Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
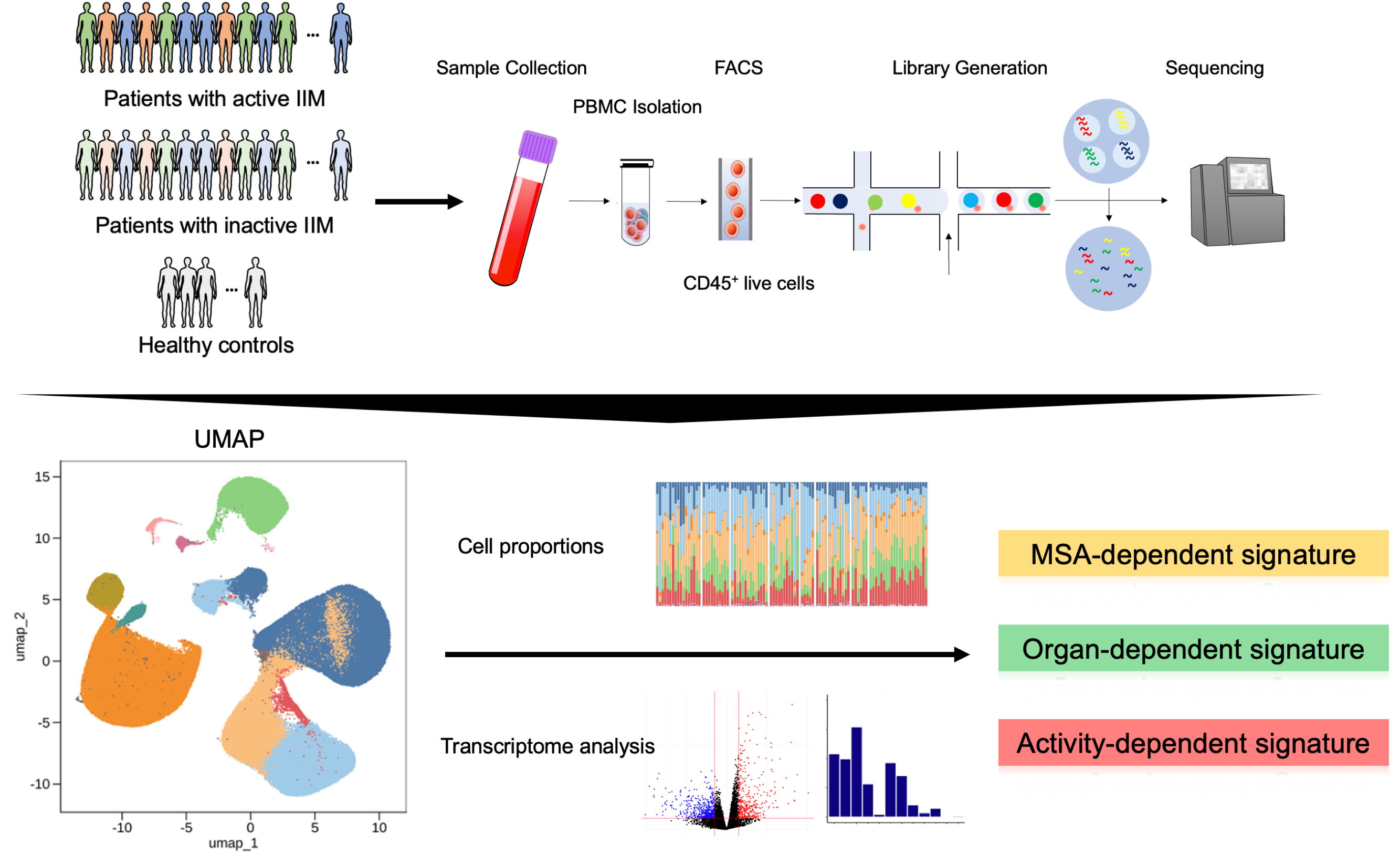
Background/Purpose: Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs) are heterogeneous diseases, making it crucial to identify distinct pathological processes to improve a treatment strategy. Transcriptomic analyses have revealed increased type I interferon signatures in dermatomyositis and oxidative phosphorylation in antisynthetase syndrome (1). However, differences among disease phenotypes and activity states remain unclear. This study aims to elucidate these variations at a single-cell resolution, providing insights into disease establishment and exacerbation in IIM patients.
Methods: We collected peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from myositis-specific antibody (MSA)-positive IIM patients, including those positive for antibodies against anti-aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (ARS), melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5), Mi-2, and transcriptional intermediary factor 1-γ (TIF1-γ), as well as healthy controls (HC) from multiple centers across Japan (Figure 1). We conducted single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) on CD45+ live cells using the ‘Chromium Single Cell Gene Expression’ platform (10X Genomics), and the libraries were sequenced on the Illumina Novaseq 6000. We evaluated the International Myositis Assessment & Clinical Studies Group Disease Activity Core Set Measures to define disease activity. We explored transcriptomic signatures associated with disease activity and clinical manifestations by conducting transcriptomic analyses.
Results: scRNA-seq was performed on over 480,000 cells from 77 IIM patients and 23 age- and sex-matched HCs. Principal component analysis (PCA) revealed that the cell proportion of CD14+ monocytes had the highest factor loading in PC1. After reclustering of myeloid cell subsets, RNASE2high and MX1high CD14+ monocytes exhibited higher proportions in active IIM patients within the five clusters of classical monocyte subsets. Additionally, differentially expressed gene (DEG) analysis identified type I interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) when comparing active vs. non-active patients and non-active vs. HC, particularly in the monocyte subsets of anti-MDA5 antibody-positive patients, suggesting ISG association with both disease exacerbation and establishment. Gene set variation analysis showed that active disease was characterized by a shift towards pro-inflammatory profiles, with elevated expression of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Cellular compositions of RNASE2high CD14+ monocytes were correlated with multiple components of the Myositis Disease Activity Assessment Tool (MDAAT) across all IIM phenotypes. Specifically, MX1high CD14+ monocytes were correlated with skin MDAAT in dermatomyositis patients.
Conclusion: Our study identified distinct disease-state and disease-activity signatures, particularly highlighting the roles of monocytes and ISGs in disease exacerbation and establishment. These findings enhance our understanding of IIM pathogenesis and could inform targeted therapy development.
Reference
[1] Sugimori Y, et al. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2023;5:93-102
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Izuka S, Komai T, Yuuki H, Ueda I, Fujimoto M, Fukui H, Takeshita M, Umezawa N, Yasuda S, Yasuda M, Fujieda Y, Atsumi T, Iwasaki T, Morinobu A, Kondo Y, Matsumoto I, Kawamoto T, Matsushita M, Tamura N, Iwamoto T, Nakajima H, Yoshida K, Isozaki T, Yajima N, Sakurai K, Kawahata K, Kamata Y, Sato K, Tanaka Y, Suzuki A, Yamamoto K, Okamura T, Fujio K. Comprehensive Single-cell Profiling of Diverse Circulating Immune Cells in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Identifies a Novel Pathogenic Subset of Monocytes [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comprehensive-single-cell-profiling-of-diverse-circulating-immune-cells-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-identifies-a-novel-pathogenic-subset-of-monocytes/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comprehensive-single-cell-profiling-of-diverse-circulating-immune-cells-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-identifies-a-novel-pathogenic-subset-of-monocytes/