Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: British Isles Lupus Assessment Group (BILAG)-based Composite Lupus Assessment (BICLA) and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Responder Index 4 (SRI4) responses are the most common primary endpoints in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) randomized controlled trials (RCTs). In this post hoc analysis of 2 SLE RCTs, we examined concordance and reasons for discordance in BICLA and SRI4 outcome measures in patients with SLE receiving placebo and standard of care.
Methods: This analysis included data from patients with evaluable BICLA and SRI4 responses in the placebo arms of the EXPLORER (n=87; NCT00137969) and ATHOS (n=80; NCT02908100) RCTs. Disease activity was measured using BILAG and SELENA-SLEDAI in EXPLORER and BILAG-2004 and SLEDAI-2K in ATHOS. For this analysis, patients were classified as either responders or nonresponders based on the BICLA and SRI4 composite indices and the presence of an intercurrent event. Concordance and discordance frequencies between BICLA and SRI4 were determined.
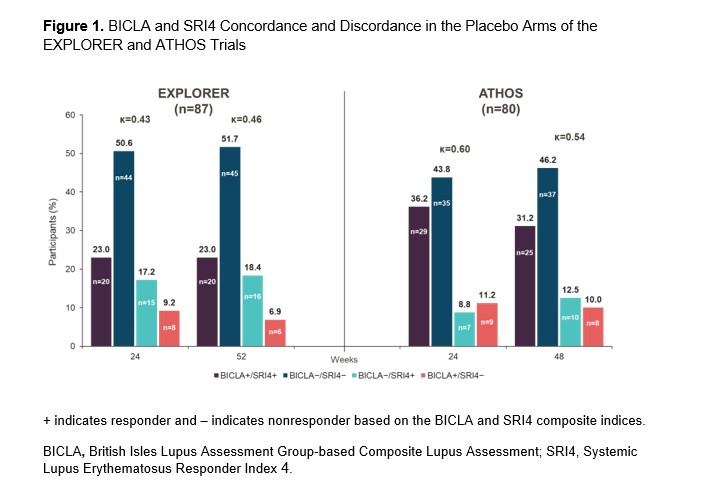
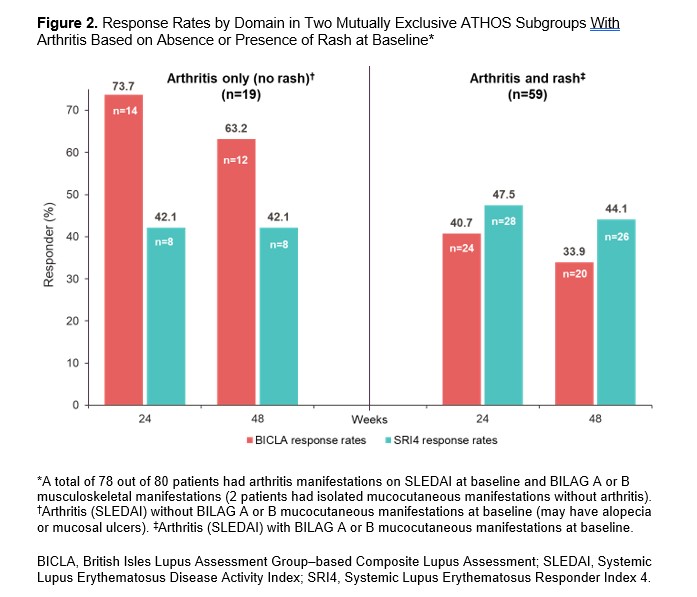
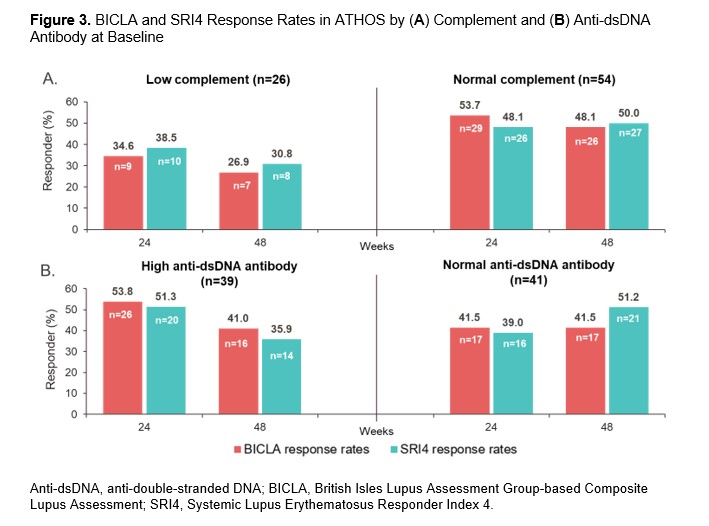
Results: In EXPLORER, BICLA placebo response rates were lower than SRI4 response rates (29.9% vs 41.4% at Week 52, respectively), whereas in ATHOS, BICLA and SRI4 placebo response rates were similar (41.2% vs 43.8% at Week 48). At Weeks 24 and 48/52, BICLA and SRI4 overall concordance (Cohen’s κ score) was 0.43 and 0.46 in EXPLORER and 0.60 and 0.54 in ATHOS, respectively (Figure 1). In EXPLORER at Week 52, BICLA+/SRI4− and BICLA−/SRI4+ discordance was 6.9% and 18.4%, respectively. In ATHOS at Week 48, BICLA+/SRI4− and BICLA−/SRI4+ discordance was low at 10.0% and 12.5%, respectively. In an analysis of ATHOS subgroups based on presence or absence of rash at baseline, BICLA response was higher at Week 52 in patients with arthritis only than in those with arthritis and mucocutaneous co-manifestations (63.2% vs 33.9%, respectively; Figure 2). BICLA+/SRI4− discordance doubled in patients with stable arthritis on SLEDAI (21.1% in arthritis-only subgroup vs 10.0% of all patients at Week 48). BICLA−/SRI4+ discordance was higher in patients with improving arthritis and co-manifestations of stable rash (arthritis and rash subgroup; 16.9%) than in all patients (12.5%) at Week 48. Both BICLA and SRI4 response rates at Week 48 were lower in patients with low vs normal complement at baseline (26.9% vs 48.1% and 30.8% vs 50.0%, respectively; Figure 3). SRI4 response rates at Week 48 were lower in patients with high vs normal anti-dsDNA antibodies at baseline (35.9% vs 51.2%, respectively). BICLA−/SRI4+ and BICLA+/SRI4− discordance was lower in patients with low vs normal complement at baseline (8% vs 15% and 4% vs 13%, respectively).
Conclusion: Newer versions of the BILAG and SLEDAI disease activity indices led to higher BICLA/SRI4 concordance in ATHOS than in EXPLORER. However, BICLA/SRI4 discordance is notable in ATHOS and originates from the gradual vs categorical nature of the tools. Patients with single-organ manifestations of arthritis showed higher rates of BICLA response, resulting in higher BICLA+/SRI4− discordance. Active serology at baseline was associated with improved BICLA/SRI4 concordance and a lower placebo arm response rate, a key element needed to demonstrate a compelling treatment effect of an investigational drug.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Askanase A, Vital E, Meier O, Turchetta A, Mao H, Maller J, Terres J, Dall'Era M. Evaluating the Concordance Between SRI4 and BICLA Using Placebo Data from Randomized Controlled Trials of Patients with Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluating-the-concordance-between-sri4-and-bicla-using-placebo-data-from-randomized-controlled-trials-of-patients-with-active-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluating-the-concordance-between-sri4-and-bicla-using-placebo-data-from-randomized-controlled-trials-of-patients-with-active-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/