Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: CAR-T cell therapy is a promising treatment for a range of systemic autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic sclerosis, and antisynthetase syndrome, among others. A number of immune-mediated complications are known to occur following CAR-T cell therapy, including cytokine release syndrome (CRS), immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS), and various skin lesions. However, post-CAR-T cell rheumatological complications are not well known, with only one case of palindromic rheumatism reported by our group (1). Our aim is to describe the various rheumatological complications post-CAR-T cell therapy in a tertiary university center.
Methods: Cases treated with CAR-T cells from January 2020 to May 2024 at a single center were analyzed. Patients treated with anti-CD19 CAR-T therapy (ARI-0001, (A3B1)4-1BB/CD3ζ ) and anti–BCMA CAR-T (ARI0002h) were included. All patients were treated for hematological malignancies. None of the patients had an underlying systemic autoimmune disease before CAR-T cell therapy.
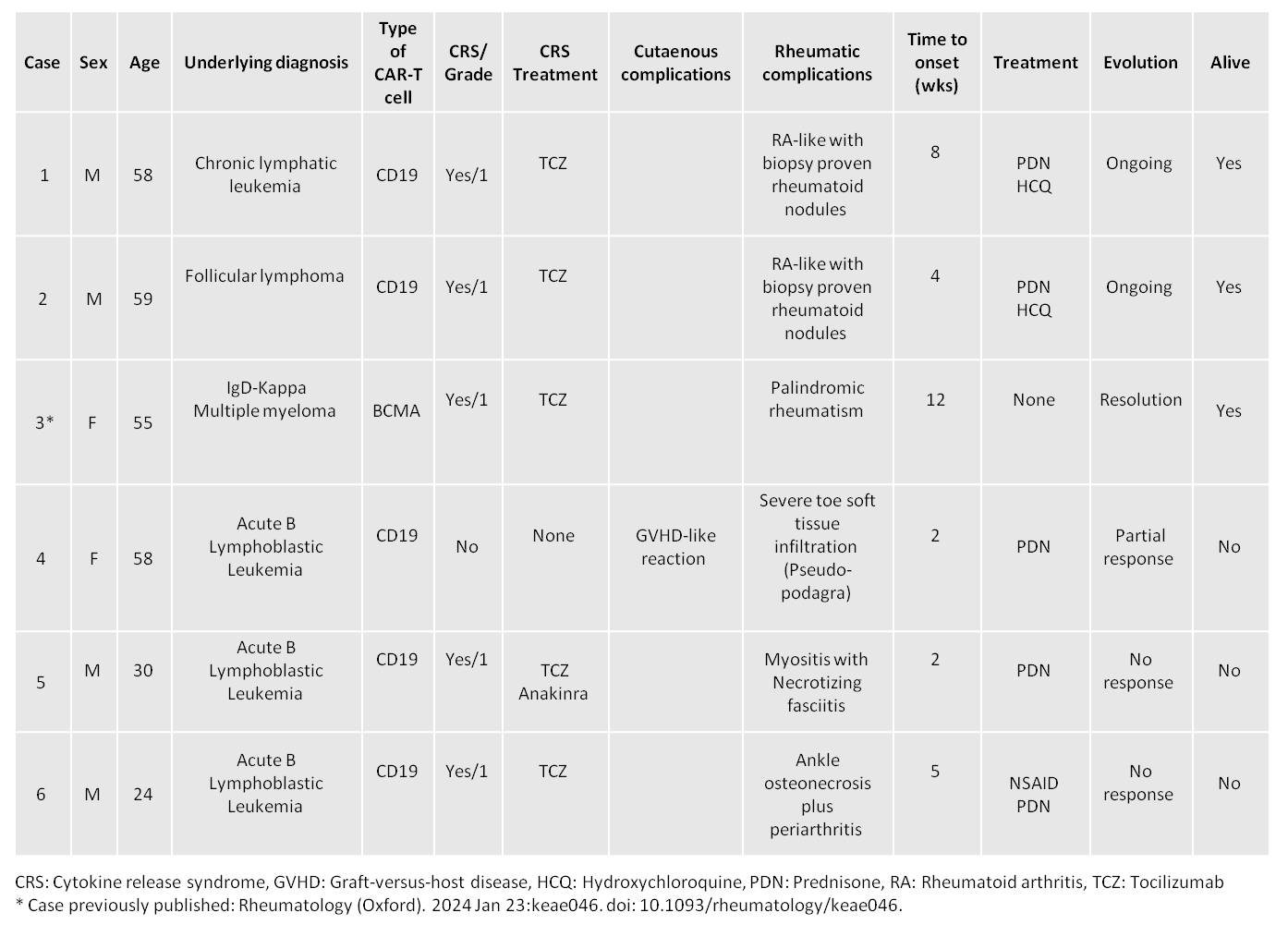
Results: During the study period, 310 patients were treated with CAR-T cell therapy, including 180 patients with CD19 and 124 with BCMA. Only 6 patients (1.9%) had rheumatologic complications (4 males). The mean age at the time of the rheumatic manifestation was 47.3 years (range 24-59 years), and the mean time to onset was 5.5 weeks (range 2-11 weeks). The underlying diagnoses for CAR-T cell therapy were acute B lymphoblastic leukemia (3), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (1), follicular lymphoma (1), and IgD-Kappa IIb multiple myeloma (1).
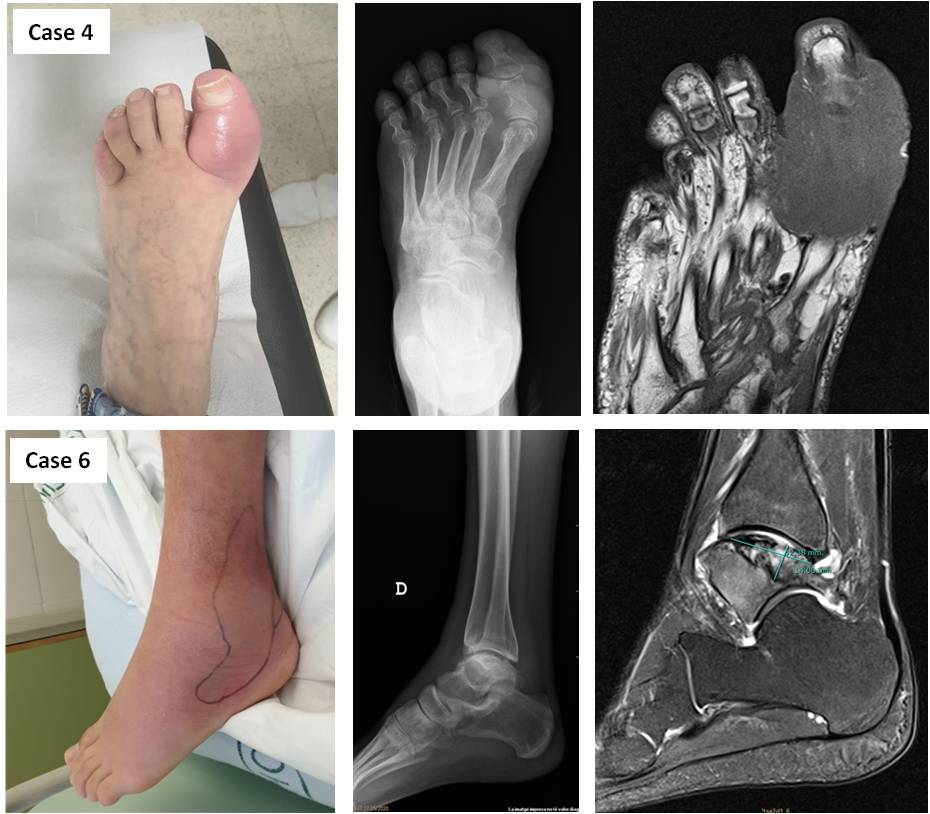
The main rheumatic syndromes included inflammatory arthritis, with two cases with RA-like with biopsy-proven nodulosis (2), and one case of palindromic rheumatism. Other diagnoses included ankle osteonecrosis with periarthritis, severe myositis with necrotizing fasciitis, and one severe inflammatory toe soft tissue reaction (pseudo-podagra). The main clinical characteristics and follow-up are summarized in the table and two cases are schematized in Figure 1. Systemic and localized reactions were observed during the first weeks (mean 3.0 weeks), and inflammatory arthritis appeared after a mean time of 2 months.
Five patients had CRS (all mild), treated with tocilizumab in 5 cases and anakinra in one. Another patient had a graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)-like reaction, and none had ICANS.
Conclusion: Rheumatological complications related to CAR-T therapy are infrequent (< 2%) and usually manifest as early inflammatory complications (within the first month) or later as inflammatory arthritis (after the second month). Given the increased use of this therapy, rheumatologists need to be aware of these previously unknown complications.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gomez-Puerta J, Monegal A, Ponce A, Peris P, Martínez N, Ortiz-Maldonado V, Triguero A, Fernández de larrea C, Delgado J, Sanmartí Sala R, Juan M. Rheumatic Complications Post-CAR-T Cell Therapy. Experience of a Single Center [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rheumatic-complications-post-car-t-cell-therapy-experience-of-a-single-center/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rheumatic-complications-post-car-t-cell-therapy-experience-of-a-single-center/