Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The primary objective of this study was to comprehensively analyze the clinical characteristics of immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM) and develop a reliable recurrence prediction model to facilitate timely intervention and improve patient outcomes.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on patients with IMNM who were treated at West China Hospital of Sichuan University between January 1, 2015, and October 1, 2023. Based on predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria, patients were carefully screened. Out of an initial pool of 256 patients, 200 were selected after rigorous evaluation. Detailed clinical information was gathered and analyzed to compare various IMNM subtypes and to distinguish between recurrent and non-recurrent cases. To identify factors predicting IMNM recurrence, a Cox proportional hazards model was utilized. The prediction model, once developed, underwent internal validation through Bootstrap methods. Its performance was evaluated using metrics such as the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), calibration curves, and decision curve analysis (DCA).
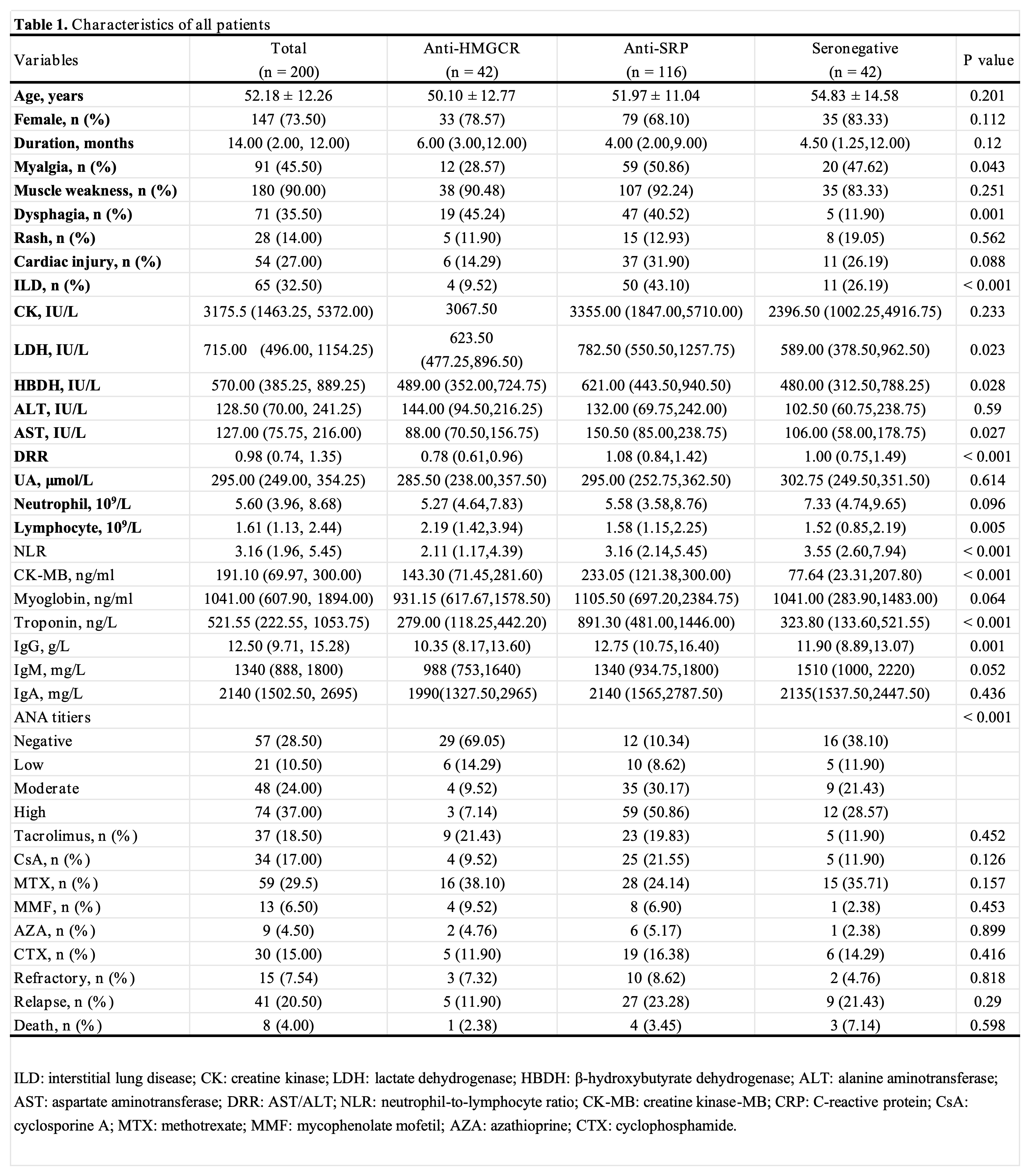
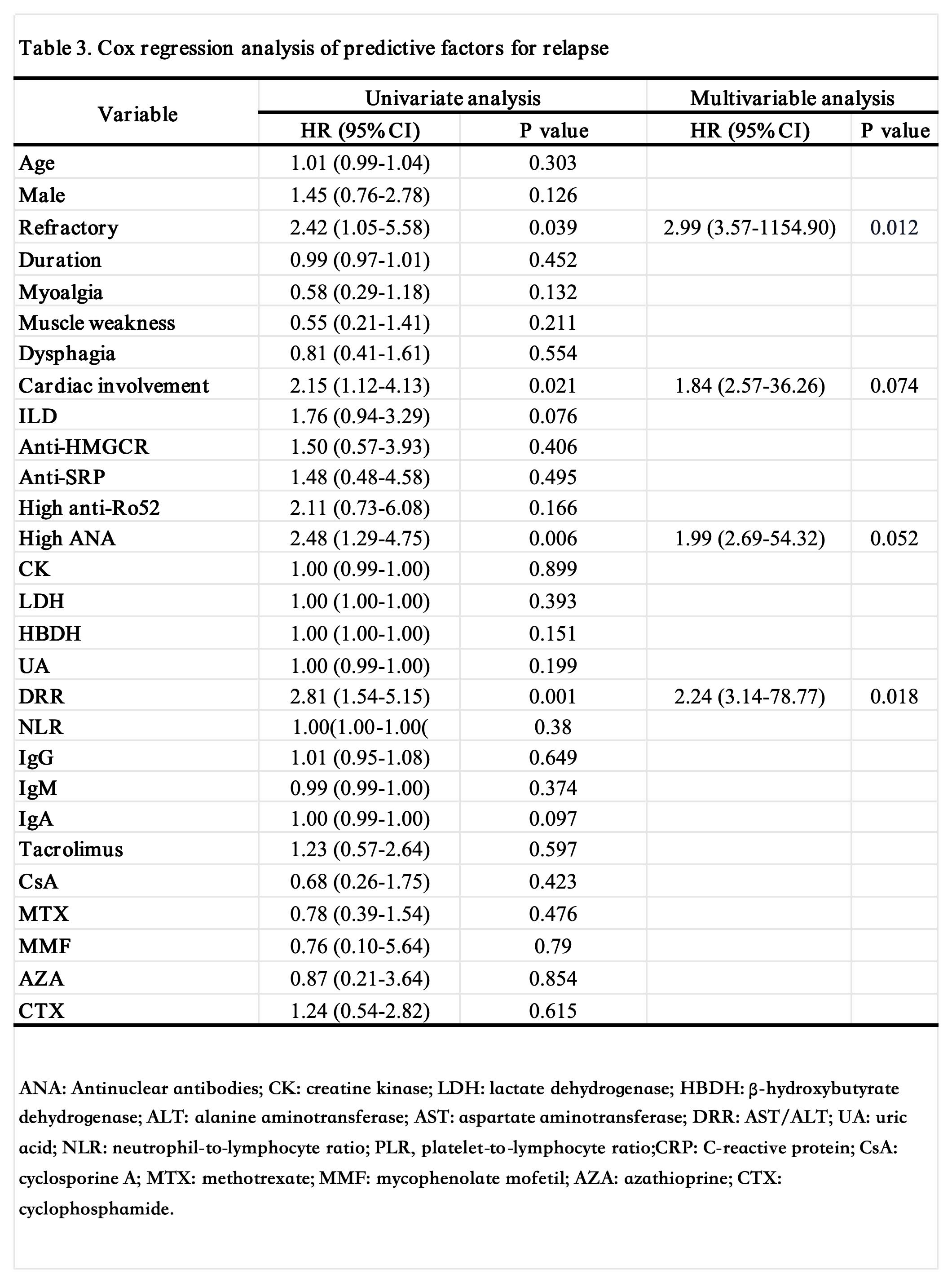
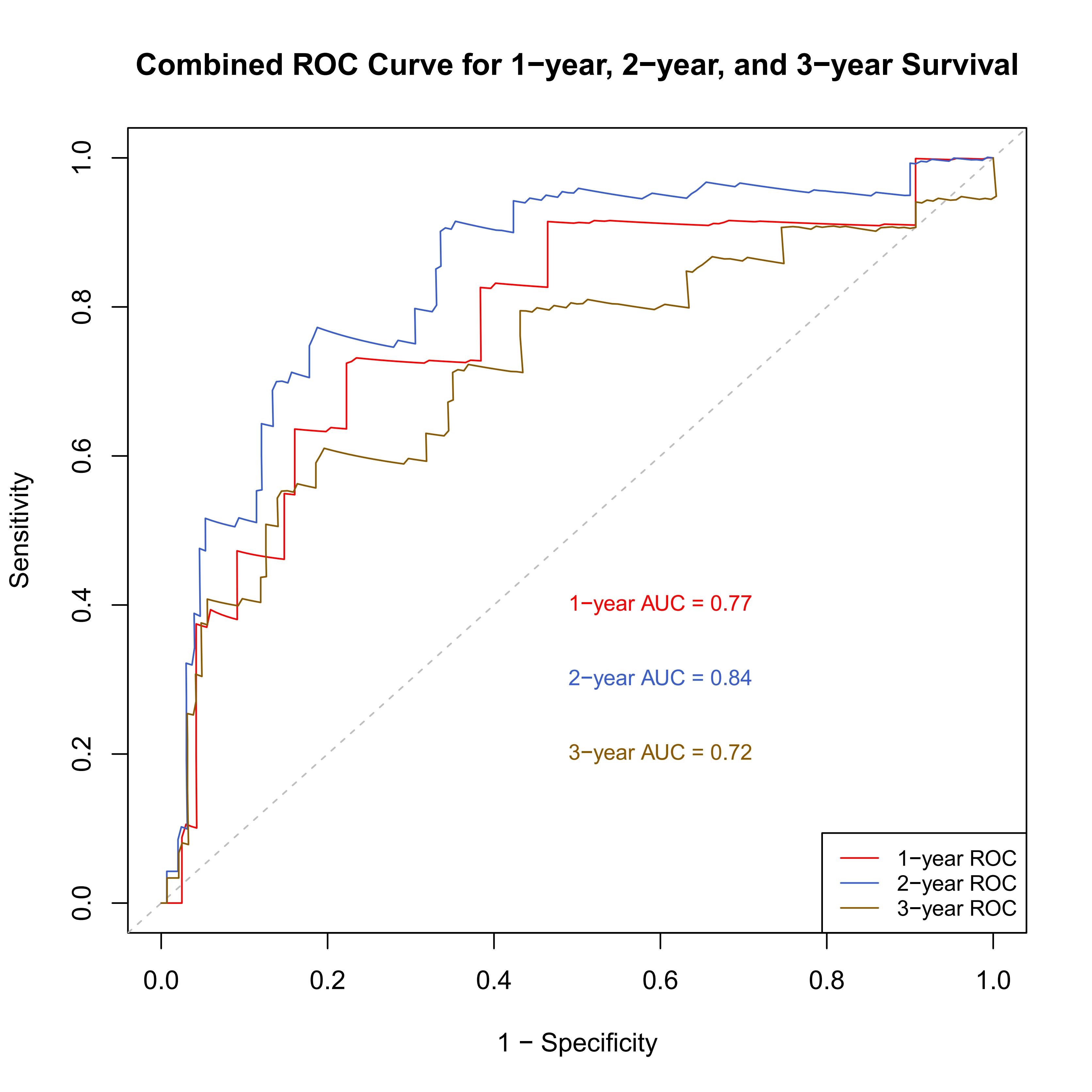
Results: Significant differences in clinical features were observed across different IMNM subtypes. Anti-SRP antibody-positive patients exhibited higher rates of muscle pain, dysphagia, and interstitial lung disease (ILD) with elevated levels of LDH, HBDH, and DRR (AST/ALT). In contrast, anti-HMGCR antibody-positive patients showed a higher rate of ANA negativity, while seronegative patients displayed higher NLR levels. Among recurrent patients, the ILD rate and DRR levels were significantly higher, with lower lymphocyte levels. The Cox model identified cardiac involvement, high ANA titer, treatment refractory, and high DRR levels as independent predictors of IMNM recurrence. The internally validated recurrence prediction model demonstrated robust performance with an AUC of 0.77 (one year), 0.84 (two years), and 0.74 (three years) and a Bootstrap mean C-index of 0.731. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis revealed a significantly lower cumulative survival time for patients with cardiac involvement, high ANA, recurrence, and high DRR levels.
Conclusion: This study provides crucial insights into the heterogeneous clinical manifestations of IMNM and develops a clinically relevant recurrence prediction model. The identified predictors of recurrence offer valuable information for risk stratification and personalized treatment plans. The validated model represents a useful tool for clinicians in optimizing management strategies and improving long-term outcomes for IMNM patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cui B, Liu H, Yin G, Xie Q. Clinical Characterization and Recurrence Prediction Model for Immune-Mediated Necrotizing Myopathy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-characterization-and-recurrence-prediction-model-for-immune-mediated-necrotizing-myopathy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-characterization-and-recurrence-prediction-model-for-immune-mediated-necrotizing-myopathy/