Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The ILD-PRO Registry is a multicenter US registry of patients with progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) other than idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). We assessed clinical characteristics, treatments, and quantitative lung fibrosis scores at enrollment among patients in this registry who had systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease-related ILDs (SARD-ILDs).
Methods: Patients had an SARD-ILD that was diagnosed or confirmed at the enrolling center, reticular abnormality and traction bronchiectasis (with or without honeycombing) on HRCT, and met criteria for ILD progression within the prior 24 months. Demographic and clinical characteristics at enrollment were assessed. HRCT images taken closest to enrollment (within the prior 24 months) were analyzed using a previously developed machine learning algorithm to derive the following scores expressed as percentages of total lung involvement: quantitative lung fibrosis (QLF); quantitative ground glass (QGG); quantitative honeycomb cysts (QHC); quantitative ILD (QILD; sum of QLF, QGG and QHC scores). HRCT patterns were categorized by central review according to international guidelines. The proportions of patients with a usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP)-like pattern (definite or probable UIP) vs. alternative fibrotic patterns (indeterminate for UIP or suggestive of an alternative diagnosis) were assessed.
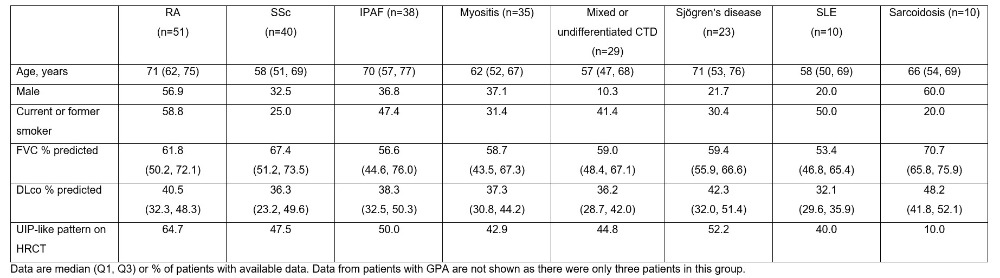
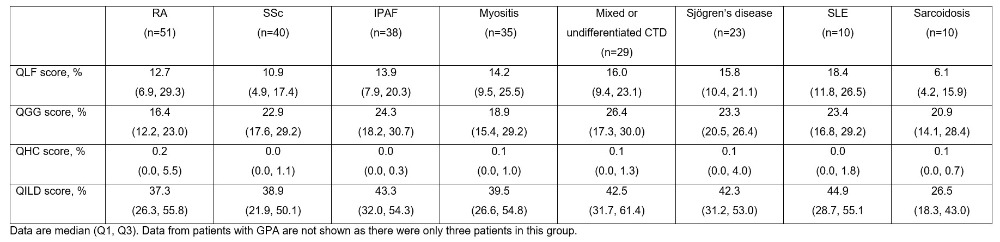
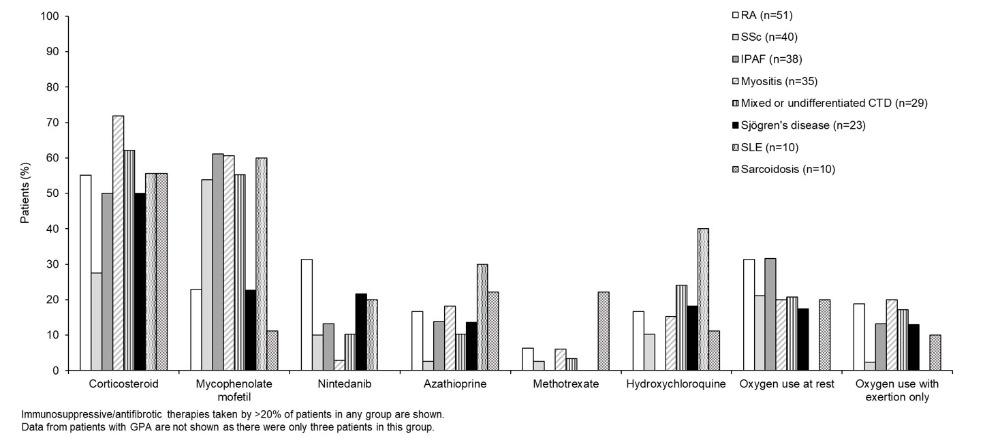
Results: Among 395 patients enrolled in the ILD-PRO Registry, 239 had ILD associated with SARDs: rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (n=51), systemic sclerosis (SSc) (n=40), idiopathic pneumonia with autoimmune features (IPAF) (n=38), myositis (n=35), mixed or undifferentiated connective tissue disease (n=29), Sjögren’s disease (n=23), systemic lupus erythematous (SLE) (n=10), sarcoidosis (n=10), granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) (n=3). Median forced vital capacity (FVC) % predicted and diffusing capacity (DLco) % predicted were lowest in patients with SLE and highest in patients with sarcoidosis (Table 1). A UIP-like pattern on HRCT was most frequently observed in patients with RA (Table 1). Median QILD score was above 35% in all the subgroups apart from sarcoidosis (Table 2). Median QLF score ranged from 6% to 18% across the subgroups (Table 2). Overall, 79.3% of patients took immunosuppressive/cytotoxic therapy, 64.1% oral steroids, 44.9% mycophenolate, 24.3% antifibrotic therapy and 24.4% supplemental oxygen at rest (Figure).
Conclusion: Patients with progressive fibrosing SARD-ILDs enrolled into the ILD-PRO Registry had pronounced impairment in lung function and marked lung involvement based on quantification of fibrotic reticulation or ground glass abnormalities on HRCT. Medication use was high, particularly oral steroids and mycophenolate.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Swaminathan A, Weber J, Todd J, Palmer S, Neely M, Li P, Chauffe A. Clinical, Imaging and Treatment Characteristics of Patients with Progressive Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Disease-related Interstitial Lung Diseases (SARD-ILDs) in the ILD-PRO Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-imaging-and-treatment-characteristics-of-patients-with-progressive-systemic-autoimmune-rheumatic-disease-related-interstitial-lung-diseases-sard-ilds-in-the-ild-pro-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-imaging-and-treatment-characteristics-of-patients-with-progressive-systemic-autoimmune-rheumatic-disease-related-interstitial-lung-diseases-sard-ilds-in-the-ild-pro-registry/