTD-RP for an open-label, single-arm, eight-week intervention with daily auditory-guided imagery were recruited over a 6-week period in the winter at a single-site. Study patients needed a computer or smartphone with access to email to complete electronic surveys. Patients already performing daily meditation practices were excluded. Participants were asked to complete a 10-minute audio-guided imagery (AGI) intervention daily over eight weeks (Table 2). This was accessed by web-link, which recorded the number of minutes used daily. Patients completed surveys, including ASRAP-SF, RCS, RPVAS, SHAQ, QIDS, and GAD7 at baseline and after 8 weeks of intervention.
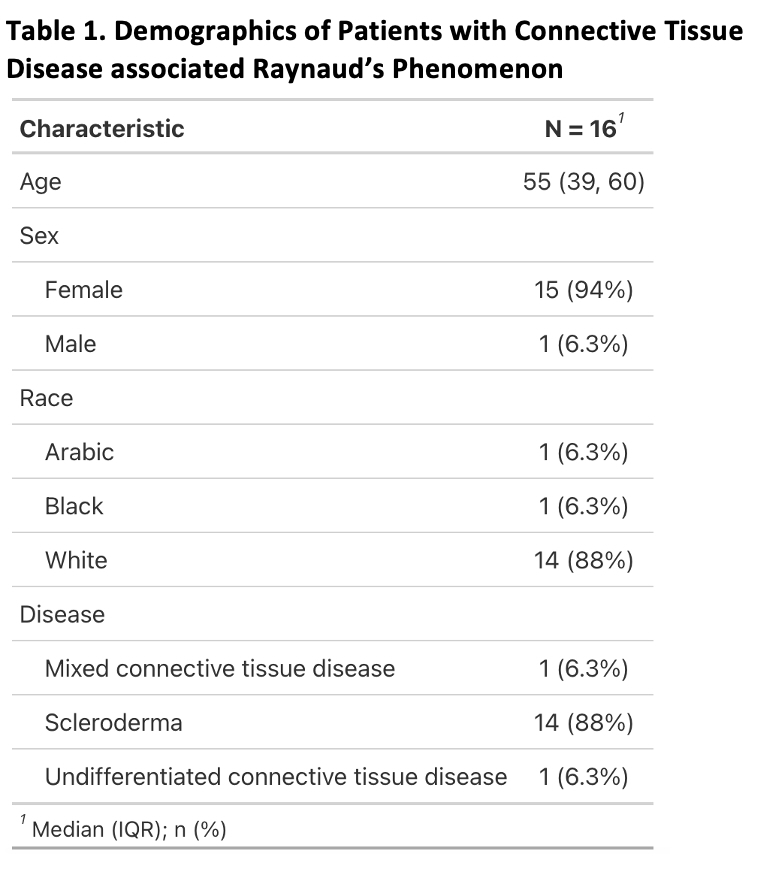
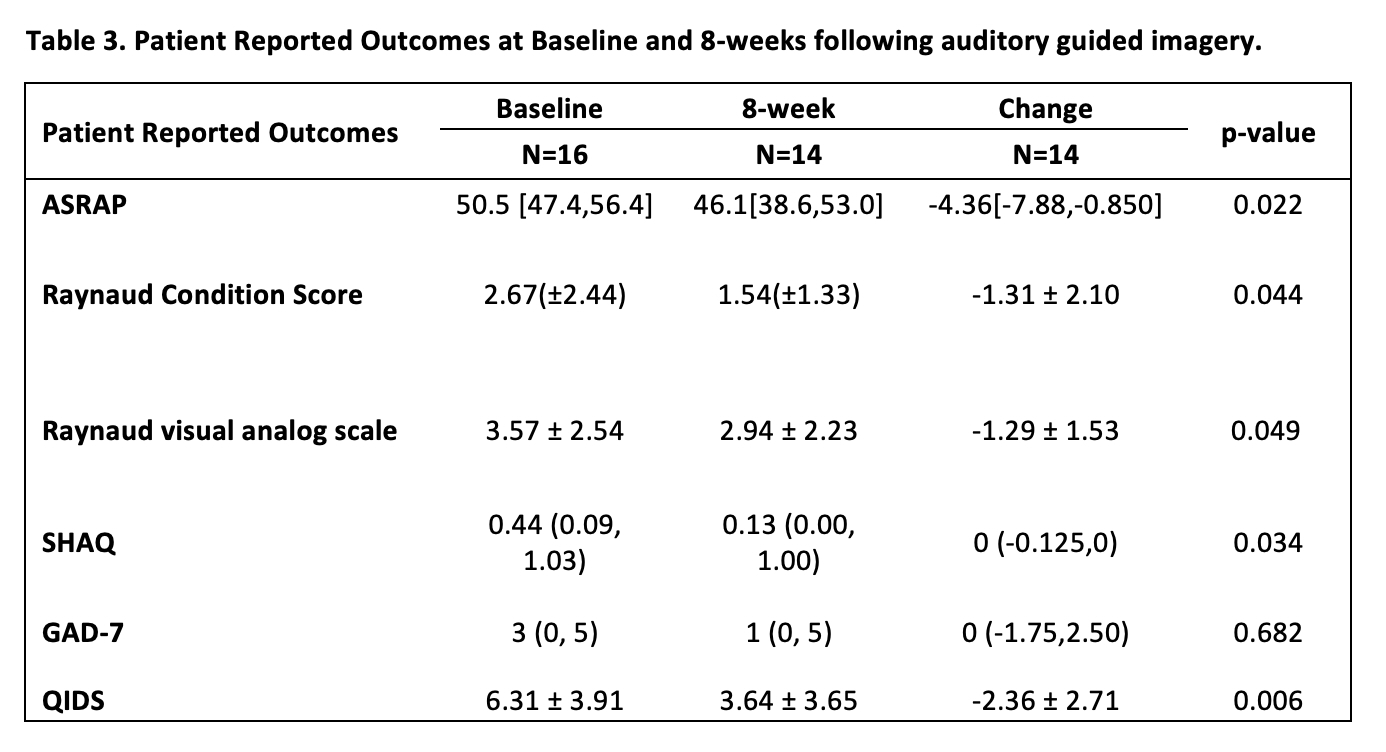
Results: Sixteen study participants were enrolled, of which fourteen had SSc, one mixed connective tissue disease and one undifferentiated CTD. AGI demonstrated significant improvement in all patient reported outcomes, except GAD7 (Table 1). This 8-week intervention shows patients with CTD-associated RP had less severe and less frequent RP episodes as well as improved quality of life and depressive symptoms.
Conclusion: Audio guided imagery use significantly improved several domains of health, including physical, emotional, and mental in patients with CTD-RP, who otherwise, more commonly struggled with more RP attacks, lower quality of life, and depression. AGI is a low cost, low risk, and convenient therapy for CTD-RP and a larger trial studying the effects of this intervention is indicated.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Padilla C, Katikineni V, Park Y, Freno L, Laffoon M, Domsic R. Audio-Guided Imagery Positively Impacted Patients with Raynaud’s Phenomenon Associated Connective Tissue Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/audio-guided-imagery-positively-impacted-patients-with-raynauds-phenomenon-associated-connective-tissue-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/audio-guided-imagery-positively-impacted-patients-with-raynauds-phenomenon-associated-connective-tissue-disease/