Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Abstracts: B Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease I
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a rare, systemic, fibroinflammatory disease characterized by unpredictable and recurring flares, leading to organ damage and decreased quality of life. The role of B cells in the pathophysiology of IgG4-RD and existing clinical experience suggest that B cell depletion may be an effective therapeutic avenue. Inebilizumab (INEB) is a humanized, glycoengineered, CD19-directed, monoclonal antibody that depletes B cells effectively in a targeted manner. The aim is to evaluate the efficacy and safety of inebilizumab monotherapy for reducing the risk of flare in adult participants with IgG4-RD.
Methods: The MITIGATE trial (NCT04540497), conducted at 80 sites in 22 countries, enrolled adult patients who met the ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for IgG4-RD with a score ≥20. Key eligibility criteria included a history of multiorgan disease and active disease at screening. Participants were stratified based on newly diagnosed vs. recurrent disease. Randomization was 1:1 with INEB 300 mg IV or Placebo (PBO) treatment on Day 1, 15, and Week 26 of the 52 week Randomized Controlled Period (RCP). Corticosteroids were normalized to 20 mg/day prednisone at the time of randomization and were tapered to discontinuation at the end of study Week 8. An IgG4-RD flare was defined as new or worsening signs and symptoms of IgG4-RD activity that met one or more organ-specific flare criteria developed for this study. The primary endpoint was time to first adjudication committee (AC)-determined and investigator-treated IgG4-RD flare during the RCP. Key secondary endpoints included annualized flare rate during the RCP and the proportion of participants achieving flare-free, treatment-free complete remission or corticosteroid-free complete remission at Week 52. Safety was evaluated.
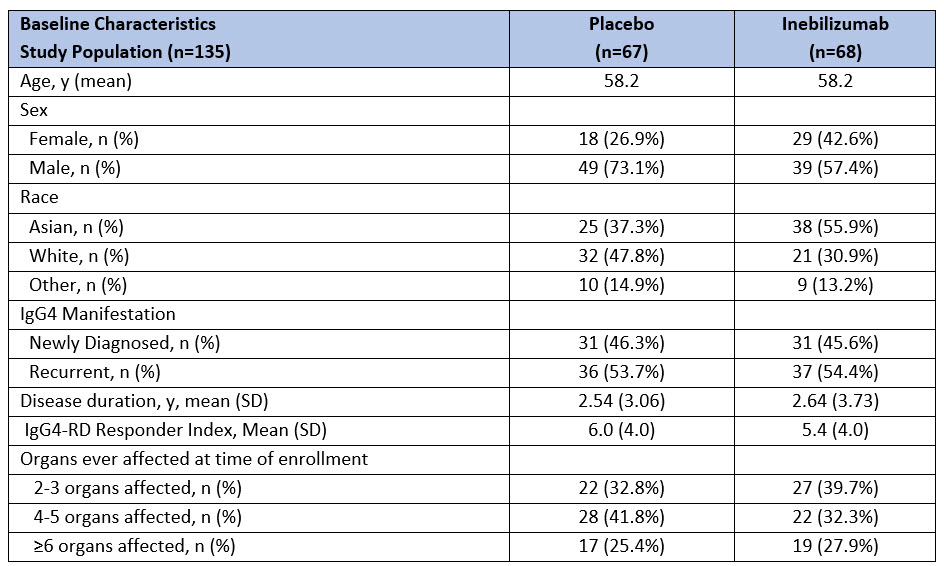
Results: 135 subjects were randomized and received at least one dose of INEB (n=68) or PBO (n=67). Baseline demographics and disease characteristics were generally balanced between those receiving INEB and PBO (Table 1).
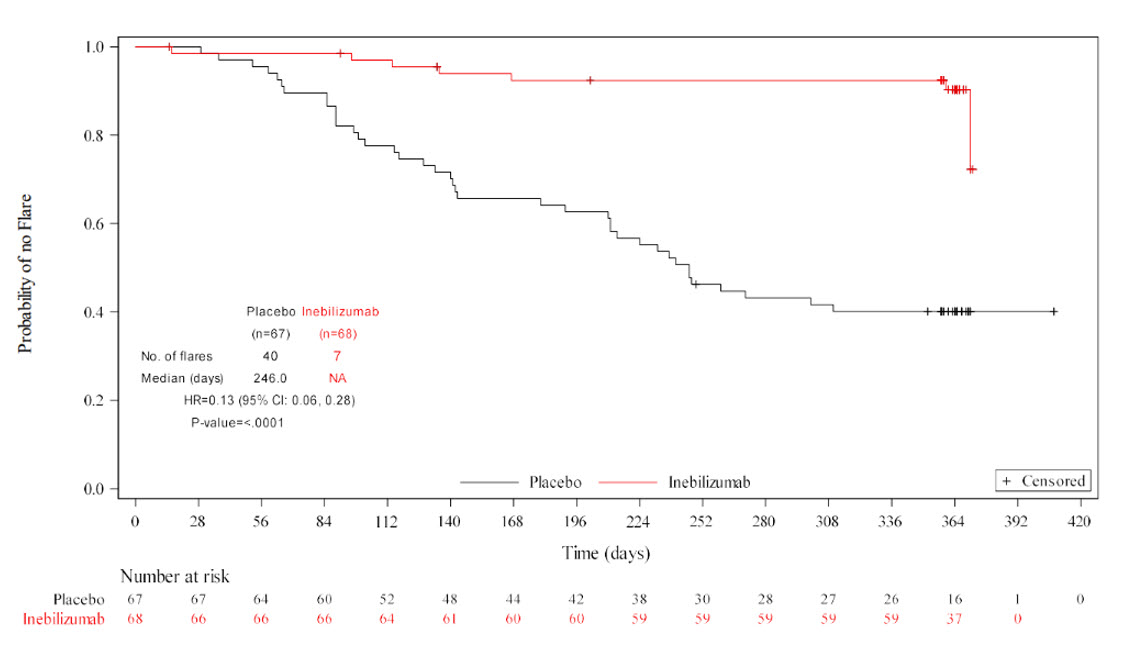
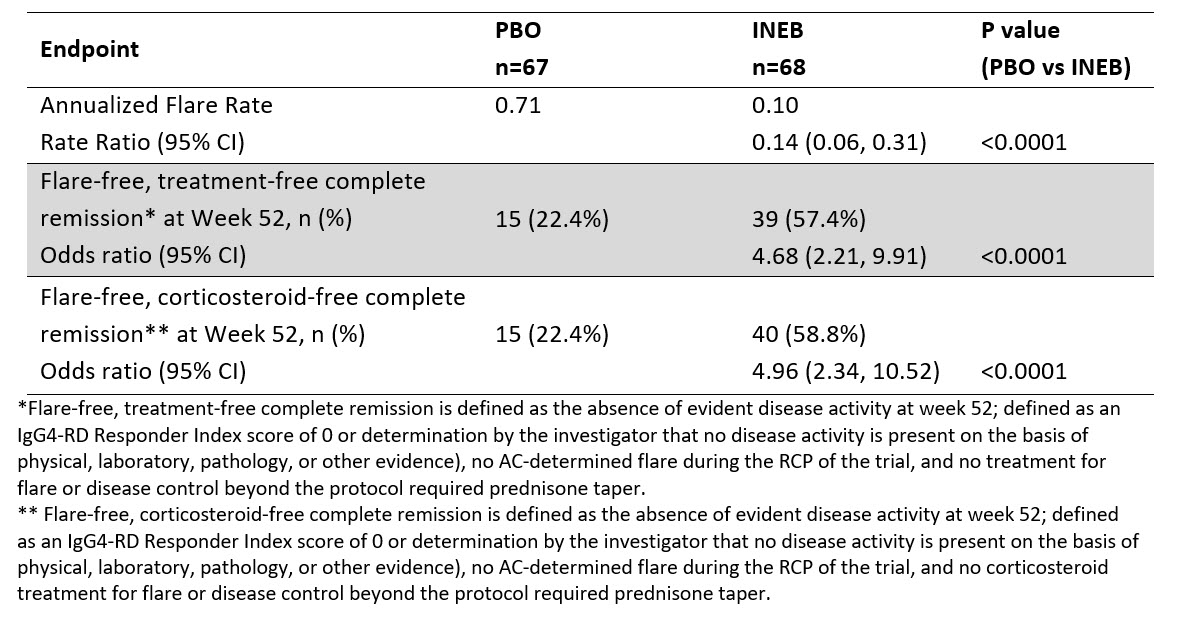
The primary endpoint was met, with INEB treatment significantly reducing the risk of IgG4-RD flares compared to PBO during RCP (hazard ratio 0.13; 95% CI: 0.06, 0.28; p< 0.0001) (Figure 1). The statistically significant treatment effect of INEB compared to PBO was seen for all key secondary endpoints (Table 2).
During the RCP, 66 (97.1%) INEB and 66 (98.5%) PBO participants had ≥1 treatment emergent adverse event (TEAE), the most frequent ( >10%) were COVID-19 (16 [23.5%] INEB, 13 [19.4%] PBO), lymphopenia (11 [16.2%] INEB, 6 [9.0%] PBO), and UTI (8 [11.8%] INEB, 4 [6.0%] PBO). No subjects died; no SAE occurred in >1 subject. AEs of special interest included infusion related reactions in 3 (4.4%) INEB and 5 (7.5%) PBO and serious and/or opportunistic infections in 6 (8.8%) INEB and 2 (3.0%) PBO. In INEB participants, serious infections included COVID-19, appendicitis, and diverticulitis, and opportunistic infections were herpes zoster.
Conclusion: The MITIGATE trial, the first randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study ever conducted in IgG4-RD, establishes the safety and efficacy of CD19-targeted B cell depletion with inebilizumab in IgG4-RD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Stone J, Culver E, Khosroshahi A, Zhang W, Della Torre E, Okazaki K, Tanaka Y, Löhr M, Schleinitz N, Dong L, Umehara H, Lanzillotta M, Wallace Z, Ebbo M, Webster G, Martinez Valle F, Nayar M, Rebours V, Perugino C, Dong X, Wu Y, Rampal N, Cimbora D. A Phase 3, Randomized, Double-Blind, Multicenter, Placebo-Controlled Study of Inebilizumab in IgG4-Related Disease (MITIGATE): Primary Efficacy and Safety Findings [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-multicenter-placebo-controlled-study-of-inebilizumab-in-igg4-related-disease-mitigate-primary-efficacy-and-safety-findings/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-multicenter-placebo-controlled-study-of-inebilizumab-in-igg4-related-disease-mitigate-primary-efficacy-and-safety-findings/