Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: Pain is the main osteoarthritis (OA) symptom and remains poorly understood. While significant attention has been given to the potential role of innate immunity, few studies have explored the role of adaptive immunity. Our aim was to identify a comprehensive systemic immunological signature of OA-related pain, with a particular emphasis on the role of Tregs and Teffs.
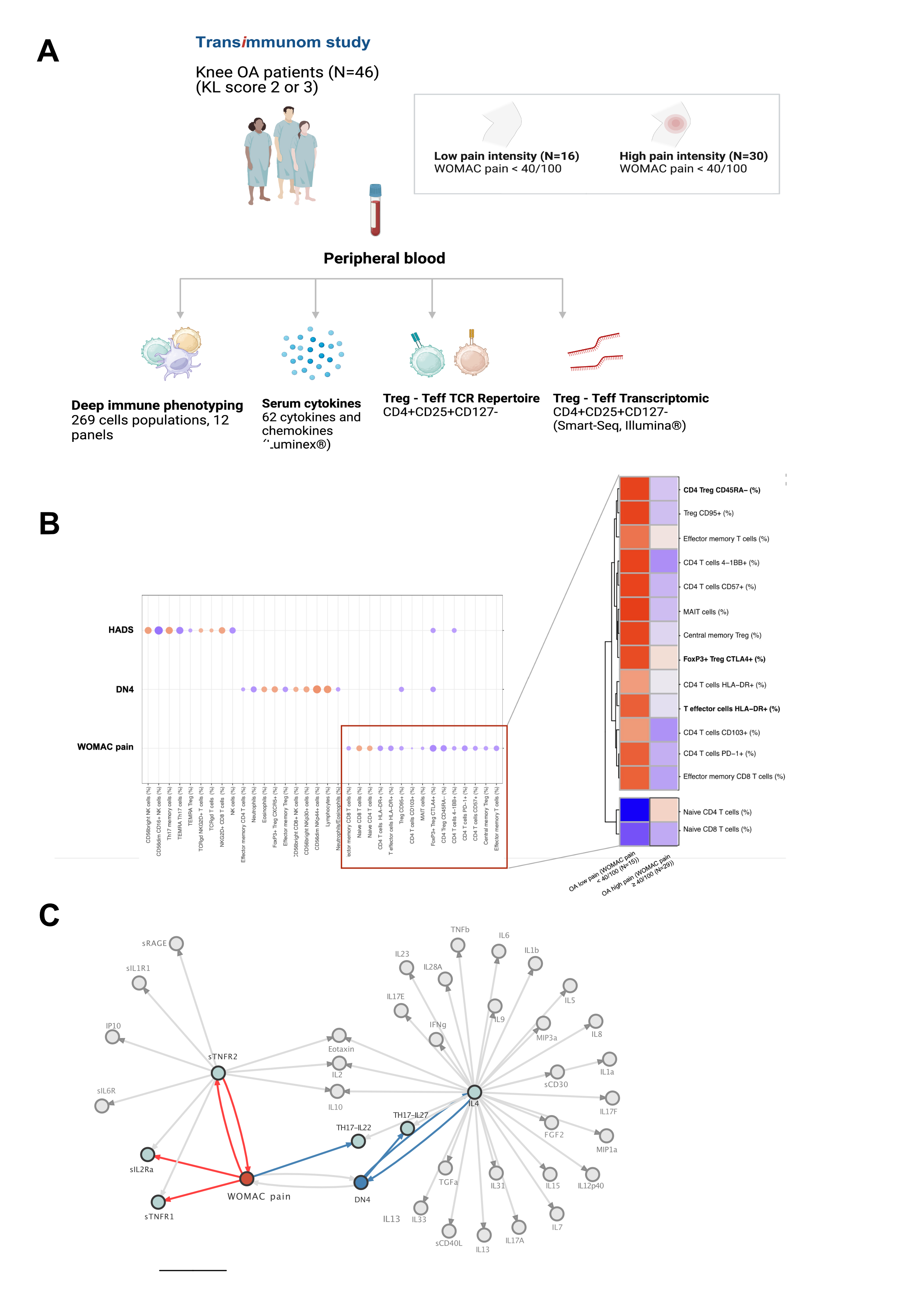
Methods: We enrolled 46 patients with radiographic knee OA as part of the TRANSIMMUNOM clinical trial (NCT02466217). Patients with total knee replacement, Kellgren-Lawrence score of 4, or associated autoimmune disease were excluded. Clinical data were collected for each patient, including WOMAC pain and DN4 scores. Blood deep immunophenotyping was performed using 12 different flow cytometry panels (Duraclone technology, Beckman Coulter). Sixty-two serum cytokines were quantified using the Luminex Multiplex Assay xMAP® Technology. TCR analysis and RNA sequencing were performed on sorted CD4+CD25+CD127- Treg cells and Teffs with a purity > 80%. TCR and RNA sequencing were performed on libraries prepared with SMART-Seq® v4 Ultra® Low Input RNA Kit on high-quality RNA. Differential gene expression analysis using DESEq2 and functional analysis using GO databases were applied.
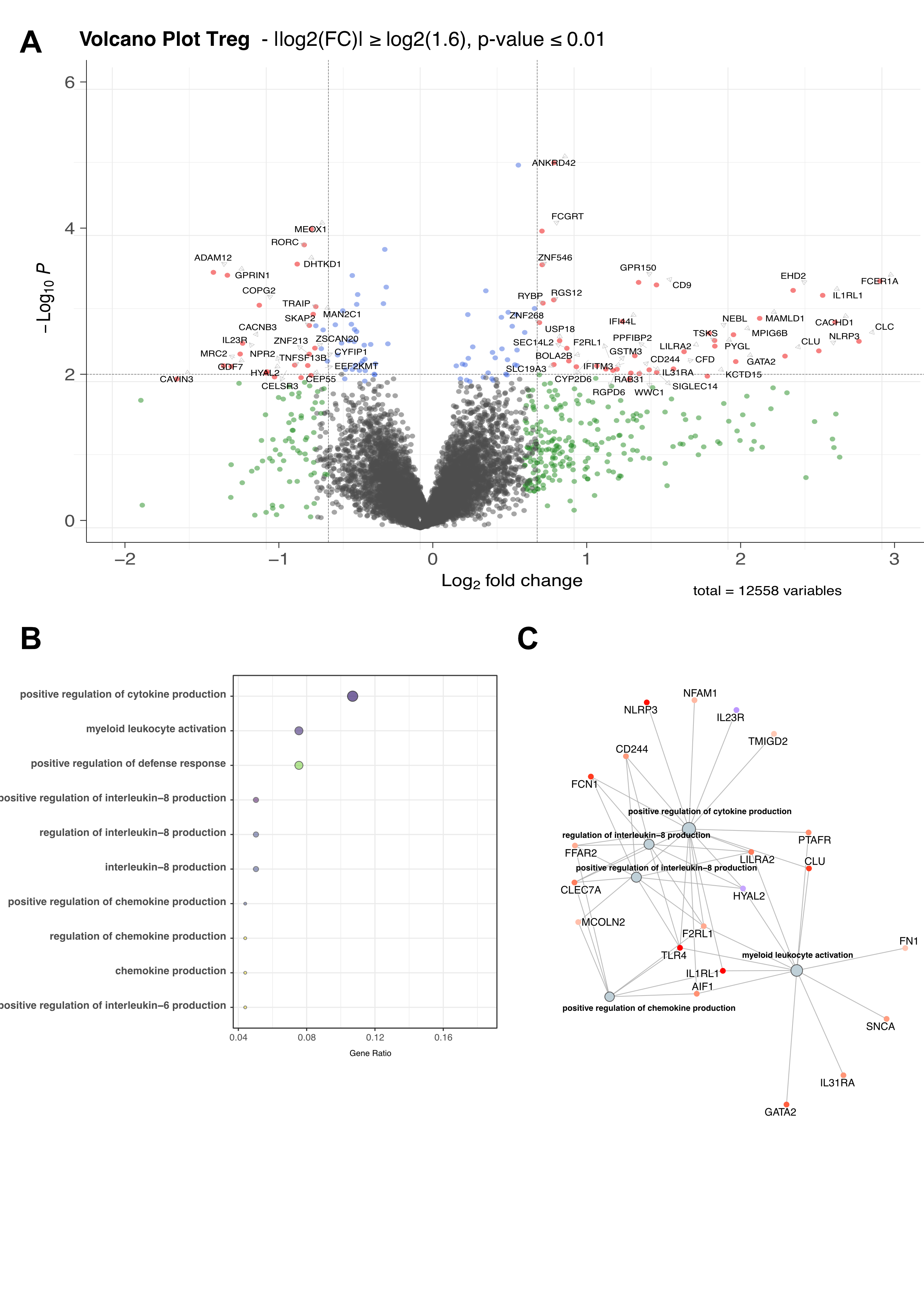
Results: The cohort consisted of 65.2% women with a mean age of 64.8 years and BMI of 29.1 kg/m2. The mean WOMAC pain score was 44.2 (SD=12.7), with no significant difference between patients with low and high pain intensity (WOMAC pain ≥ 40/100) in terms of age, BMI, sex, and radiographic severity. Unsupervised analysis of 269 immune cell based on a deep immunophenotyping identified 19 and 22 cell populations that correlated with WOMAC pain and DN4, respectively (p< 0.05 |r|≥0.2). Among these, four populations related to Treg activation and functionality (FoxP3+CTLA4+, CD4+CD57+, Treg CD95+, and CD4 Treg CD45RA+) were negatively correlated with the WOMAC pain score. Cytokine analysis revealed that soluble factors associated with Treg expansion and activation (sIL2-RA, sTNFR1, sTNFR2, IL-22) were also associated with WOMAC pain score (figure 1). Clonal distribution of Tregs and Teffs cells using T-cell receptor repertoire (TCR) sequencing showed a positive correlation (p< 0.001, r= 0.6) between CD4+ Teff TCR diversity and WOMAC score. Differential gene expression analysis of Tregs between patients with low and high WOMAC pain scores identified 320 upregulated genes, including inflammasome-related genes such as IL1RL1, IL31RA, IFITM3, NLRP3, INFG, and TNFRSF14, and 123 downregulated genes (|log2(FC)|≥log2(1.6), p< 0.01). There was also an overrepresentation and enrichment of GO pathways related to innate immune regulation, cytokine production, IL-8 activation, and IFN-gamma production (p< 0.01) (figure 2).
Conclusion: This study reports an extensive blood immune profiling of knee OA pain, emphasizing systemic dysregulation of Tregs with a potential pro-inflammatory state and loss of functionality. These findings underscore the involvement of the adaptive immune system in OA pain, extending beyond conventional low-grade inflammation paradigms and offering novel pathophysiological insights.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Binvignat M, Marco-Salvador M, Dubois J, Stys P, Courties A, Pitoiset F, Roux A, Barbier M, Lorenzon R, Hassler S, Ribet C, Vantomme h, Adda L, Mhanna V, Coatnoan N, Fourcade G, Didelot V, Barennes P, Minssen L, Aheng C, Bhattacharya S, Marie Y, butte A, Six A, Tchitcheck N, Rosenzwajg M, Berenbaum F, Klatzmann D, Mariotti-Ferrandiz E, Sellam J. Immunological Profiling of Pain in Knee Osteoarthritis: Treg Cells as Potential New Key Players in Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunological-profiling-of-pain-in-knee-osteoarthritis-treg-cells-as-potential-new-key-players-in-symptomatic-knee-osteoarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunological-profiling-of-pain-in-knee-osteoarthritis-treg-cells-as-potential-new-key-players-in-symptomatic-knee-osteoarthritis/