Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Plenary II
Session Type: Plenary Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: We generated a vertically integrated dataset on treatment naïve patients with dcSSc (diffuse Systemic Sclerosis) skin that includes bulk RNA-seq, single nuclei multiome, and paired spatial transcriptomic analyses to comprehensively describe the molecular changes in these individuals. Given the well-established immune-fibroblast axis in SSc, we sought to understand the dynamics between macrophages and fibroblasts to identify key pathways driving the disease.
Methods: Skin biopsies and paired PBMC samples were collected from 10 treatment-naïve individuals diagnosed with dcSSc, along with 4 age- and sex- matched healthy controls (HC). Multiple biopsies were taken: one for bulk RNA-seq analysis and molecular subtype assignment, another for single nuclear RNA-seq and ATAC-seq (snMultiome), and the third for spatial transcriptomics. 10X Genomics platforms were used for sequencing, including 10X Visium. Data were analyzed in R, using packages such as Signac, Seurat, PRECAST, CARD, and CellChat. SSc-derived self-assembled (SA) 3D skin-like tissue models were used to test response to therapeutics in vitro.
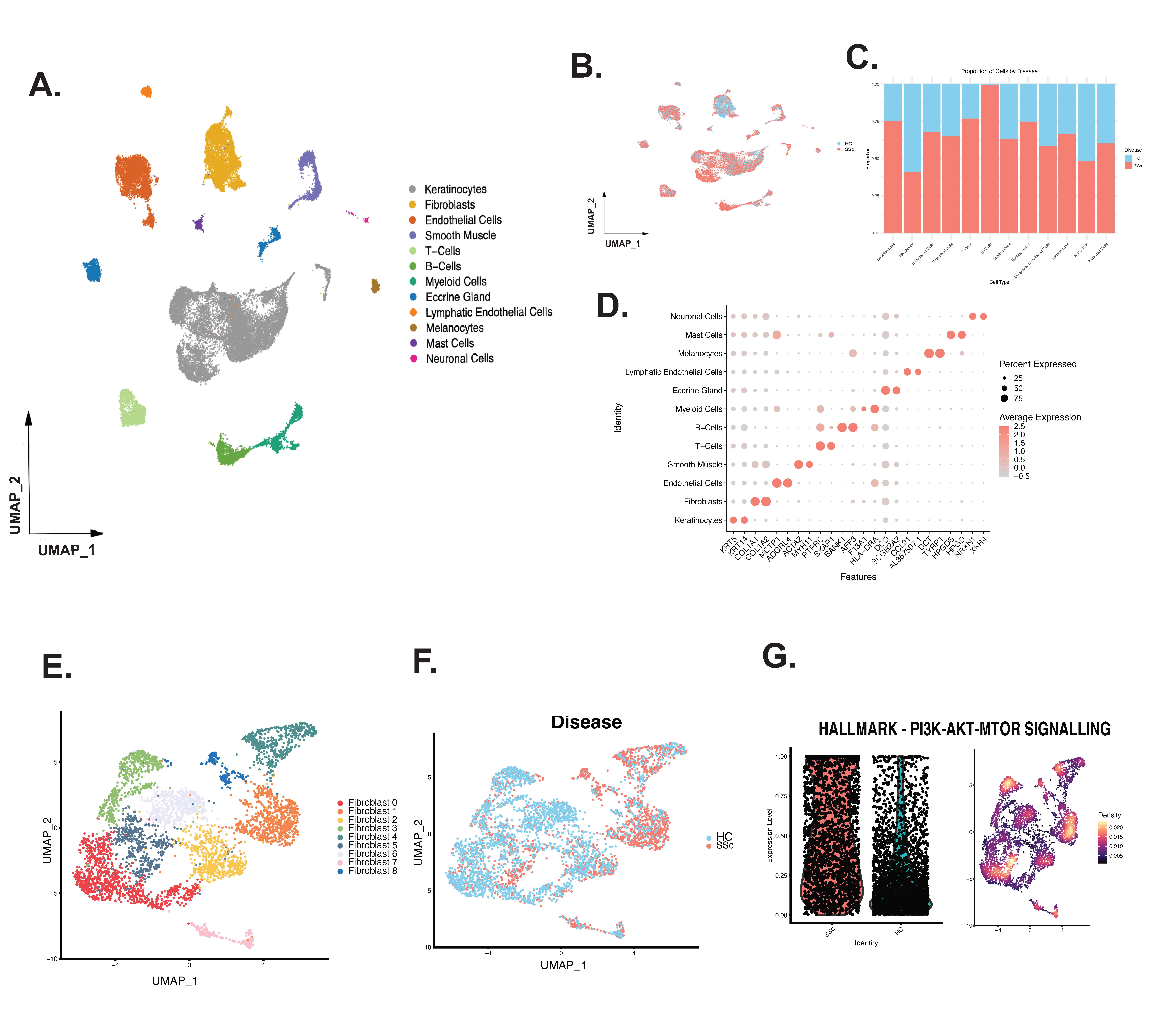
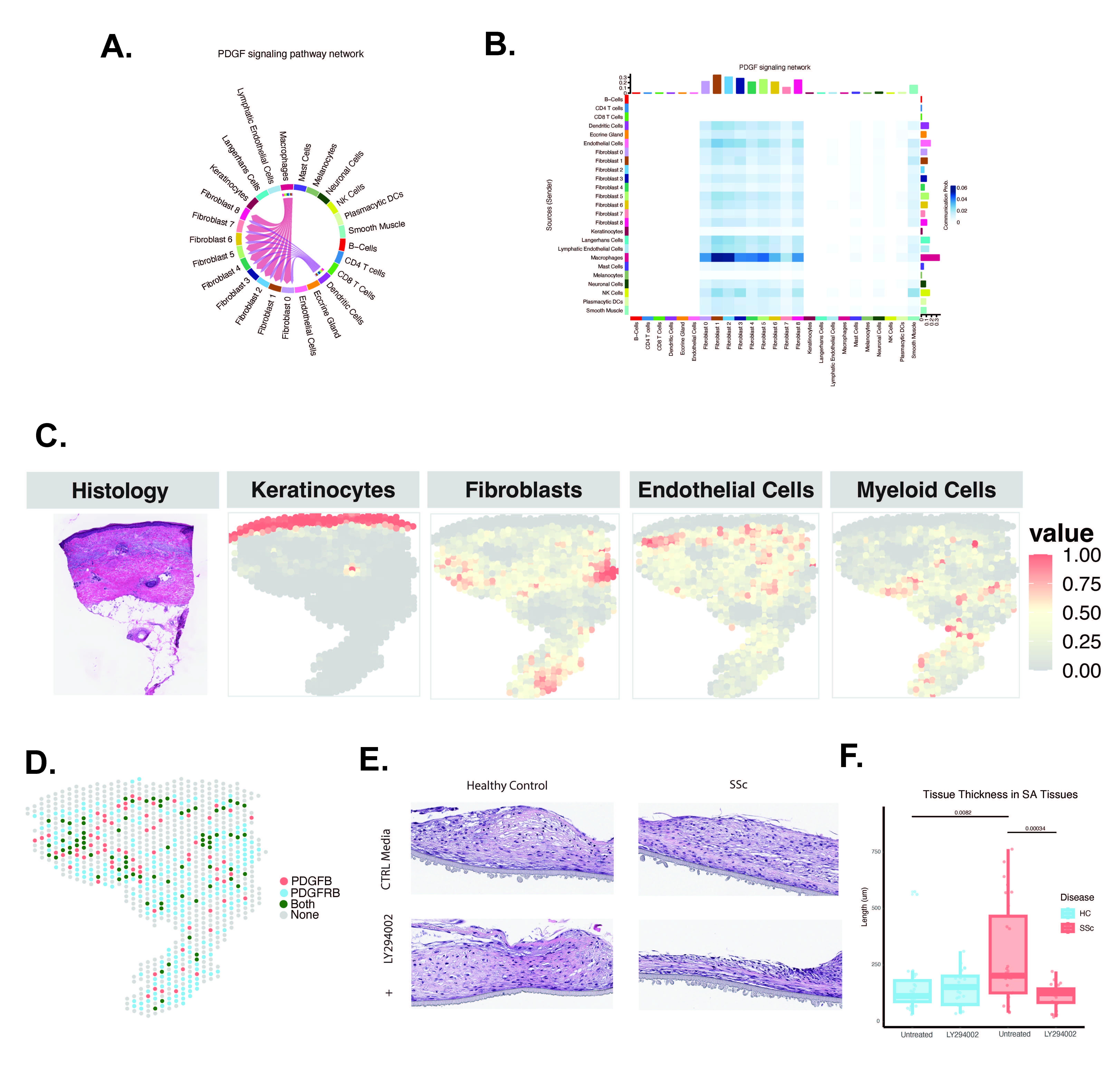
Results: We integrated multiple data types in a cohort of 10 individuals with untreated, early-stage dcSSc. SnMultiome was performed on all cell types; cell clustering showed major population shifts for B-cells and T-cells in SSc samples (Fig 1 A-D). Fibroblast subclustering and pathway analyses showed that SSc patient fibroblasts exhibited enriched PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway expression largely driven by PDGF and other growth factor signaling (Fig 1 E-G). Transcription factors specific to the PI3K pathway, SRF and Stat5a, were enriched in inflammatory, SSc-dominated fibroblast clusters characterized by high expression of C7, PLA2G2A, CXCL12, and APOE. Ligand-receptor analysis identified signaling pathways between immune cells and fibroblasts. Macrophages had the highest probability of secreting PDGF to interact with the inflammatory SSc-dominant fibroblast subclusters (Fig 2 A-B). Spatial transcriptomic analyses showed that samples with high myeloid cell infiltration had increased PDGF secretion by innate immune cells, matching the increased expression of PDGFR in fibroblasts (Fig 2 C-D). Self-assembled 3D skin-like tissues constructed from SSc fibroblasts treated with a PI3K inhibitor (LY294002) showed significantly reduced tissue thickness post-treatment (Fig 2 E-F). In contrast, tissues constructed from healthy control cells produced thinner tissues and did not show a significant reduction in thickness after treatment with the PI3K inhibitor.
Conclusion: Vertical integration of multiomic data provides unique insights into the molecular interactions between cell types in early, untreated SSc skin. Increased PDGF and downstream PI3K activity is a hallmark of SSc skin fibrosis. PI3K inhibition reduces tissue thickness, providing a specific druggable target for disrupting the immune-fibrosis axis in SSc skin.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jarnagin H, Popovich D, Parvizi R, Gedert R, Tsoi L, Wasikowski R, Gong Z, Morrisson M, Perreard L, Kolling IV F, Khanna D, Gudjonsson J, Whitfield M. Single Nuclei Multiome and Spatial Transcriptomic Analysis of Early, Untreated SSc Skin Identifies Signaling Interactions Between Macrophages and Fibroblasts [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/single-nuclei-multiome-and-spatial-transcriptomic-analysis-of-early-untreated-ssc-skin-identifies-signaling-interactions-between-macrophages-and-fibroblasts/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/single-nuclei-multiome-and-spatial-transcriptomic-analysis-of-early-untreated-ssc-skin-identifies-signaling-interactions-between-macrophages-and-fibroblasts/