Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: An elevated type I interferon gene signature (IFNGS) is associated with more active disease in patients with LN.1 Anifrolumab, a type I interferon receptor antagonist, has shown therapeutic potential in patients with LN.2 Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses in patients with SLE found that anifrolumab treatment modulated multiple immunoregulatory pathways.3 Here, we evaluated the immunomodulatory impact of anifrolumab treatment vs placebo alongside standard therapy on the plasma proteome of patients with LN in the phase 2 TULIP-LN trial.
Methods: In the randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind 2-year TULIP-LN trial (NCT02547922), adults with SLE and biopsy-proven active LN (Class III/IV [±V]) received either intravenous basic regimen (BR; 300 mg) or intensified regimen (IR; 900 mg for the first 3 doses, 300 mg thereafter) anifrolumab or placebo every 4 weeks plus standard therapy (mycophenolate mofetil and glucocorticoids); primary endpoint was assessed at Week 52.2 Plasma samples were collected at Weeks 0 (baseline), 12, 24, and 52 and concentrations of 2,943 proteins were measured with the Olink® Explore 3072 high-throughput protein biomarker discovery platform; relative protein abundance is presented in Normalized Protein eXpression (NPX) values. The impact of anifrolumab BR or IR compared with placebo on protein levels was evaluated using a linear mixed effects model, adjusted for baseline type I IFNGS (high/low) in blood and 24-hour urine-protein creatinine ratios >3/≤3 mg/mg. Differentially regulated Gene Ontology-Biological Process pathways were identified using string-db. P-values were adjusted for multiple testing using the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure.
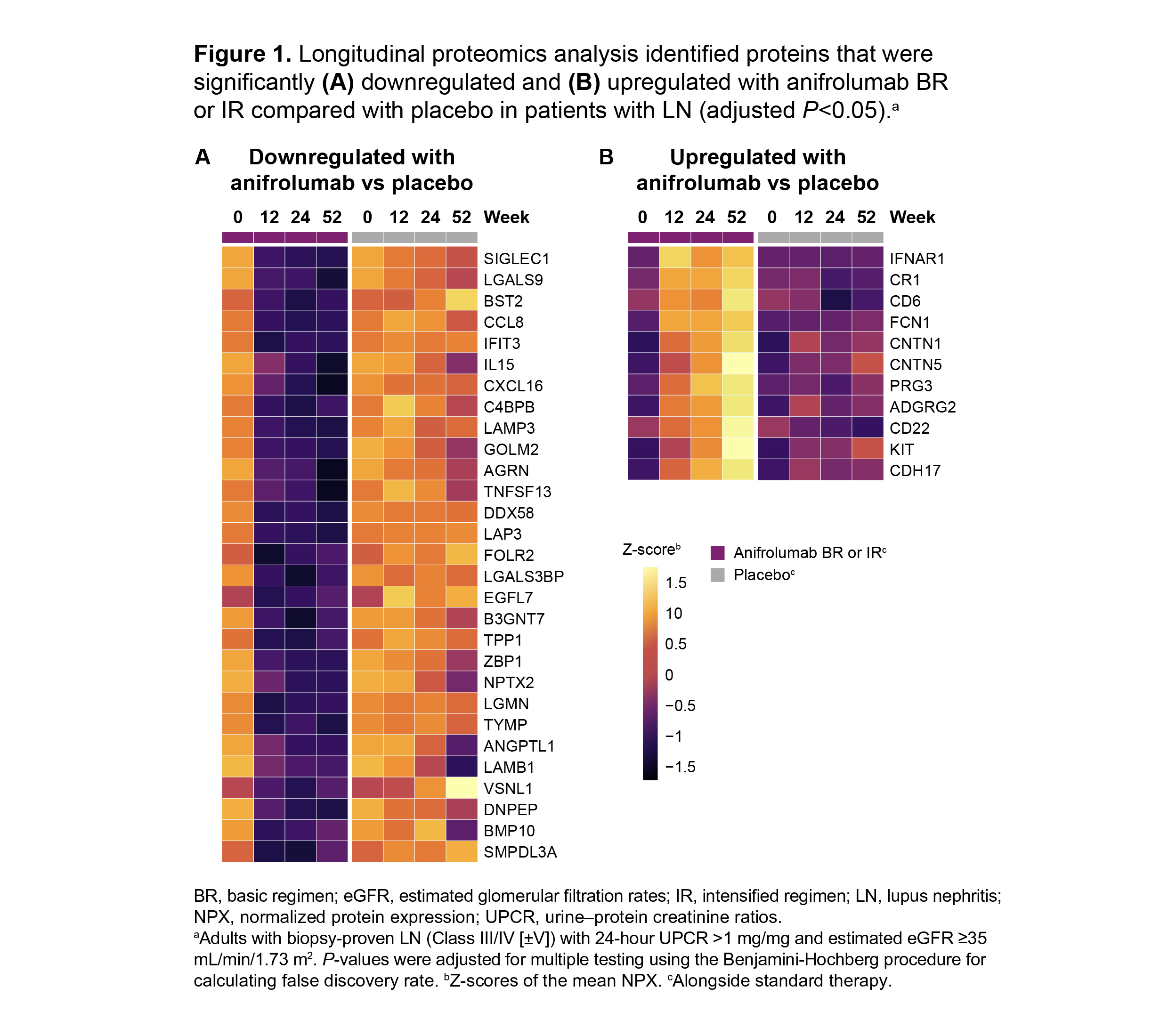
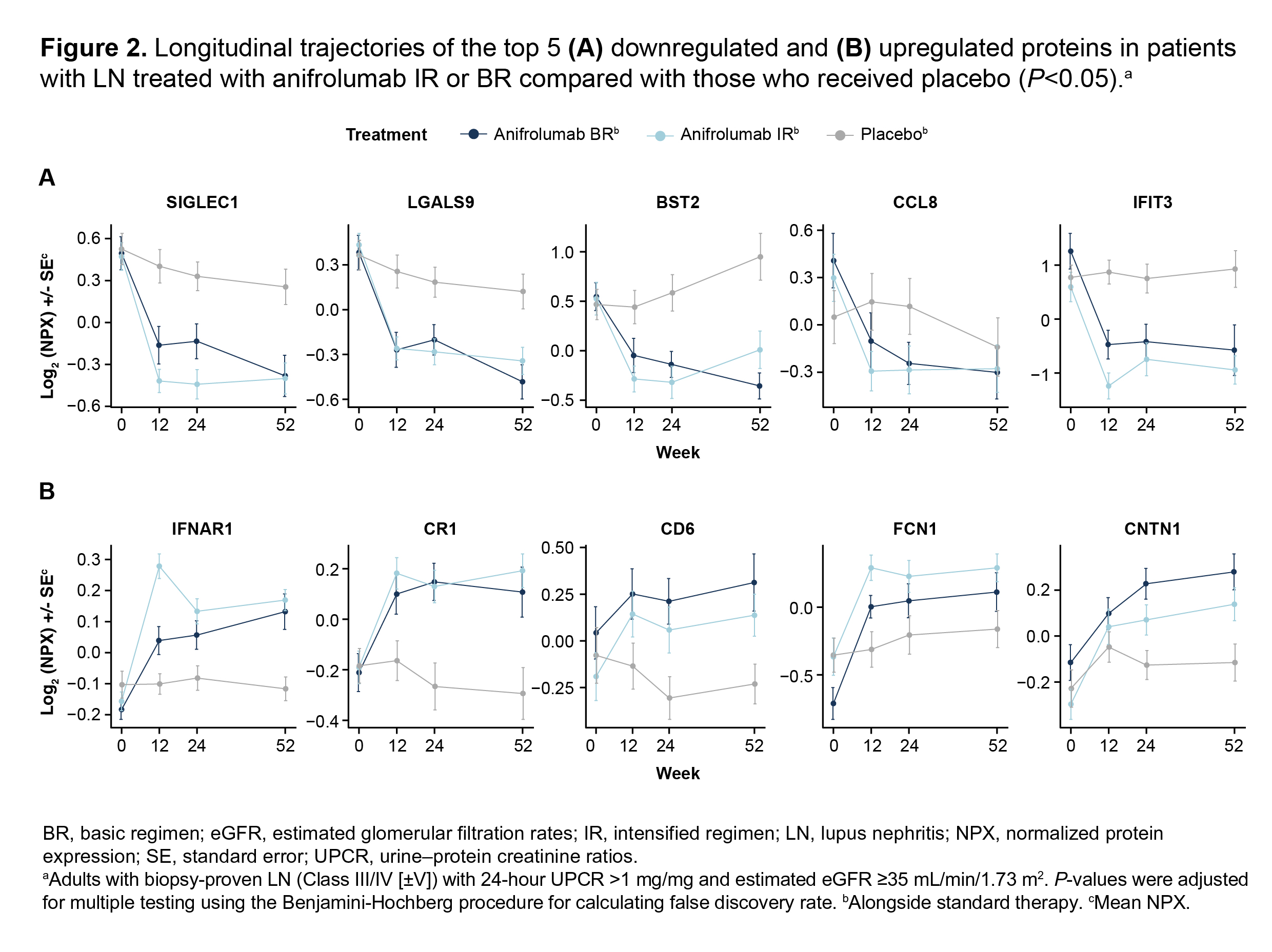
Results: From baseline to Week 52, 45 plasma proteins were significantly modulated in patients with LN in the combined BR+IR anifrolumab group (n=82 [BR, n=38; IR, n=44]) compared with placebo (n=40; adjusted P< 0.05): 29 proteins were downregulated, 11 proteins were upregulated, and 5 proteins were stable in the anifrolumab group but increased or decreased in the placebo group. The top 5 downregulated proteins were SIGLEC1, LGALS9, BST2, CCL8, and IFIT3 and the top 5 upregulated proteins were IFNAR1, CR1, CD6, FCN1, and CNTN1 (Figures 1 and 2). A larger number of plasma proteins were significantly modulated compared with placebo in patients treated with anifrolumab IR vs BR at Weeks 12 and 24 (adjusted P< 0.05). Several modulated proteins at Week 12 in patients treated with anifrolumab IR were involved in immunomodulatory pathways including response to IFN-α, negative regulation of leukocyte-mediated immunity, and innate immune response (FDR< 0.05%).
Conclusion: In patients with LN, treatment with anifrolumab significantly modulated several proteins involved in immune system regulation. When compared with placebo, broader effects on the plasma proteome were found in the anifrolumab IR vs BR group in patients with LN. Overall, our results contribute to an enhanced understanding of the immunomodulatory impact of type I IFN inhibition on the plasma proteomic landscape of LN.
References
1. Feng X. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2006;54:2951–62.
2. Jayne D. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022;81:496–506.
3. Baker T. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024:ard-2023-225445.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fava A, Petri M, Jayne D, Gavin P, Csomor E, Brohawn P, Muthas D, Platt A, Lindholm C, Ferrari N. Plasma Proteomic Analysis Reveals Type I Interferon Blockade Effects of Anifrolumab in Lupus Nephritis: Insights from a Phase 2 Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/plasma-proteomic-analysis-reveals-type-i-interferon-blockade-effects-of-anifrolumab-in-lupus-nephritis-insights-from-a-phase-2-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/plasma-proteomic-analysis-reveals-type-i-interferon-blockade-effects-of-anifrolumab-in-lupus-nephritis-insights-from-a-phase-2-trial/